Umair Arshad
Hierarchical Text Classification of Urdu News using Deep Neural Network
Jul 07, 2021



Abstract:Digital text is increasing day by day on the internet. It is very challenging to classify a large and heterogeneous collection of data, which require improved information processing methods to organize text. To classify large size of corpus, one common approach is to use hierarchical text classification, which aims to classify textual data in a hierarchical structure. Several approaches have been proposed to tackle classification of text but most of the research has been done on English language. This paper proposes a deep learning model for hierarchical text classification of news in Urdu language - consisting of 51,325 sentences from 8 online news websites belonging to the following genres: Sports; Technology; and Entertainment. The objectives of this paper are twofold: (1) to develop a large human-annotated dataset of news in Urdu language for hierarchical text classification; and (2) to classify Urdu news hierarchically using our proposed model based on LSTM mechanism named as Hierarchical Multi-layer LSTMs (HMLSTM). Our model consists of two modules: Text Representing Layer, for obtaining text representation in which we use Word2vec embedding to transform the words to vector and Urdu Hierarchical LSTM Layer (UHLSTML) an end-to-end fully connected deep LSTMs network to perform automatic feature learning, we train one LSTM layer for each level of the class hierarchy. We have performed extensive experiments on our self created dataset named as Urdu News Dataset for Hierarchical Text Classification (UNDHTC). The result shows that our proposed method is very effective for hierarchical text classification and it outperforms baseline methods significantly and also achieved good results as compare to deep neural model.
Transfer learning from High-Resource to Low-Resource Language Improves Speech Affect Recognition Classification Accuracy
Mar 04, 2021
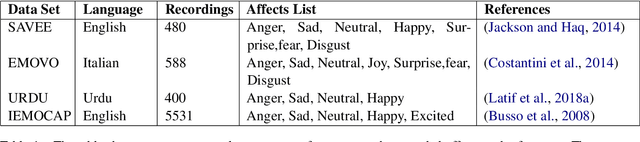
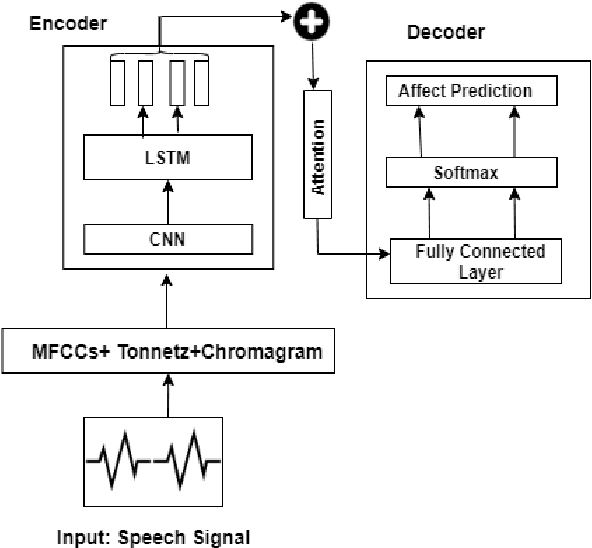
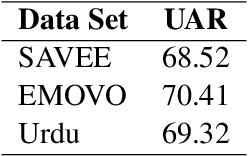
Abstract:Speech Affect Recognition is a problem of extracting emotional affects from audio data. Low resource languages corpora are rear and affect recognition is a difficult task in cross-corpus settings. We present an approach in which the model is trained on high resource language and fine-tune to recognize affects in low resource language. We train the model in same corpus setting on SAVEE, EMOVO, Urdu, and IEMOCAP by achieving baseline accuracy of 60.45, 68.05, 80.34, and 56.58 percent respectively. For capturing the diversity of affects in languages cross-corpus evaluations are discussed in detail. We find that accuracy improves by adding the domain target data into the training data. Finally, we show that performance is improved for low resource language speech affect recognition by achieving the UAR OF 69.32 and 68.2 for Urdu and Italian speech affects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge