Tomáš Vinař
Dynamic Pooling Improves Nanopore Base Calling Accuracy
May 16, 2021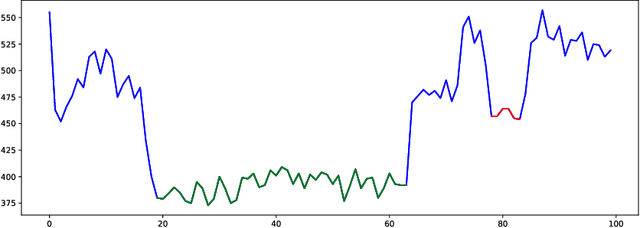
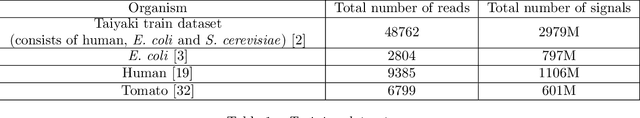
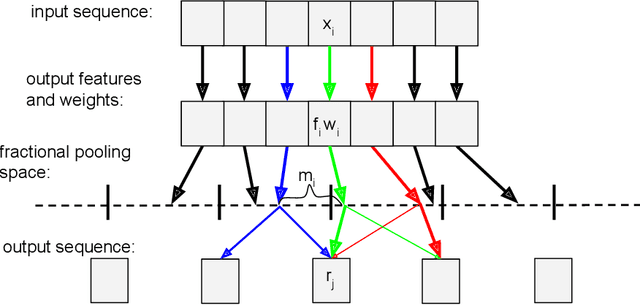
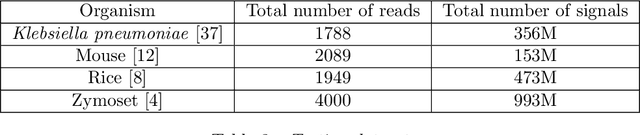
Abstract:In nanopore sequencing, electrical signal is measured as DNA molecules pass through the sequencing pores. Translating these signals into DNA bases (base calling) is a highly non-trivial task, and its quality has a large impact on the sequencing accuracy. The most successful nanopore base callers to date use convolutional neural networks (CNN) to accomplish the task. Convolutional layers in CNNs are typically composed of filters with constant window size, performing best in analysis of signals with uniform speed. However, the speed of nanopore sequencing varies greatly both within reads and between sequencing runs. Here, we present dynamic pooling, a novel neural network component, which addresses this problem by adaptively adjusting the pooling ratio. To demonstrate the usefulness of dynamic pooling, we developed two base callers: Heron and Osprey. Heron improves the accuracy beyond the experimental high-accuracy base caller Bonito developed by Oxford Nanopore. Osprey is a fast base caller that can compete in accuracy with Guppy high-accuracy mode, but does not require GPU acceleration and achieves a near real-time speed on common desktop CPUs. Availability: https://github.com/fmfi-compbio/osprey, https://github.com/fmfi-compbio/heron Keywords: nanopore sequencing, base calling, convolutional neural networks, pooling
Nanopore Base Calling on the Edge
Nov 09, 2020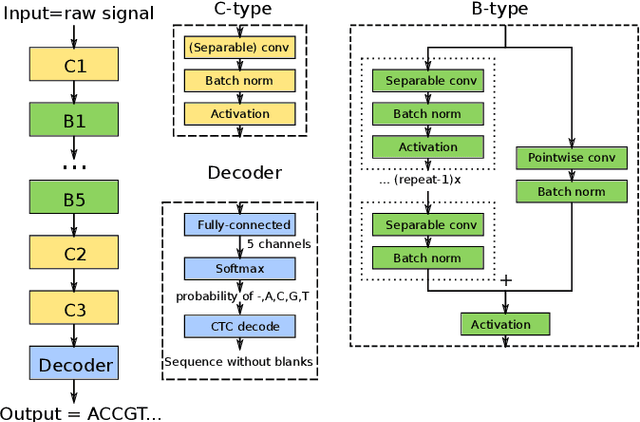
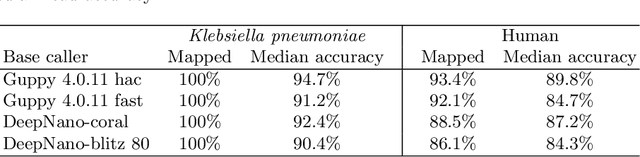
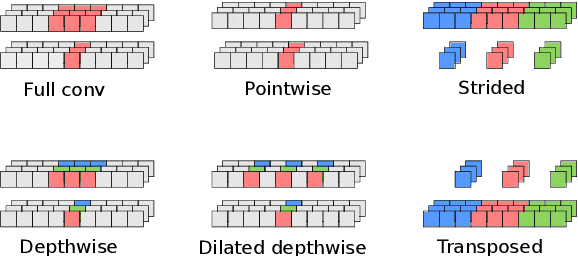
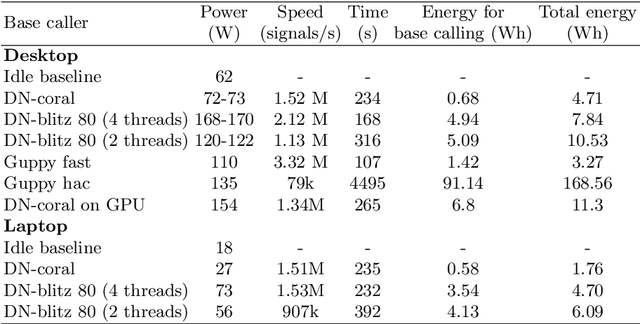
Abstract:We developed a new base caller DeepNano-coral for nanopore sequencing, which is optimized to run on the Coral Edge Tensor Processing Unit, a small USB-attached hardware accelerator. To achieve this goal, we have designed new versions of two key components used in convolutional neural networks for speech recognition and base calling. In our components, we propose a new way of factorization of a full convolution into smaller operations, which decreases memory access operations, memory access being a bottleneck on this device. DeepNano-coral achieves real-time base calling during sequencing with the accuracy slightly better than the fast mode of the Guppy base caller and is extremely energy efficient, using only 10W of power. Availability: https://github.com/fmfi-compbio/coral-basecaller
Bayesian History Reconstruction of Complex Human Gene Clusters on a Phylogeny
Jun 15, 2009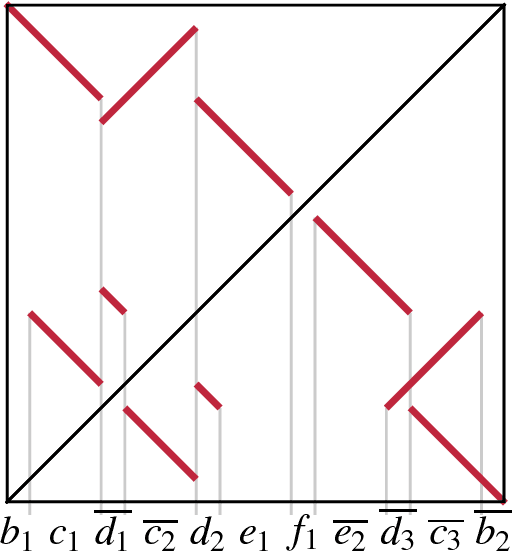
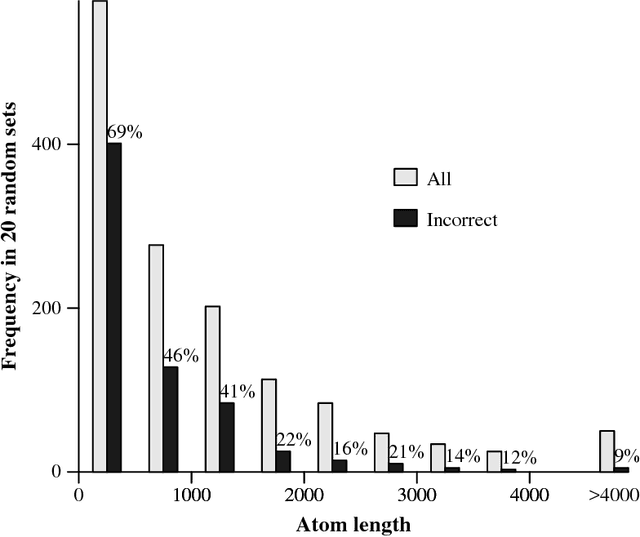
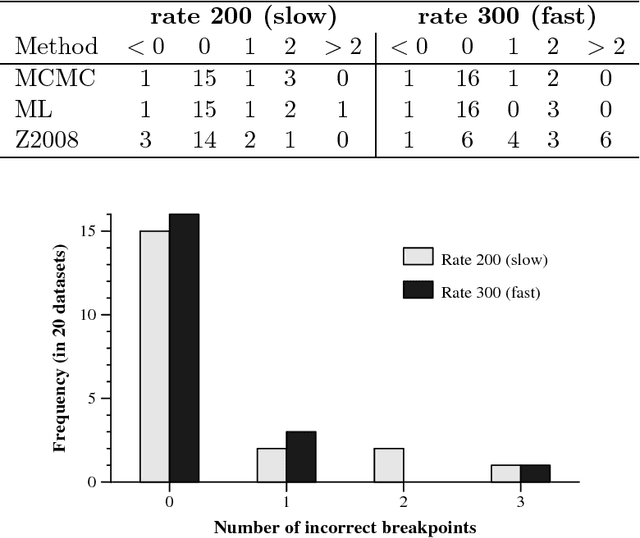
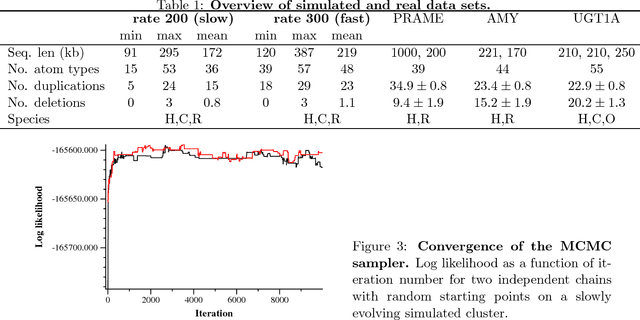
Abstract:Clusters of genes that have evolved by repeated segmental duplication present difficult challenges throughout genomic analysis, from sequence assembly to functional analysis. Improved understanding of these clusters is of utmost importance, since they have been shown to be the source of evolutionary innovation, and have been linked to multiple diseases, including HIV and a variety of cancers. Previously, Zhang et al. (2008) developed an algorithm for reconstructing parsimonious evolutionary histories of such gene clusters, using only human genomic sequence data. In this paper, we propose a probabilistic model for the evolution of gene clusters on a phylogeny, and an MCMC algorithm for reconstruction of duplication histories from genomic sequences in multiple species. Several projects are underway to obtain high quality BAC-based assemblies of duplicated clusters in multiple species, and we anticipate that our method will be useful in analyzing these valuable new data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge