Tom Dooney
DeepExtractor: Time-domain reconstruction of signals and glitches in gravitational wave data with deep learning
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Gravitational wave (GW) interferometers, detect faint signals from distant astrophysical events, such as binary black hole mergers. However, their high sensitivity also makes them susceptible to background noise, which can obscure these signals. This noise often includes transient artifacts called "glitches" that can mimic astrophysical signals or mask their characteristics. Fast and accurate reconstruction of both signals and glitches is crucial for reliable scientific inference. In this study, we present DeepExtractor, a deep learning framework designed to reconstruct signals and glitches with power exceeding interferometer noise, regardless of their source. We design DeepExtractor to model the inherent noise distribution of GW interferometers, following conventional assumptions that the noise is Gaussian and stationary over short time scales. It operates by predicting and subtracting the noise component of the data, retaining only the clean reconstruction. Our approach achieves superior generalization capabilities for arbitrary signals and glitches compared to methods that directly map inputs to the clean training waveforms. We validate DeepExtractor's effectiveness through three experiments: (1) reconstructing simulated glitches injected into simulated detector noise, (2) comparing performance with the state-of-the-art BayesWave algorithm, and (3) analyzing real data from the Gravity Spy dataset to demonstrate effective glitch subtraction from LIGO strain data. DeepExtractor achieves a median mismatch of only 0.9% for simulated glitches, outperforming several deep learning baselines. Additionally, DeepExtractor surpasses BayesWave in glitch recovery, offering a dramatic computational speedup by reconstructing one glitch sample in approx. 0.1 seconds on a CPU, compared to BayesWave's processing time of approx. one hour per glitch.
cDVGAN: One Flexible Model for Multi-class Gravitational Wave Signal and Glitch Generation
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:Simulating realistic time-domain observations of gravitational waves (GWs) and GW detector glitches can help in advancing GW data analysis. Simulated data can be used in downstream tasks by augmenting datasets for signal searches, balancing data sets for machine learning, and validating detection schemes. In this work, we present Conditional Derivative GAN (cDVGAN), a novel conditional model in the Generative Adversarial Network framework for simulating multiple classes of time-domain observations that represent gravitational waves (GWs) and detector glitches. cDVGAN can also generate generalized hybrid samples that span the variation between classes through interpolation in the conditioned class vector. cDVGAN introduces an additional player into the typical 2-player adversarial game of GANs, where an auxiliary discriminator analyzes the first-order derivative time-series. Our results show that this provides synthetic data that better captures the features of the original data. cDVGAN conditions on three classes, two denoised from LIGO blip and tomte glitch events from its 3rd observing run (O3), and the third representing binary black hole (BBH) mergers. Our proposed cDVGAN outperforms 4 different baseline GAN models in replicating the features of the three classes. Specifically, our experiments show that training convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with our cDVGAN-generated data improves the detection of samples embedded in detector noise beyond the synthetic data from other state-of-the-art GAN models. Our best synthetic dataset yields as much as a 4.2% increase in area-under-the-curve (AUC) performance compared to synthetic datasets from baseline GANs. Moreover, training the CNN with hybrid samples from our cDVGAN outperforms CNNs trained only on the standard classes, when identifying real samples embedded in LIGO detector background (4% AUC improvement for cDVGAN).
DVGAN: Stabilize Wasserstein GAN training for time-domain Gravitational Wave physics
Sep 29, 2022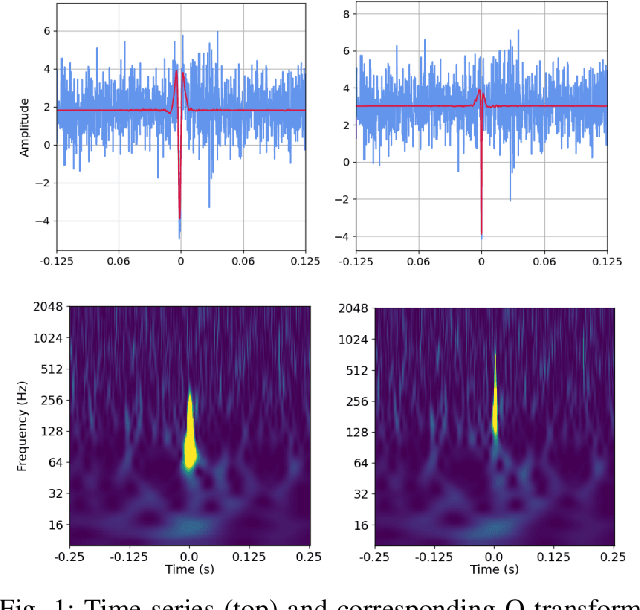
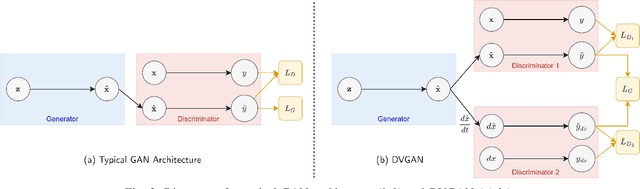
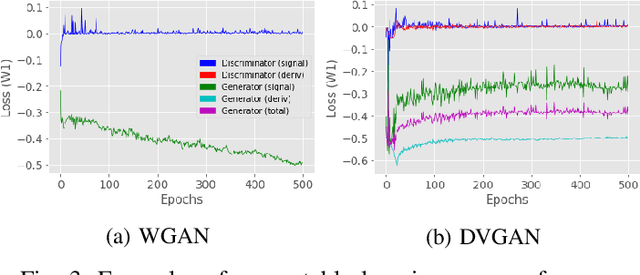

Abstract:Simulating time-domain observations of gravitational wave (GW) detector environments will allow for a better understanding of GW sources, augment datasets for GW signal detection and help in characterizing the noise of the detectors, leading to better physics. This paper presents a novel approach to simulating fixed-length time-domain signals using a three-player Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network (WGAN), called DVGAN, that includes an auxiliary discriminator that discriminates on the derivatives of input signals. An ablation study is used to compare the effects of including adversarial feedback from an auxiliary derivative discriminator with a vanilla two-player WGAN. We show that discriminating on derivatives can stabilize the learning of GAN components on 1D continuous signals during their training phase. This results in smoother generated signals that are less distinguishable from real samples and better capture the distributions of the training data. DVGAN is also used to simulate real transient noise events captured in the advanced LIGO GW detector.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge