Tomoya Nitta
Fine-grained length controllable video captioning with ordinal embeddings
Aug 27, 2024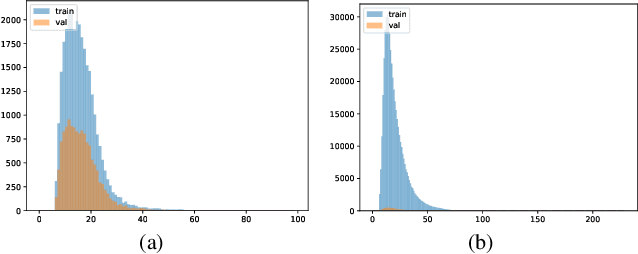
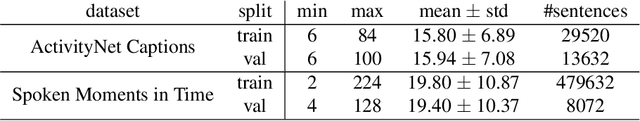
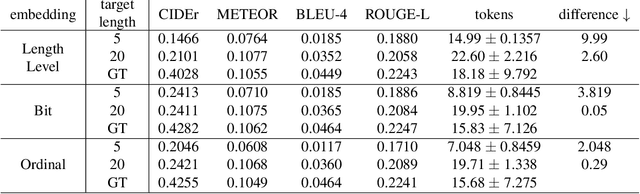
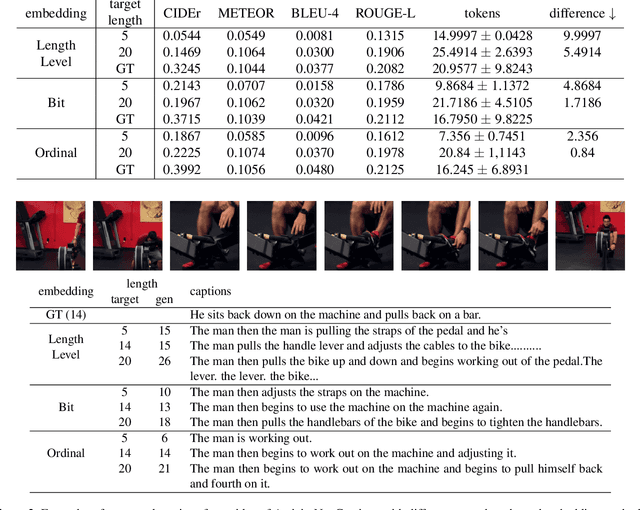
Abstract:This paper proposes a method for video captioning that controls the length of generated captions. Previous work on length control often had few levels for expressing length. In this study, we propose two methods of length embedding for fine-grained length control. A traditional embedding method is linear, using a one-hot vector and an embedding matrix. In this study, we propose methods that represent length in multi-hot vectors. One is bit embedding that expresses length in bit representation, and the other is ordinal embedding that uses the binary representation often used in ordinal regression. These length representations of multi-hot vectors are converted into length embedding by a nonlinear MLP. This method allows for not only the length control of caption sentences but also the control of the time when reading the caption. Experiments using ActivityNet Captions and Spoken Moments in Time show that the proposed method effectively controls the length of the generated captions. Analysis of the embedding vectors with ICA shows that length and semantics were learned separately, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed embedding methods.
Object-ABN: Learning to Generate Sharp Attention Maps for Action Recognition
Jul 27, 2022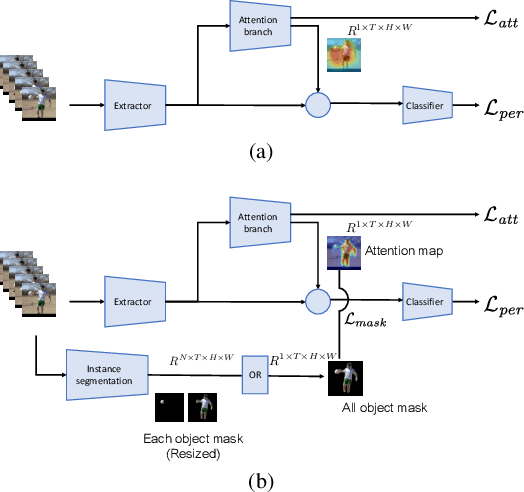
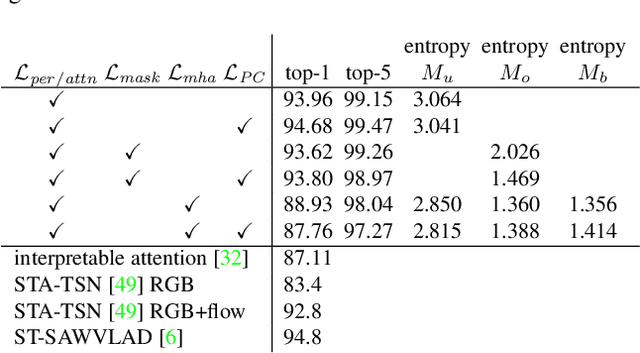
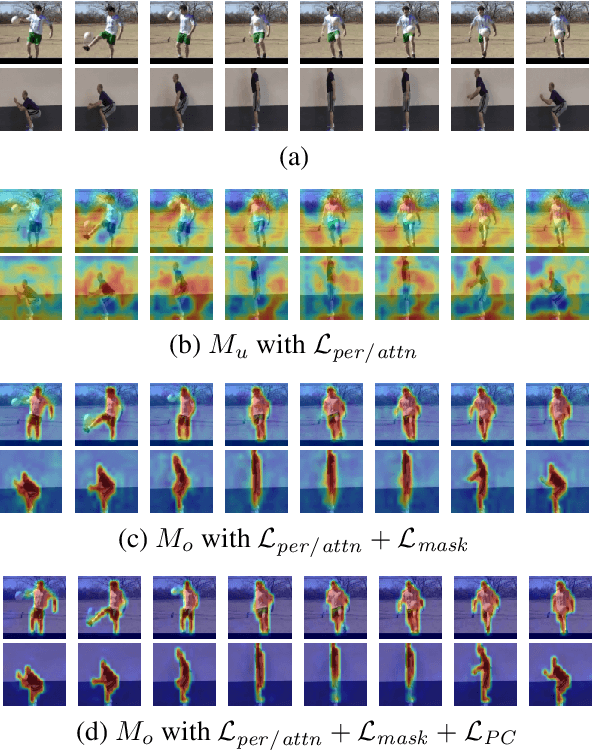
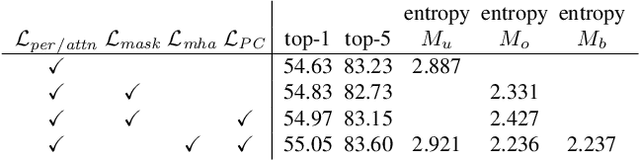
Abstract:In this paper we propose an extension of the Attention Branch Network (ABN) by using instance segmentation for generating sharper attention maps for action recognition. Methods for visual explanation such as Grad-CAM usually generate blurry maps which are not intuitive for humans to understand, particularly in recognizing actions of people in videos. Our proposed method, Object-ABN, tackles this issue by introducing a new mask loss that makes the generated attention maps close to the instance segmentation result. Further the PC loss and multiple attention maps are introduced to enhance the sharpness of the maps and improve the performance of classification. Experimental results with UCF101 and SSv2 shows that the generated maps by the proposed method are much clearer qualitatively and quantitatively than those of the original ABN.
ObjectMix: Data Augmentation by Copy-Pasting Objects in Videos for Action Recognition
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a data augmentation method for action recognition using instance segmentation. Although many data augmentation methods have been proposed for image recognition, few methods have been proposed for action recognition. Our proposed method, ObjectMix, extracts each object region from two videos using instance segmentation and combines them to create new videos. Experiments on two action recognition datasets, UCF101 and HMDB51, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method and show its superiority over VideoMix, a prior work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge