Valentin T. Bickel
ETH Zurich
A Practical Framework of Key Performance Indicators for Multi-Robot Lunar and Planetary Field Tests
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Robotic prospecting for critical resources on the Moon, such as ilmenite, rare earth elements, and water ice, requires robust exploration methods given the diverse terrain and harsh environmental conditions. Although numerous analog field trials address these goals, comparing their results remains challenging because of differences in robot platforms and experimental setups. These missions typically assess performance using selected, scenario-specific engineering metrics that fail to establish a clear link between field performance and science-driven objectives. In this paper, we address this gap by deriving a structured framework of KPI from three realistic multi-robot lunar scenarios reflecting scientific objectives and operational constraints. Our framework emphasizes scenario-dependent priorities in efficiency, robustness, and precision, and is explicitly designed for practical applicability in field deployments. We validated the framework in a multi-robot field test and found it practical and easy to apply for efficiency- and robustness-related KPI, whereas precision-oriented KPI require reliable ground-truth data that is not always feasible to obtain in outdoor analog environments. Overall, we propose this framework as a common evaluation standard enabling consistent, goal-oriented comparison of multi-robot field trials and supporting systematic development of robotic systems for future planetary exploration.
Using Machine Learning to Reduce Observational Biases When Detecting New Impacts on Mars
Jul 12, 2022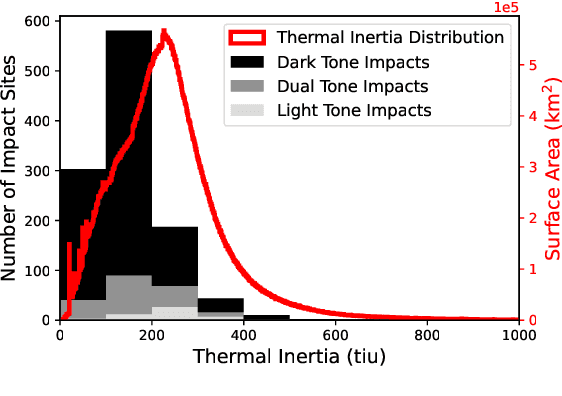
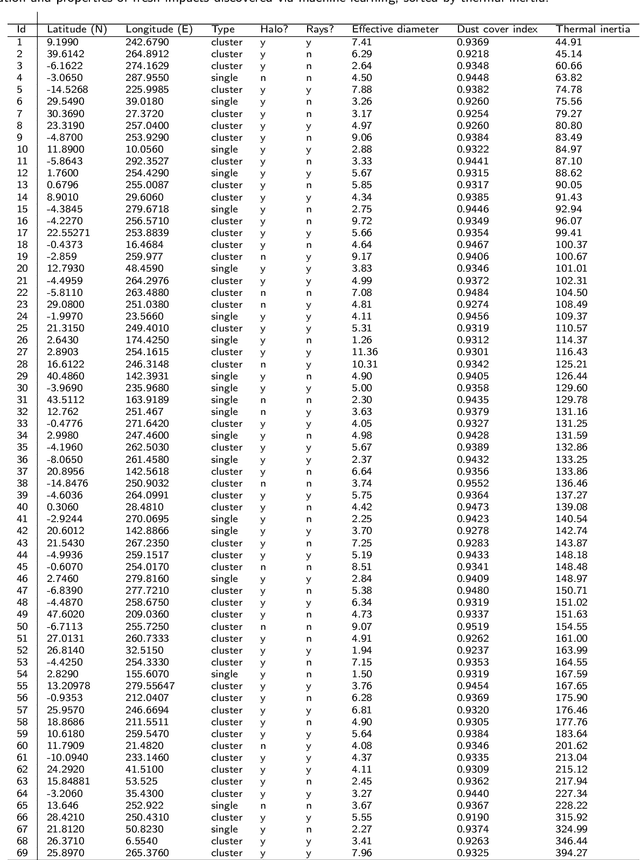
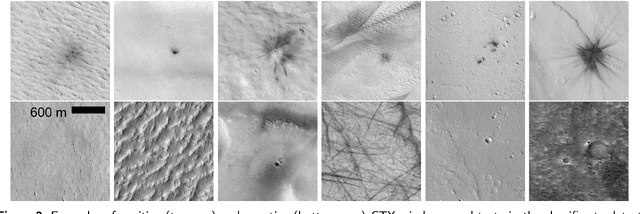
Abstract:The current inventory of recent (fresh) impacts on Mars shows a strong bias towards areas of low thermal inertia. These areas are generally visually bright, and impacts create dark scours and rays that make them easier to detect. It is expected that impacts occur at a similar rate in areas of higher thermal inertia, but those impacts are under-detected. This study investigates the use of a trained machine learning classifier to increase the detection of fresh impacts on Mars using CTX data. This approach discovered 69 new fresh impacts that have been confirmed with follow-up HiRISE images. We found that examining candidates partitioned by thermal inertia (TI) values, which is only possible due to the large number of machine learning candidates, helps reduce the observational bias and increase the number of known high-TI impacts.
* 17 pages, 10 figures, 2 tables (Author's preprint, accepted version)
Unsupervised Distribution Learning for Lunar Surface Anomaly Detection
Jan 14, 2020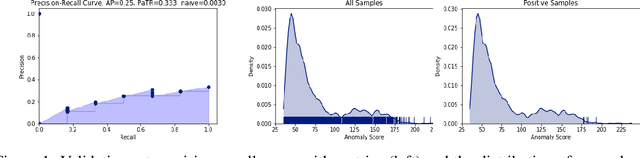
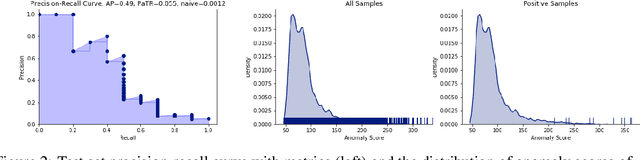

Abstract:In this work we show that modern data-driven machine learning techniques can be successfully applied on lunar surface remote sensing data to learn, in an unsupervised way, sufficiently good representations of the data distribution to enable lunar technosignature and anomaly detection. In particular we train an unsupervised distribution learning neural network model to find the Apollo 15 landing module in a testing dataset, with no dataset specific model or hyperparameter tuning. Sufficiently good unsupervised data density estimation has the promise of enabling myriad useful downstream tasks, including locating lunar resources for future space flight and colonization, finding new impact craters or lunar surface reshaping, and algorithmically deciding the importance of unlabeled samples to send back from power- and bandwidth-constrained missions. We show in this work that such unsupervised learning can be successfully done in the lunar remote sensing and space science contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge