Victor Costa
Exploring Generative Adversarial Networks for Text-to-Image Generation with Evolution Strategies
Jul 06, 2022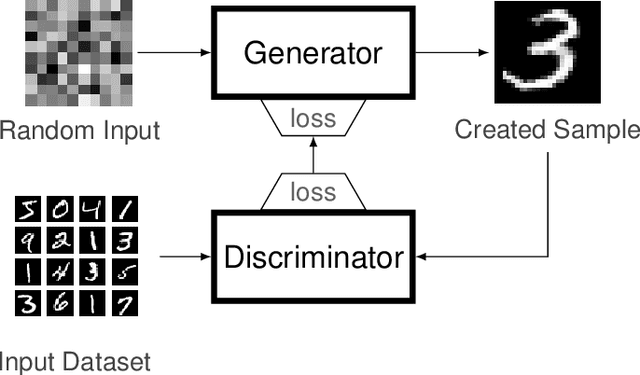
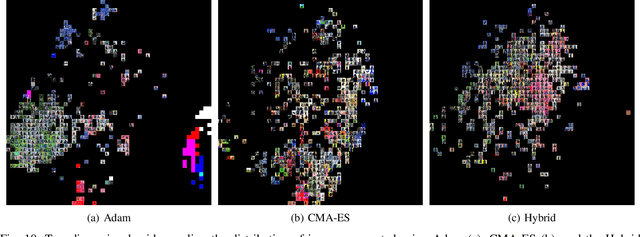

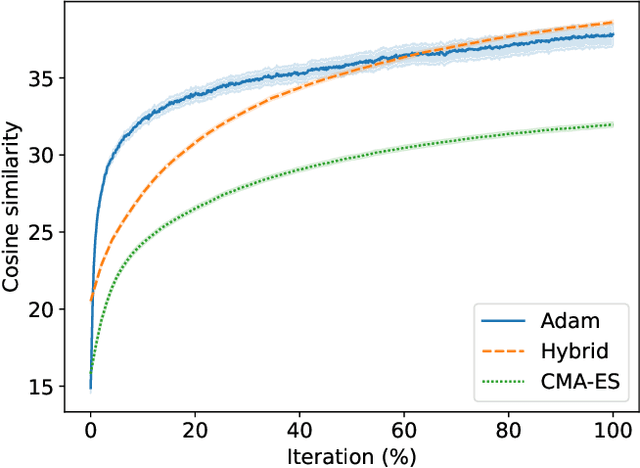
Abstract:In the context of generative models, text-to-image generation achieved impressive results in recent years. Models using different approaches were proposed and trained in huge datasets of pairs of texts and images. However, some methods rely on pre-trained models such as Generative Adversarial Networks, searching through the latent space of the generative model by using a gradient-based approach to update the latent vector, relying on loss functions such as the cosine similarity. In this work, we follow a different direction by proposing the use of Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy to explore the latent space of Generative Adversarial Networks. We compare this approach to the one using Adam and a hybrid strategy. We design an experimental study to compare the three approaches using different text inputs for image generation by adapting an evaluation method based on the projection of the resulting samples into a two-dimensional grid to inspect the diversity of the distributions. The results evidence that the evolutionary method achieves more diversity in the generation of samples, exploring different regions of the resulting grids. Besides, we show that the hybrid method combines the explored areas of the gradient-based and evolutionary approaches, leveraging the quality of the results.
Demonstrating the Evolution of GANs through t-SNE
Feb 25, 2021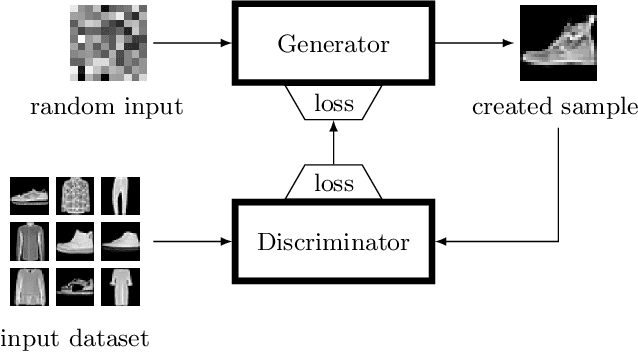
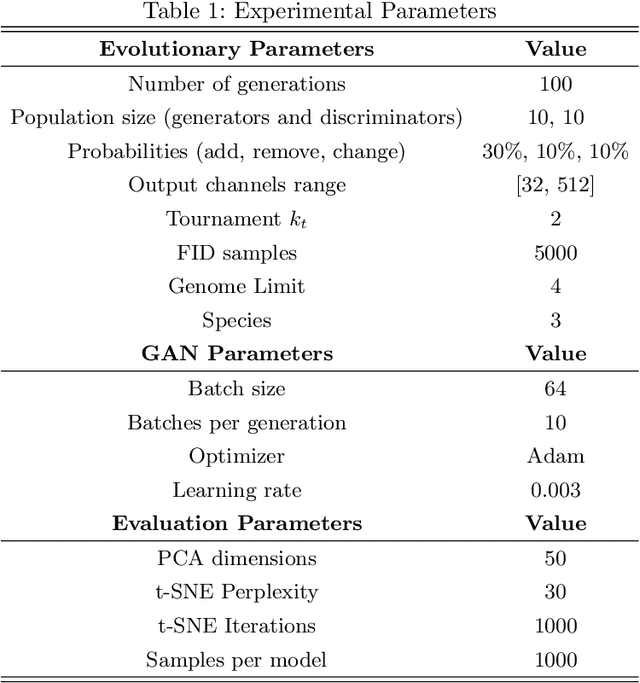
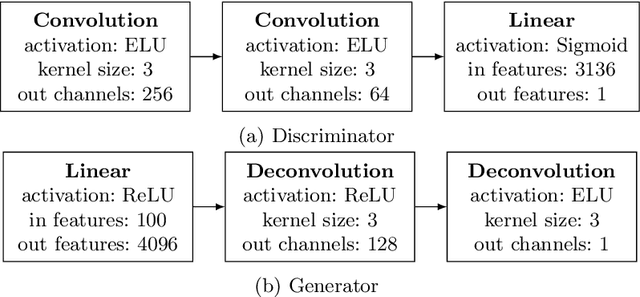
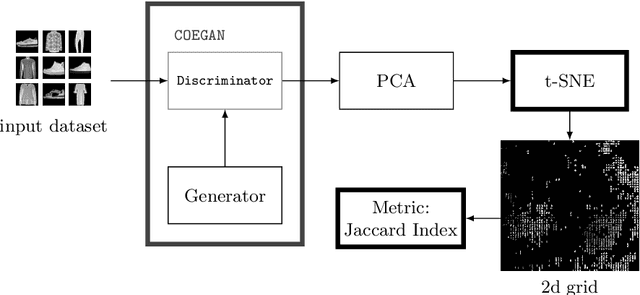
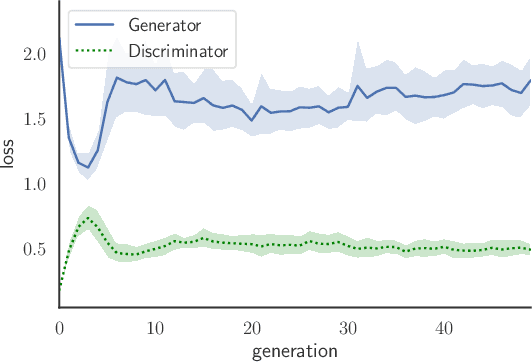
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are powerful generative models that achieved strong results, mainly in the image domain. However, the training of GANs is not trivial, presenting some challenges tackled by different strategies. Evolutionary algorithms, such as COEGAN, were recently proposed as a solution to improve the GAN training, overcoming common problems that affect the model, such as vanishing gradient and mode collapse. In this work, we propose an evaluation method based on t-distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding (t-SNE) to assess the progress of GANs and visualize the distribution learned by generators in training. We propose the use of the feature space extracted from trained discriminators to evaluate samples produced by generators and from the input dataset. A metric based on the resulting t-SNE maps and the Jaccard index is proposed to represent the model quality. Experiments were conducted to assess the progress of GANs when trained using COEGAN. The results show both by visual inspection and metrics that the Evolutionary Algorithm gradually improves discriminators and generators through generations, avoiding problems such as mode collapse.
Exploring the Evolution of GANs through Quality Diversity
Jul 13, 2020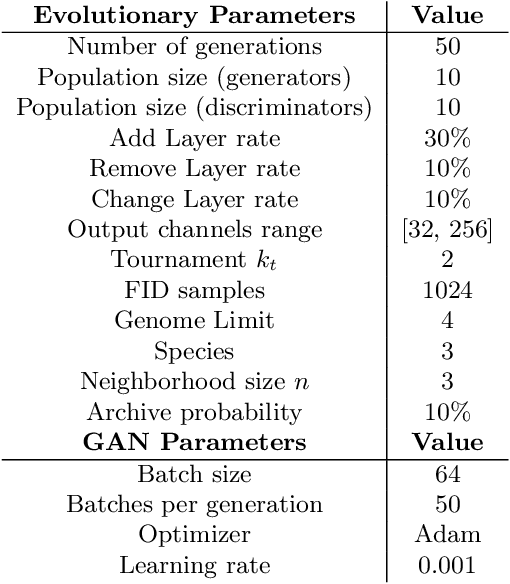
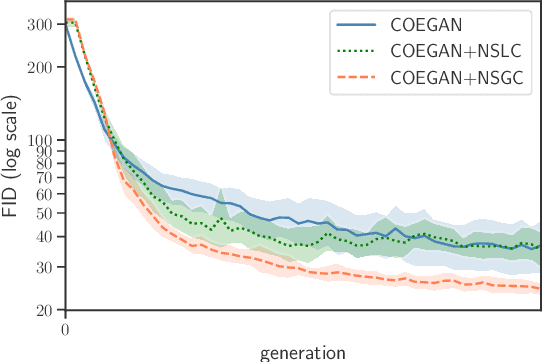
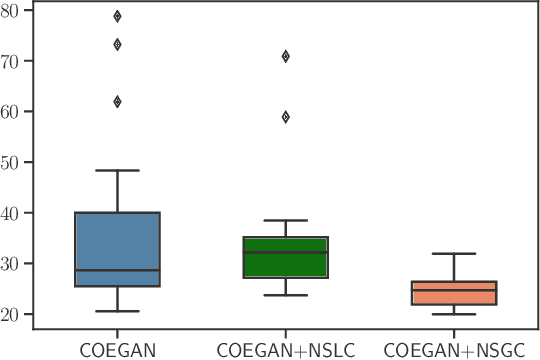
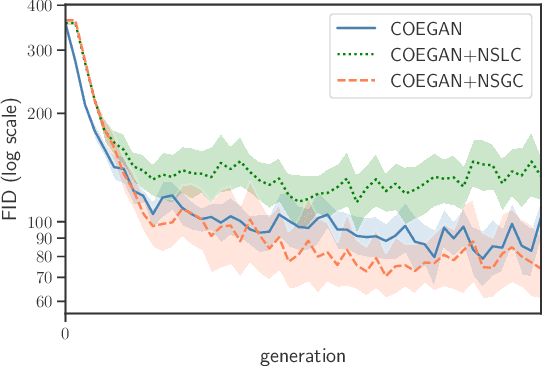
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) achieved relevant advances in the field of generative algorithms, presenting high-quality results mainly in the context of images. However, GANs are hard to train, and several aspects of the model should be previously designed by hand to ensure training success. In this context, evolutionary algorithms such as COEGAN were proposed to solve the challenges in GAN training. Nevertheless, the lack of diversity and premature optimization can be found in some of these solutions. We propose in this paper the application of a quality-diversity algorithm in the evolution of GANs. The solution is based on the Novelty Search with Local Competition (NSLC) algorithm, adapting the concepts used in COEGAN to this new proposal. We compare our proposal with the original COEGAN model and with an alternative version using a global competition approach. The experimental results evidenced that our proposal increases the diversity of the discovered solutions and leverage the performance of the models found by the algorithm. Furthermore, the global competition approach was able to consistently find better models for GANs.
Using Skill Rating as Fitness on the Evolution of GANs
Apr 09, 2020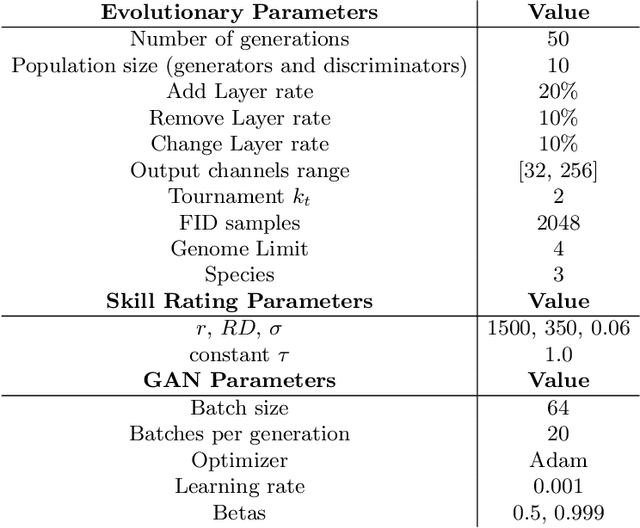
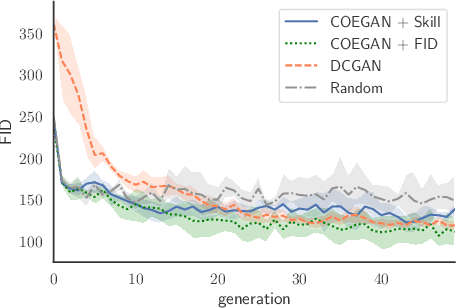
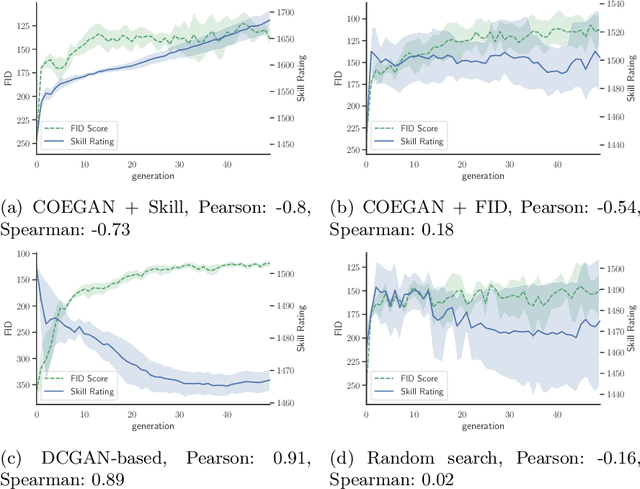
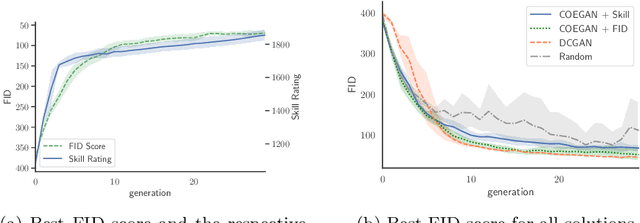
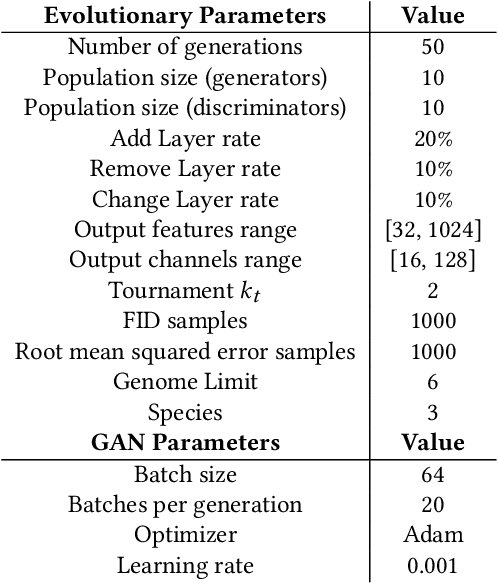
Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are an adversarial model that achieved impressive results on generative tasks. In spite of the relevant results, GANs present some challenges regarding stability, making the training usually a hit-and-miss process. To overcome these challenges, several improvements were proposed to better handle the internal characteristics of the model, such as alternative loss functions or architectural changes on the neural networks used by the generator and the discriminator. Recent works proposed the use of evolutionary algorithms on GAN training, aiming to solve these challenges and to provide an automatic way to find good models. In this context, COEGAN proposes the use of coevolution and neuroevolution to orchestrate the training of GANs. However, previous experiments detected that some of the fitness functions used to guide the evolution are not ideal. In this work we propose the evaluation of a game-based fitness function to be used within the COEGAN method. Skill rating is a metric to quantify the skill of players in a game and has already been used to evaluate GANs. We extend this idea using the skill rating in an evolutionary algorithm to train GANs. The results show that skill rating can be used as fitness to guide the evolution in COEGAN without the dependence of an external evaluator.
COEGAN: Evaluating the Coevolution Effect in Generative Adversarial Networks
Dec 12, 2019
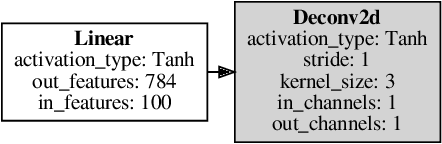
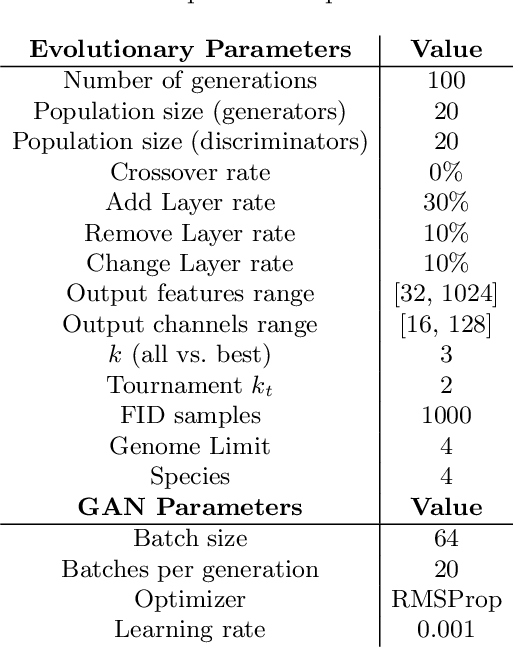
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GAN) present state-of-the-art results in the generation of samples following the distribution of the input dataset. However, GANs are difficult to train, and several aspects of the model should be previously designed by hand. Neuroevolution is a well-known technique used to provide the automatic design of network architectures which was recently expanded to deep neural networks. COEGAN is a model that uses neuroevolution and coevolution in the GAN training algorithm to provide a more stable training method and the automatic design of neural network architectures. COEGAN makes use of the adversarial aspect of the GAN components to implement coevolutionary strategies in the training algorithm. Our proposal was evaluated in the Fashion-MNIST and MNIST dataset. We compare our results with a baseline based on DCGAN and also with results from a random search algorithm. We show that our method is able to discover efficient architectures in the Fashion-MNIST and MNIST datasets. The results also suggest that COEGAN can be used as a training algorithm for GANs to avoid common issues, such as the mode collapse problem.
Coevolution of Generative Adversarial Networks
Dec 12, 2019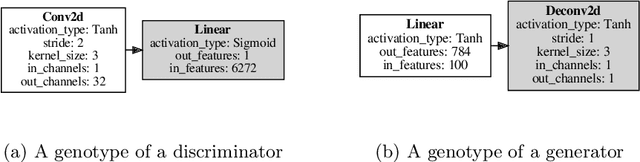


Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GAN) became a hot topic, presenting impressive results in the field of computer vision. However, there are still open problems with the GAN model, such as the training stability and the hand-design of architectures. Neuroevolution is a technique that can be used to provide the automatic design of network architectures even in large search spaces as in deep neural networks. Therefore, this project proposes COEGAN, a model that combines neuroevolution and coevolution in the coordination of the GAN training algorithm. The proposal uses the adversarial characteristic between the generator and discriminator components to design an algorithm using coevolution techniques. Our proposal was evaluated in the MNIST dataset. The results suggest the improvement of the training stability and the automatic discovery of efficient network architectures for GANs. Our model also partially solves the mode collapse problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge