Usama Ijaz Bajwa
A Robust Deep Networks based Multi-Object MultiCamera Tracking System for City Scale Traffic
May 01, 2025Abstract:Vision sensors are becoming more important in Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) for traffic monitoring, management, and optimization as the number of network cameras continues to rise. However, manual object tracking and matching across multiple non-overlapping cameras pose significant challenges in city-scale urban traffic scenarios. These challenges include handling diverse vehicle attributes, occlusions, illumination variations, shadows, and varying video resolutions. To address these issues, we propose an efficient and cost-effective deep learning-based framework for Multi-Object Multi-Camera Tracking (MO-MCT). The proposed framework utilizes Mask R-CNN for object detection and employs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) to select target objects from overlapping detections. Transfer learning is employed for re-identification, enabling the association and generation of vehicle tracklets across multiple cameras. Moreover, we leverage appropriate loss functions and distance measures to handle occlusion, illumination, and shadow challenges. The final solution identification module performs feature extraction using ResNet-152 coupled with Deep SORT based vehicle tracking. The proposed framework is evaluated on the 5th AI City Challenge dataset (Track 3), comprising 46 camera feeds. Among these 46 camera streams, 40 are used for model training and validation, while the remaining six are utilized for model testing. The proposed framework achieves competitive performance with an IDF1 score of 0.8289, and precision and recall scores of 0.9026 and 0.8527 respectively, demonstrating its effectiveness in robust and accurate vehicle tracking.
Resource-efficient domain adaptive pre-training for medical images
Apr 28, 2022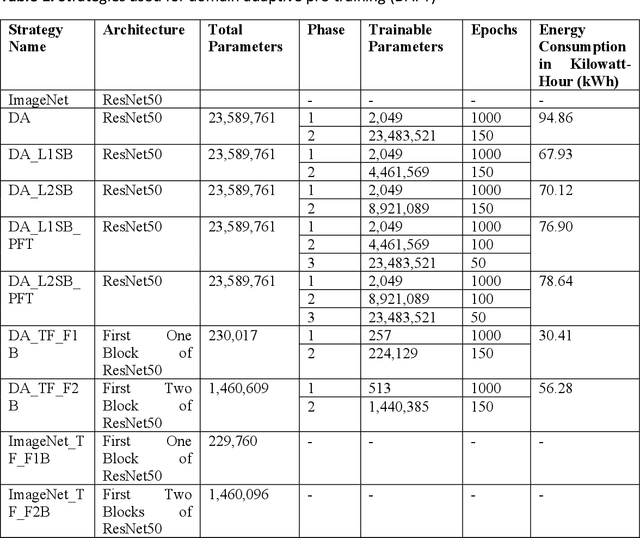


Abstract:The deep learning-based analysis of medical images suffers from data scarcity because of high annotation costs and privacy concerns. Researchers in this domain have used transfer learning to avoid overfitting when using complex architectures. However, the domain differences between pre-training and downstream data hamper the performance of the downstream task. Some recent studies have successfully used domain-adaptive pre-training (DAPT) to address this issue. In DAPT, models are initialized with the generic dataset pre-trained weights, and further pre-training is performed using a moderately sized in-domain dataset (medical images). Although this technique achieved good results for the downstream tasks in terms of accuracy and robustness, it is computationally expensive even when the datasets for DAPT are moderately sized. These compute-intensive techniques and models impact the environment negatively and create an uneven playing field for researchers with limited resources. This study proposed computationally efficient DAPT without compromising the downstream accuracy and robustness. This study proposes three techniques for this purpose, where the first (partial DAPT) performs DAPT on a subset of layers. The second one adopts a hybrid strategy (hybrid DAPT) by performing partial DAPT for a few epochs and then full DAPT for the remaining epochs. The third technique performs DAPT on simplified variants of the base architecture. The results showed that compared to the standard DAPT (full DAPT), the hybrid DAPT technique achieved better performance on the development and external datasets. In contrast, simplified architectures (after DAPT) achieved the best robustness while achieving modest performance on the development dataset .
Deception Detection in Videos using the Facial Action Coding System
May 28, 2021



Abstract:Facts are important in decision making in every situation, which is why it is important to catch deceptive information before they are accepted as facts. Deception detection in videos has gained traction in recent times for its various real-life application. In our approach, we extract facial action units using the facial action coding system which we use as parameters for training a deep learning model. We specifically use long short-term memory (LSTM) which we trained using the real-life trial dataset and it provided one of the best facial only approaches to deception detection. We also tested cross-dataset validation using the Real-life trial dataset, the Silesian Deception Dataset, and the Bag-of-lies Deception Dataset which has not yet been attempted by anyone else for a deception detection system. We tested and compared all datasets amongst each other individually and collectively using the same deep learning training model. The results show that adding different datasets for training worsen the accuracy of the model. One of the primary reasons is that the nature of these datasets vastly differs from one another.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge