Tuan V. Tran
Improving Object Detection in Medical Image Analysis through Multiple Expert Annotators: An Empirical Investigation
Mar 29, 2023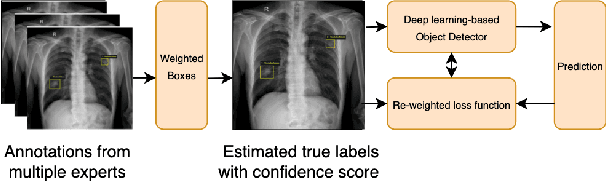

Abstract:The work discusses the use of machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection in medical image analysis and how the performance of these algorithms depends on the number of annotators and the quality of labels. To address the issue of subjectivity in labeling with a single annotator, we introduce a simple and effective approach that aggregates annotations from multiple annotators with varying levels of expertise. We then aim to improve the efficiency of predictive models in abnormal detection tasks by estimating hidden labels from multiple annotations and using a re-weighted loss function to improve detection performance. Our method is evaluated on a real-world medical imaging dataset and outperforms relevant baselines that do not consider disagreements among annotators.
Learning from Multiple Expert Annotators for Enhancing Anomaly Detection in Medical Image Analysis
Mar 20, 2022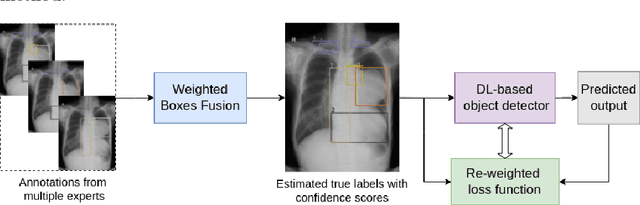
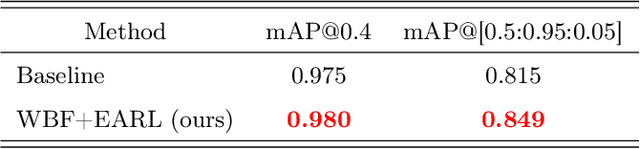
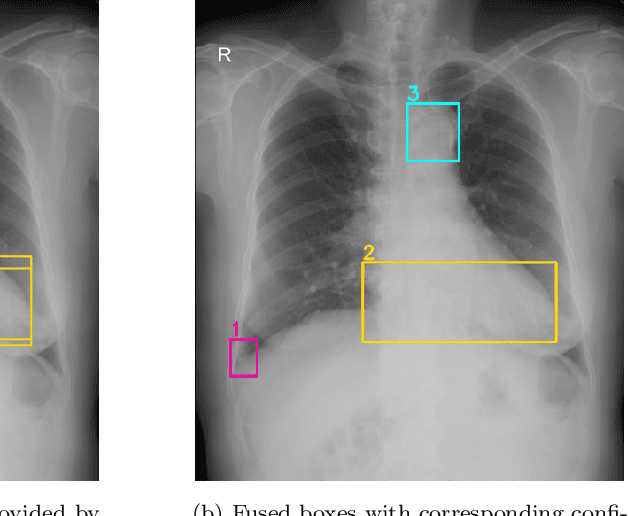
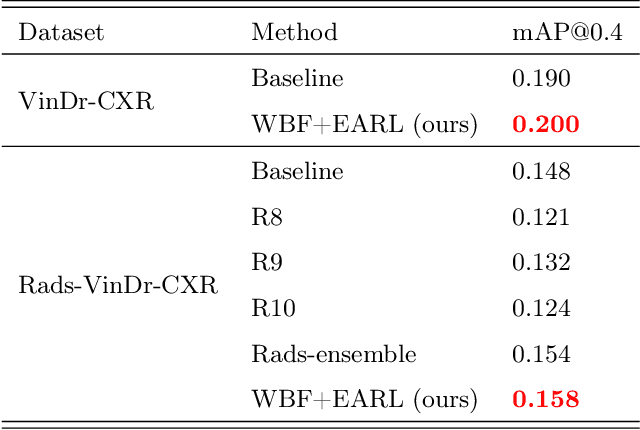
Abstract:Building an accurate computer-aided diagnosis system based on data-driven approaches requires a large amount of high-quality labeled data. In medical imaging analysis, multiple expert annotators often produce subjective estimates about "ground truth labels" during the annotation process, depending on their expertise and experience. As a result, the labeled data may contain a variety of human biases with a high rate of disagreement among annotators, which significantly affect the performance of supervised machine learning algorithms. To tackle this challenge, we propose a simple yet effective approach to combine annotations from multiple radiology experts for training a deep learning-based detector that aims to detect abnormalities on medical scans. The proposed method first estimates the ground truth annotations and confidence scores of training examples. The estimated annotations and their scores are then used to train a deep learning detector with a re-weighted loss function to localize abnormal findings. We conduct an extensive experimental evaluation of the proposed approach on both simulated and real-world medical imaging datasets. The experimental results show that our approach significantly outperforms baseline approaches that do not consider the disagreements among annotators, including methods in which all of the noisy annotations are treated equally as ground truth and the ensemble of different models trained on different label sets provided separately by annotators.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge