Tushar Jain
Evaluation of neural network algorithms for atmospheric turbulence mitigation
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:A variety of neural networks architectures are being studied to tackle blur in images and videos caused by a non-steady camera and objects being captured. In this paper, we present an overview of these existing networks and perform experiments to remove the blur caused by atmospheric turbulence. Our experiments aim to examine the reusability of existing networks and identify desirable aspects of the architecture in a system that is geared specifically towards atmospheric turbulence mitigation. We compare five different architectures, including a network trained in an end-to-end fashion, thereby removing the need for a stabilization step.
VQ-Flows: Vector Quantized Local Normalizing Flows
Mar 22, 2022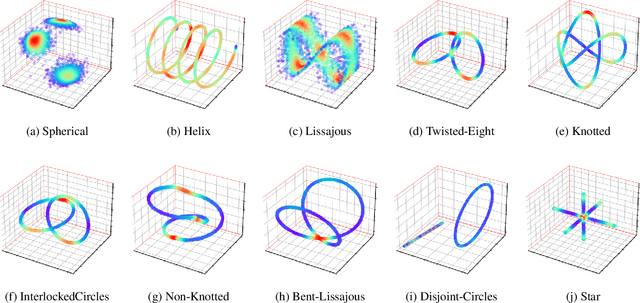
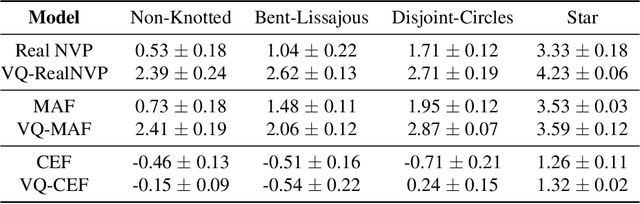
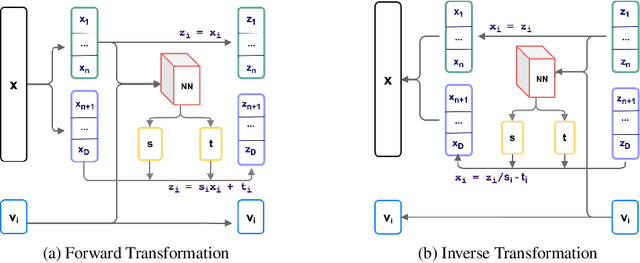
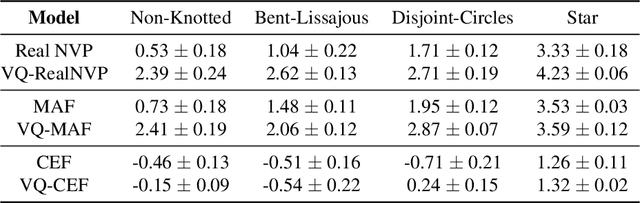
Abstract:Normalizing flows provide an elegant approach to generative modeling that allows for efficient sampling and exact density evaluation of unknown data distributions. However, current techniques have significant limitations in their expressivity when the data distribution is supported on a low-dimensional manifold or has a non-trivial topology. We introduce a novel statistical framework for learning a mixture of local normalizing flows as "chart maps" over the data manifold. Our framework augments the expressivity of recent approaches while preserving the signature property of normalizing flows, that they admit exact density evaluation. We learn a suitable atlas of charts for the data manifold via a vector quantized auto-encoder (VQ-AE) and the distributions over them using a conditional flow. We validate experimentally that our probabilistic framework enables existing approaches to better model data distributions over complex manifolds.
Learning when to Communicate at Scale in Multiagent Cooperative and Competitive Tasks
Dec 23, 2018



Abstract:Learning when to communicate and doing that effectively is essential in multi-agent tasks. Recent works show that continuous communication allows efficient training with back-propagation in multi-agent scenarios, but have been restricted to fully-cooperative tasks. In this paper, we present Individualized Controlled Continuous Communication Model (IC3Net) which has better training efficiency than simple continuous communication model, and can be applied to semi-cooperative and competitive settings along with the cooperative settings. IC3Net controls continuous communication with a gating mechanism and uses individualized rewards foreach agent to gain better performance and scalability while fixing credit assignment issues. Using variety of tasks including StarCraft BroodWars explore and combat scenarios, we show that our network yields improved performance and convergence rates than the baselines as the scale increases. Our results convey that IC3Net agents learn when to communicate based on the scenario and profitability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge