Thomas Bierweiler
Low-Power Vibration-Based Predictive Maintenance for Industry 4.0 using Neural Networks: A Survey
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:The advancements in smart sensors for Industry 4.0 offer ample opportunities for low-powered predictive maintenance and condition monitoring. However, traditional approaches in this field rely on processing in the cloud, which incurs high costs in energy and storage. This paper investigates the potential of neural networks for low-power on-device computation of vibration sensor data for predictive maintenance. We review the literature on Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) and Artificial Neuronal Networks (ANNs) for vibration-based predictive maintenance by analyzing datasets, data preprocessing, network architectures, and hardware implementations. Our findings suggest that no satisfactory standard benchmark dataset exists for evaluating neural networks in predictive maintenance tasks. Furthermore frequency domain transformations are commonly employed for preprocessing. SNNs mainly use shallow feed forward architectures, whereas ANNs explore a wider range of models and deeper networks. Finally, we highlight the need for future research on hardware implementations of neural networks for low-power predictive maintenance applications and the development of a standardized benchmark dataset.
Towards Robust and Transferable IIoT Sensor based Anomaly Classification using Artificial Intelligence
Oct 07, 2021
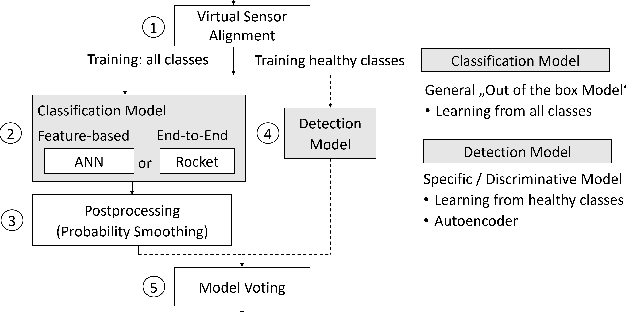
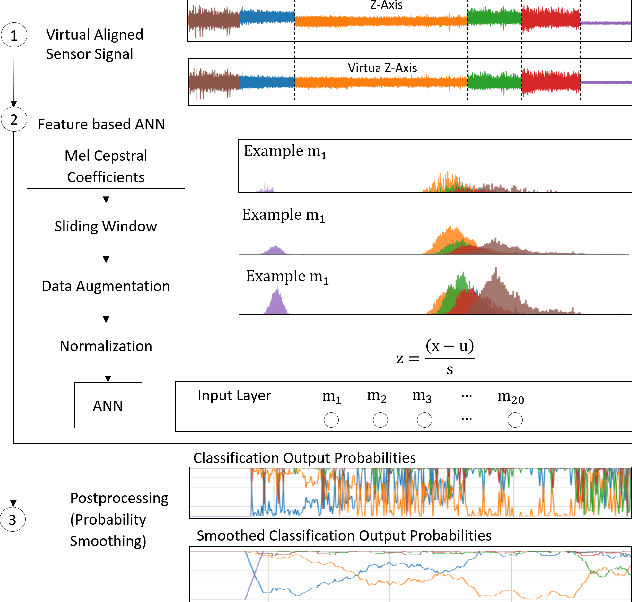
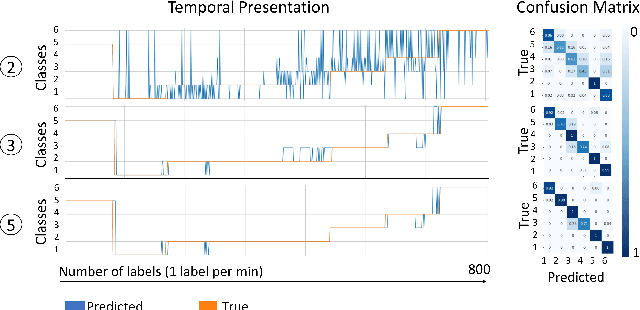
Abstract:The increasing deployment of low-cost industrial IoT (IIoT) sensor platforms on industrial assets enables great opportunities for anomaly classification in industrial plants. The performance of such a classification model depends highly on the available training data. Models perform well when the training data comes from the same machine. However, as soon as the machine is changed, repaired, or put into operation in a different environment, the prediction often fails. For this reason, we investigate whether it is feasible to have a robust and transferable method for AI based anomaly classification using different models and pre-processing steps on centrifugal pumps which are dismantled and put back into operation in the same as well as in different environments. Further, we investigate the model performance on different pumps from the same type compared to those from the training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge