Thomas C. Henderson
An Investigation of COVID-19 Spreading Factors with Explainable AI Techniques
May 05, 2020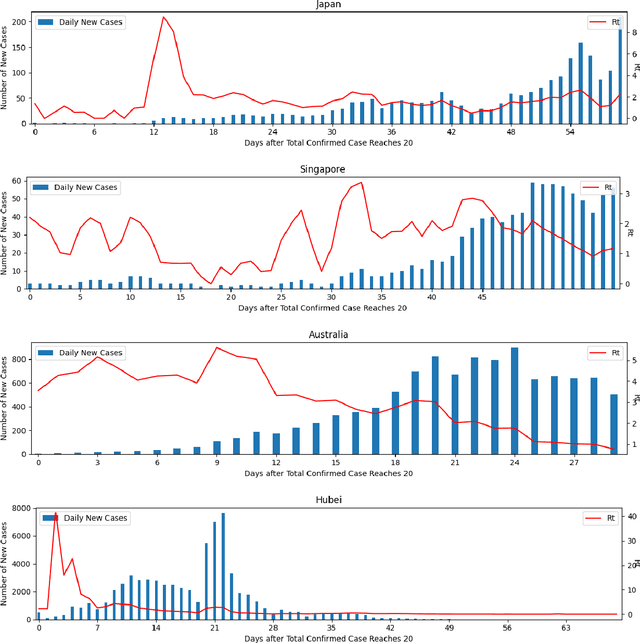
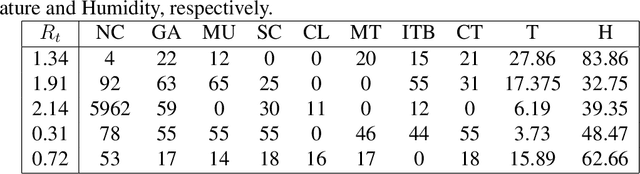
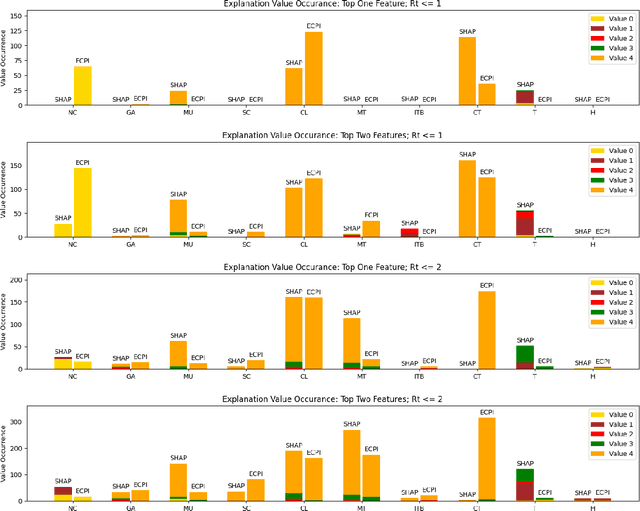
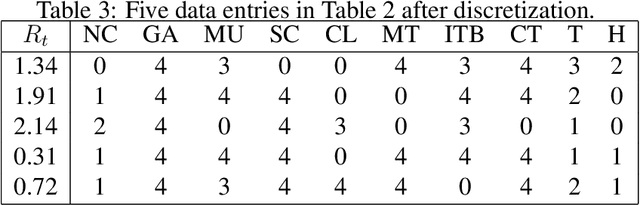
Abstract:Since COVID-19 was first identified in December 2019, various public health interventions have been implemented across the world. As different measures are implemented at different countries at different times, we conduct an assessment of the relative effectiveness of the measures implemented in 18 countries and regions using data from 22/01/2020 to 02/04/2020. We compute the top one and two measures that are most effective for the countries and regions studied during the period. Two Explainable AI techniques, SHAP and ECPI, are used in our study; such that we construct (machine learning) models for predicting the instantaneous reproduction number ($R_t$) and use the models as surrogates to the real world and inputs that the greatest influence to our models are seen as measures that are most effective. Across-the-board, city lockdown and contact tracing are the two most effective measures. For ensuring $R_t<1$, public wearing face masks is also important. Mass testing alone is not the most effective measure although when paired with other measures, it can be effective. Warm temperature helps for reducing the transmission.
Explainable AI for Classification using Probabilistic Logic Inference
May 05, 2020



Abstract:The overarching goal of Explainable AI is to develop systems that not only exhibit intelligent behaviours, but also are able to explain their rationale and reveal insights. In explainable machine learning, methods that produce a high level of prediction accuracy as well as transparent explanations are valuable. In this work, we present an explainable classification method. Our method works by first constructing a symbolic Knowledge Base from the training data, and then performing probabilistic inferences on such Knowledge Base with linear programming. Our approach achieves a level of learning performance comparable to that of traditional classifiers such as random forests, support vector machines and neural networks. It identifies decisive features that are responsible for a classification as explanations and produces results similar to the ones found by SHAP, a state of the art Shapley Value based method. Our algorithms perform well on a range of synthetic and non-synthetic data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge