Takumi Fukuzawa
M3DDM+: An improved video outpainting by a modified masking strategy
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:M3DDM provides a computationally efficient framework for video outpainting via latent diffusion modeling. However, it exhibits significant quality degradation -- manifested as spatial blur and temporal inconsistency -- under challenging scenarios characterized by limited camera motion or large outpainting regions, where inter-frame information is limited. We identify the cause as a training-inference mismatch in the masking strategy: M3DDM's training applies random mask directions and widths across frames, whereas inference requires consistent directional outpainting throughout the video. To address this, we propose M3DDM+, which applies uniform mask direction and width across all frames during training, followed by fine-tuning of the pretrained M3DDM model. Experiments demonstrate that M3DDM+ substantially improves visual fidelity and temporal coherence in information-limited scenarios while maintaining computational efficiency. The code is available at https://github.com/tamaki-lab/M3DDM-Plus.
Fine-grained length controllable video captioning with ordinal embeddings
Aug 27, 2024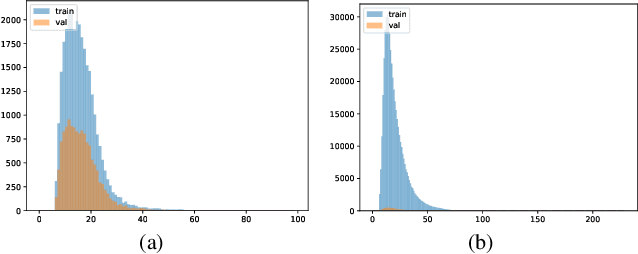
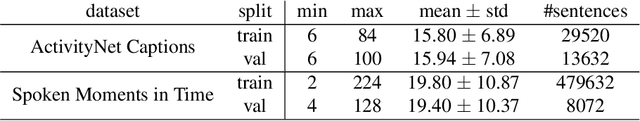
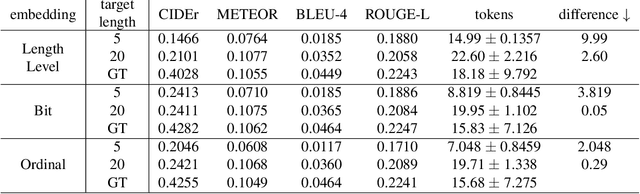
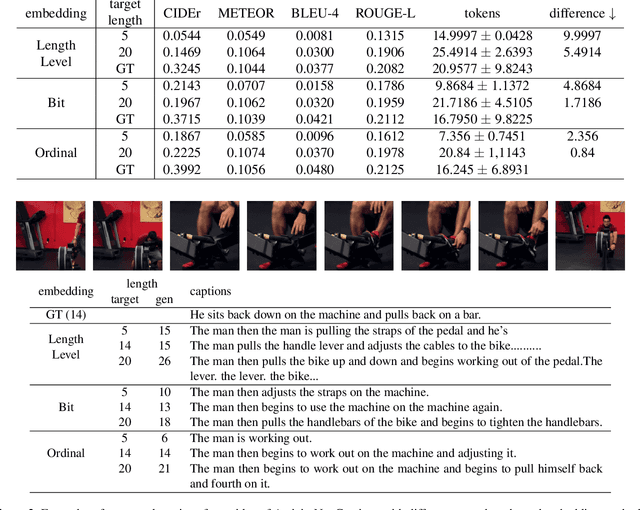
Abstract:This paper proposes a method for video captioning that controls the length of generated captions. Previous work on length control often had few levels for expressing length. In this study, we propose two methods of length embedding for fine-grained length control. A traditional embedding method is linear, using a one-hot vector and an embedding matrix. In this study, we propose methods that represent length in multi-hot vectors. One is bit embedding that expresses length in bit representation, and the other is ordinal embedding that uses the binary representation often used in ordinal regression. These length representations of multi-hot vectors are converted into length embedding by a nonlinear MLP. This method allows for not only the length control of caption sentences but also the control of the time when reading the caption. Experiments using ActivityNet Captions and Spoken Moments in Time show that the proposed method effectively controls the length of the generated captions. Analysis of the embedding vectors with ICA shows that length and semantics were learned separately, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed embedding methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge