Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Venkata Sai Sundar Kandarpa
Systematic Review on Learning-based Spectral CT
Apr 15, 2023Authors:Alexandre Bousse, Venkata Sai Sundar Kandarpa, Simon Rit, Alessandro Perelli, Mengzhou Li, Guobao Wang, Jian Zhou, Ge Wang
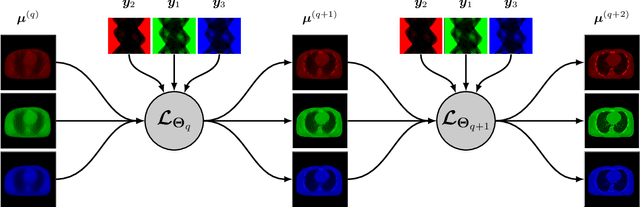
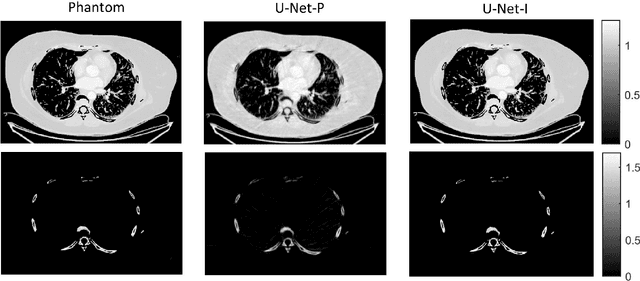
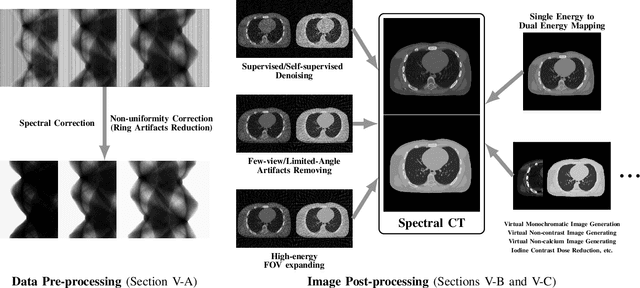
Figures and Tables: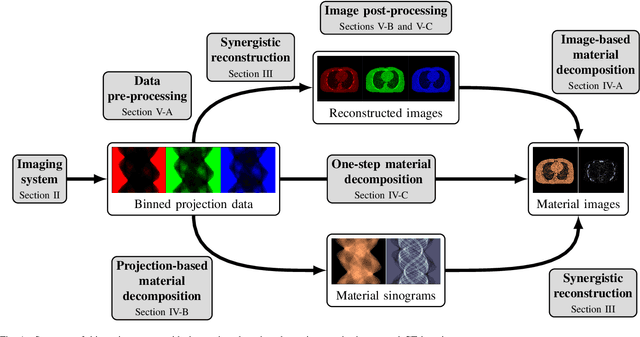




Abstract:Spectral computed tomography (CT) has recently emerged as an advanced version of medical CT and significantly improves conventional (single-energy) CT. Spectral CT has two main forms: dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) and photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT), which offer image improvement, material decomposition, and feature quantification relative to conventional CT. However, the inherent challenges of spectral CT, evidenced by data and image artifacts, remain a bottleneck for clinical applications. To address these problems, machine learning techniques have been widely applied to spectral CT. In this review, we present the state-of-the-art data-driven techniques for spectral CT.
* 28 pages, 9 figures
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge