Vasantha Ramani
Semantic segmentation of longitudinal thermal images for identification of hot and cool spots in urban areas
Oct 06, 2023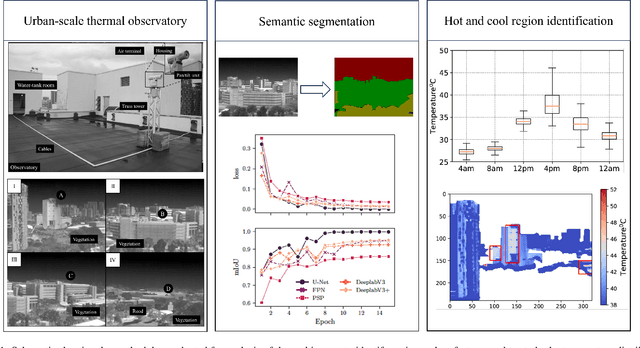
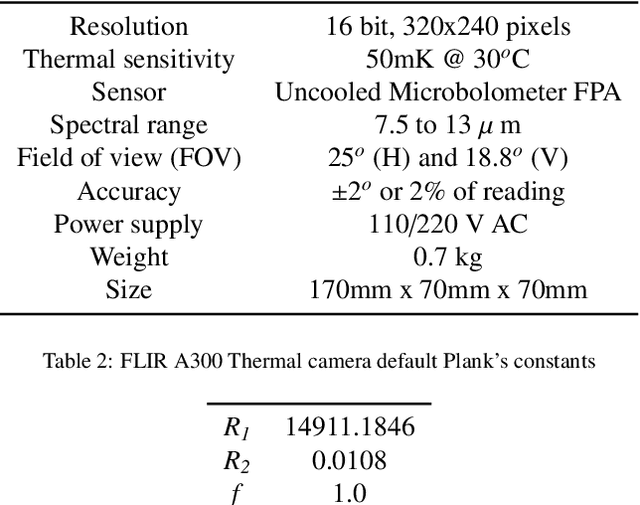
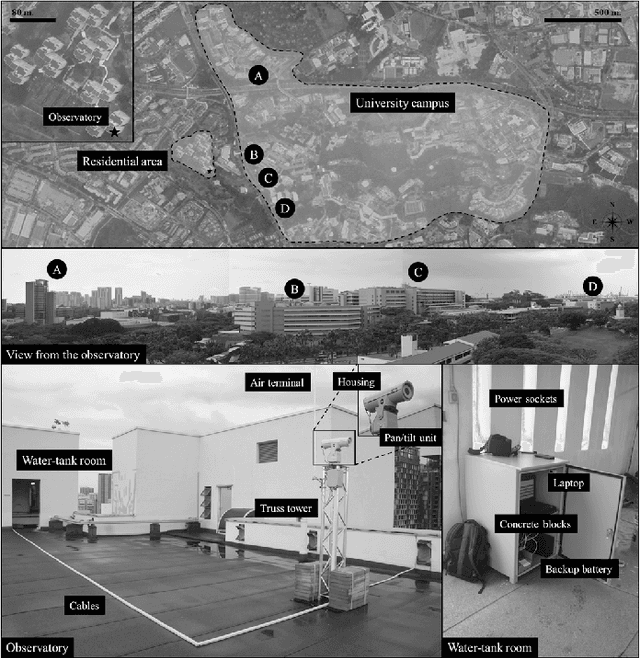
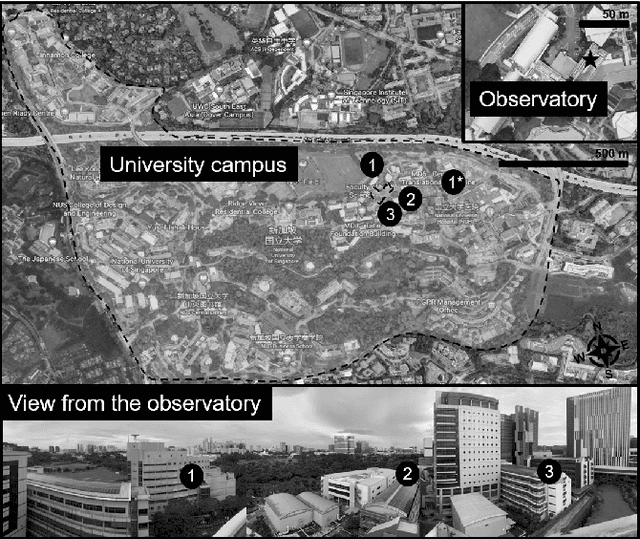
Abstract:This work presents the analysis of semantically segmented, longitudinally, and spatially rich thermal images collected at the neighborhood scale to identify hot and cool spots in urban areas. An infrared observatory was operated over a few months to collect thermal images of different types of buildings on the educational campus of the National University of Singapore. A subset of the thermal image dataset was used to train state-of-the-art deep learning models to segment various urban features such as buildings, vegetation, sky, and roads. It was observed that the U-Net segmentation model with `resnet34' CNN backbone has the highest mIoU score of 0.99 on the test dataset, compared to other models such as DeepLabV3, DeeplabV3+, FPN, and PSPnet. The masks generated using the segmentation models were then used to extract the temperature from thermal images and correct for differences in the emissivity of various urban features. Further, various statistical measure of the temperature extracted using the predicted segmentation masks is shown to closely match the temperature extracted using the ground truth masks. Finally, the masks were used to identify hot and cool spots in the urban feature at various instances of time. This forms one of the very few studies demonstrating the automated analysis of thermal images, which can be of potential use to urban planners for devising mitigation strategies for reducing the urban heat island (UHI) effect, improving building energy efficiency, and maximizing outdoor thermal comfort.
District-scale surface temperatures generated from high-resolution longitudinal thermal infrared images
May 03, 2023Abstract:The paper describes a dataset that was collected by infrared thermography, which is a non-contact, non-intrusive technique to collect data and analyze the built environment in various aspects. While most studies focus on the city and building scales, the rooftop observatory provides high temporal and spatial resolution observations with dynamic interactions on the district scale. The rooftop infrared thermography observatory with a multi-modal platform that is capable of assessing a wide range of dynamic processes in urban systems was deployed in Singapore. It was placed on the top of two buildings that overlook the outdoor context of the campus of the National University of Singapore. The platform collects remote sensing data from tropical areas on a temporal scale, allowing users to determine the temperature trend of individual features such as buildings, roads, and vegetation. The dataset includes 1,365,921 thermal images collected on average at approximately 10 seconds intervals from two locations during ten months.
Longitudinal thermal imaging for scalable non-residential HVAC and occupant behaviour characterization
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:This work presents a study on the characterization of the air-conditioning (AC) usage pattern of non-residential buildings from thermal images collected from an urban-scale infrared (IR) observatory. To achieve this first, an image processing scheme, for cleaning and extraction of the temperature time series from the thermal images is implemented. To test the accuracy of the thermal measurements using IR camera, the extracted temperature is compared against the ground truth surface temperature measurements. It is observed that the detrended thermal measurements match well with the ground truth surface temperature measurements. Subsequently, the operational pattern of the water-cooled systems and window AC units are extracted from the analysis of the thermal signature. It is observed that for the water-cooled system, the difference between the rate of change of the window and wall can be used to extract the operational pattern. While, in the case of the window AC units, wavelet transform of the AC unit temperature is used to extract the frequency and time domain information of the AC unit operation. The results of the analysis are compared against the indoor temperature sensors installed in the office spaces of the building. It is realized that the accuracy in the prediction of the operational pattern is highest between 8 pm to 10 am, and it reduces during the day because of solar radiation and high daytime temperature. Subsequently, a characterization study is conducted for eight window/split AC units from the thermal image collected during the nighttime. This forms one of the first studies on the operational behavior of HVAC systems for non-residential buildings using the longitudinal thermal imaging technique. The output from this study can be used to better understand the operational and occupant behavior, without requiring to deploy a large array of sensors in the building space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge