Theresa Jansen
Real-time multichannel deep speech enhancement in hearing aids: Comparing monaural and binaural processing in complex acoustic scenarios
May 03, 2024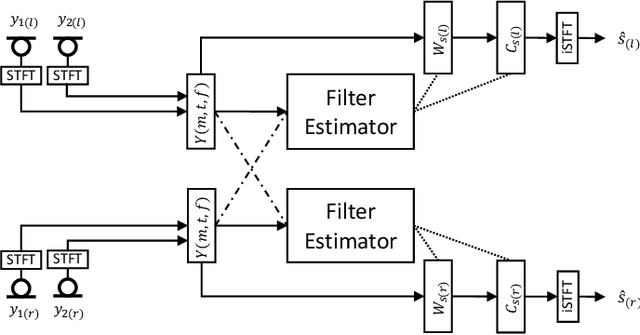
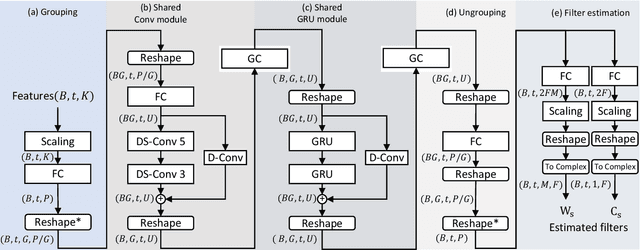
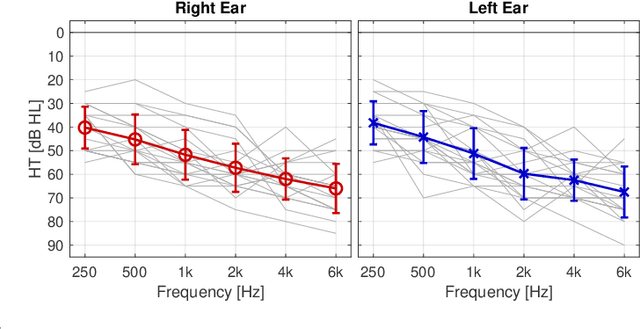
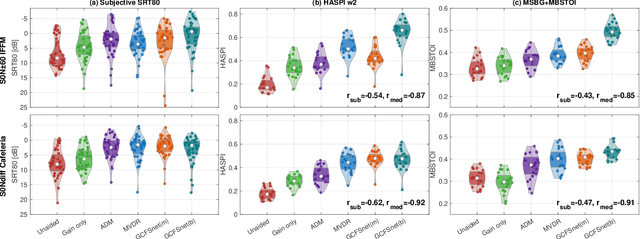
Abstract:Deep learning has the potential to enhance speech signals and increase their intelligibility for users of hearing aids. Deep models suited for real-world application should feature a low computational complexity and low processing delay of only a few milliseconds. In this paper, we explore deep speech enhancement that matches these requirements and contrast monaural and binaural processing algorithms in two complex acoustic scenes. Both algorithms are evaluated with objective metrics and in experiments with hearing-impaired listeners performing a speech-in-noise test. Results are compared to two traditional enhancement strategies, i.e., adaptive differential microphone processing and binaural beamforming. While in diffuse noise, all algorithms perform similarly, the binaural deep learning approach performs best in the presence of spatial interferers. Through a post-analysis, this can be attributed to improvements at low SNRs and to precise spatial filtering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge