Tory Jarmain
Improving Skin Condition Classification with a Visual Symptom Checker Trained using Reinforcement Learning
Mar 30, 2019



Abstract:We present a visual symptom checker that combines a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with a Reinforcement Learning (RL) agent as a Question Answering (QA) model. This method increases the classification confidence and accuracy of the visual symptom checker, and decreases the average number of questions asked to narrow down the differential diagnosis. A Deep Q-Network (DQN)-based RL agent learns how to ask the patient about the presence of symptoms in order to maximize the probability of correctly identifying the underlying condition. The RL agent uses the visual information provided by CNN in addition to the answers to the asked questions to guide the QA system. We demonstrate that the RL-based approach increases the accuracy more than 20% compared to the CNN-only approach, which only uses the visual information to predict the condition. Moreover, the increased accuracy is up to 10% compared to the approach that uses the visual information provided by CNN along with a conventional decision tree-based QA system. We finally show that the RL-based approach not only outperforms the decision tree-based approach, but also narrows down the diagnosis faster in terms of the average number of asked questions.
Improving Skin Condition Classification with a Question Answering Model
Nov 15, 2018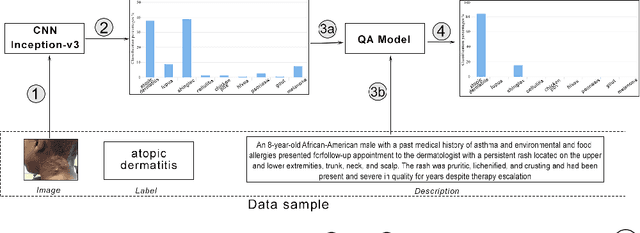
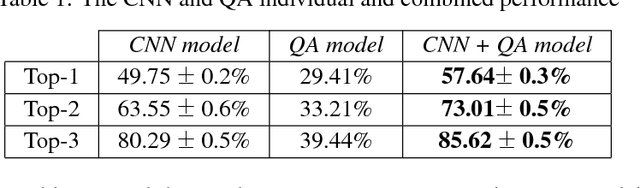
Abstract:We present a skin condition classification methodology based on a sequential pipeline of a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and a Question Answering (QA) model. This method enables us to not only increase the classification confidence and accuracy of the deployed CNN system, but also enables the emulation of the conventional approach of doctors asking the relevant questions in refining the ultimate diagnosis and differential. By combining the CNN output in the form of classification probabilities as a prior to the QA model and the image textual description, we greedily ask the best symptom that maximizes the information gain over symptoms. We demonstrate that combining the QA model with the CNN increases the accuracy up to 10% as compared to the CNN alone, and more than 30% as compared to the QA model alone.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge