Vaibhav Mathur
Watch and Match: Supercharging Imitation with Regularized Optimal Transport
Jun 30, 2022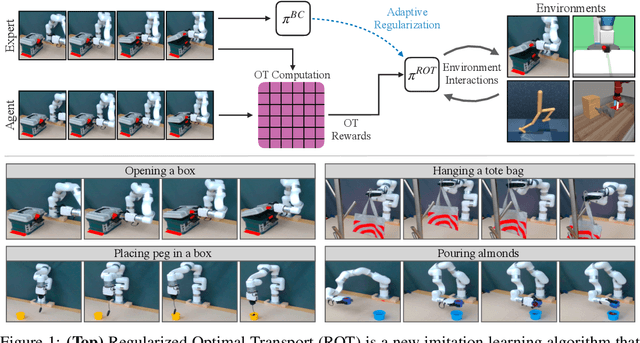
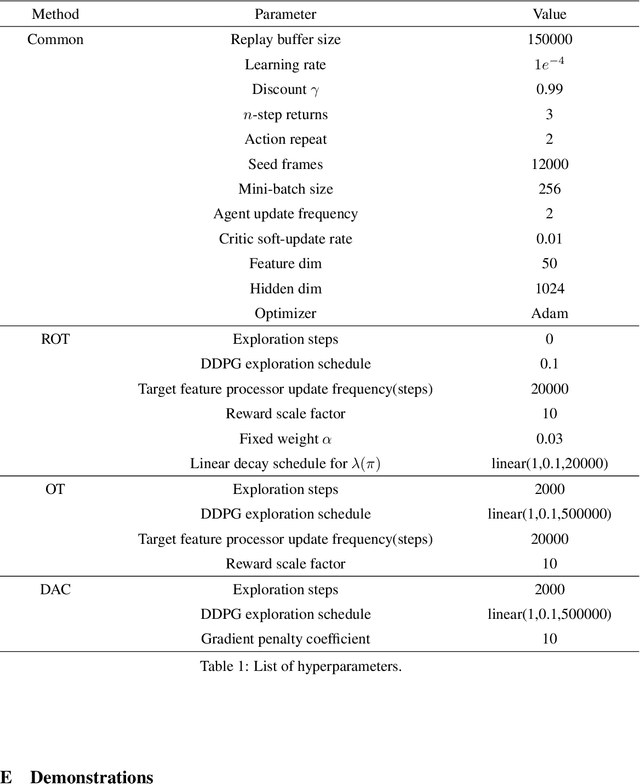
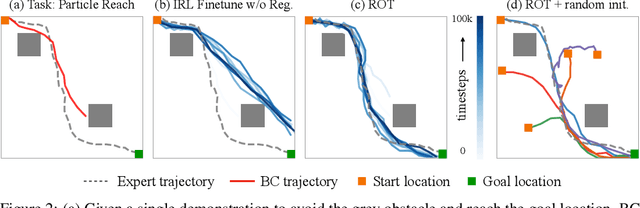
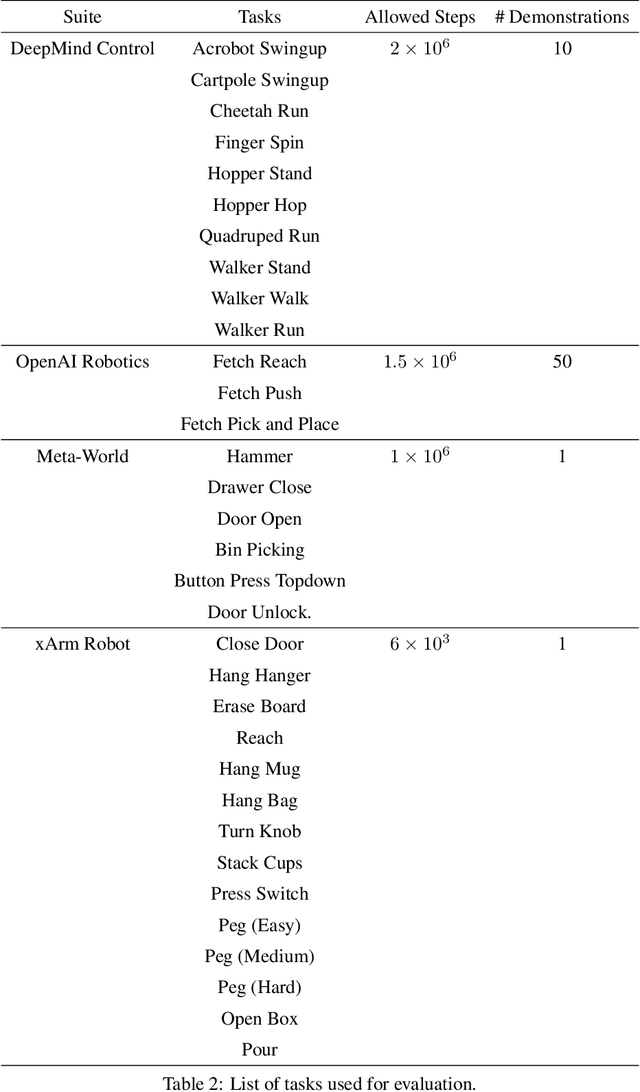
Abstract:Imitation learning holds tremendous promise in learning policies efficiently for complex decision making problems. Current state-of-the-art algorithms often use inverse reinforcement learning (IRL), where given a set of expert demonstrations, an agent alternatively infers a reward function and the associated optimal policy. However, such IRL approaches often require substantial online interactions for complex control problems. In this work, we present Regularized Optimal Transport (ROT), a new imitation learning algorithm that builds on recent advances in optimal transport based trajectory-matching. Our key technical insight is that adaptively combining trajectory-matching rewards with behavior cloning can significantly accelerate imitation even with only a few demonstrations. Our experiments on 20 visual control tasks across the DeepMind Control Suite, the OpenAI Robotics Suite, and the Meta-World Benchmark demonstrate an average of 7.8X faster imitation to reach 90% of expert performance compared to prior state-of-the-art methods. On real-world robotic manipulation, with just one demonstration and an hour of online training, ROT achieves an average success rate of 90.1% across 14 tasks.
Hydra: A Peer to Peer Distributed Training & Data Collection Framework
Nov 24, 2018Abstract:The world needs diverse and unbiased data to train deep learning models. Currently data comes from a variety of sources that are unmoderated to a large extent. The outcomes of training neural networks with unverified data yields biased models with various strains of homophobia, sexism and racism. Another trend observed in the world of deep learning is the rise of distributed training. Although cloud companies provide high performance compute for training models in the form of GPU's connected with a low latency network, using these services comes at a high cost. We propose Hydra, a system that seeks to solve both of these problems in a novel manner by proposing a decentralized distributed framework which utilizes the substantial amount of idle compute of everyday electronic devices like smartphones and desktop computers for training and data collection purposes. Hydra couples a specialized distributed training framework on a network of these low powered devices with a reward scheme that incentivizes users to provide high quality data to unleash the compute capability on this training framework. Such a system has the ability to capture data from a wide variety of diverse sources which has been an issue in the current scenario of deep learning. Hydra brings in several new innovations in training on low powered devices including a fault tolerant version of the All Reduce algorithm. Furthermore we introduce a reinforcement learning policy to decide the size of training jobs on different machines on a heterogeneous cluster of devices with varying network latencies for Synchronous SGD. The novel thing about such a network is the ability of each machine to shut down and resume training capabilities at any point of time without restarting the overall training. To enable such an asynchronous behaviour we propose a communication framework inspired by the Bittorrent protocol and the Kademlia DHT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge