Thanh T. Tran
SemViQA: A Semantic Question Answering System for Vietnamese Information Fact-Checking
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:The rise of misinformation, exacerbated by Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT and Gemini, demands robust fact-checking solutions, especially for low-resource languages like Vietnamese. Existing methods struggle with semantic ambiguity, homonyms, and complex linguistic structures, often trading accuracy for efficiency. We introduce SemViQA, a novel Vietnamese fact-checking framework integrating Semantic-based Evidence Retrieval (SER) and Two-step Verdict Classification (TVC). Our approach balances precision and speed, achieving state-of-the-art results with 78.97\% strict accuracy on ISE-DSC01 and 80.82\% on ViWikiFC, securing 1st place in the UIT Data Science Challenge. Additionally, SemViQA Faster improves inference speed 7x while maintaining competitive accuracy. SemViQA sets a new benchmark for Vietnamese fact verification, advancing the fight against misinformation. The source code is available at: https://github.com/DAVID-NGUYEN-S16/SemViQA.
VinDr-PCXR: An open, large-scale chest radiograph dataset for interpretation of common thoracic diseases in children
Mar 20, 2022
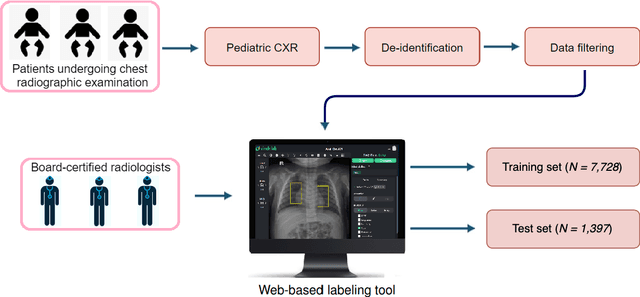
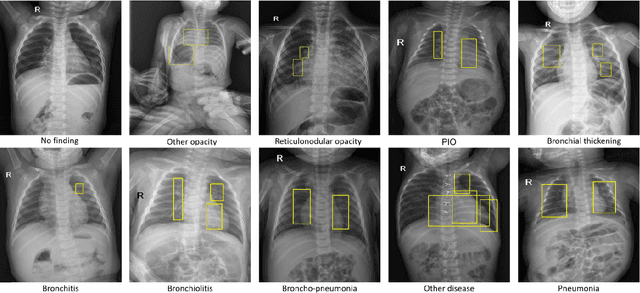
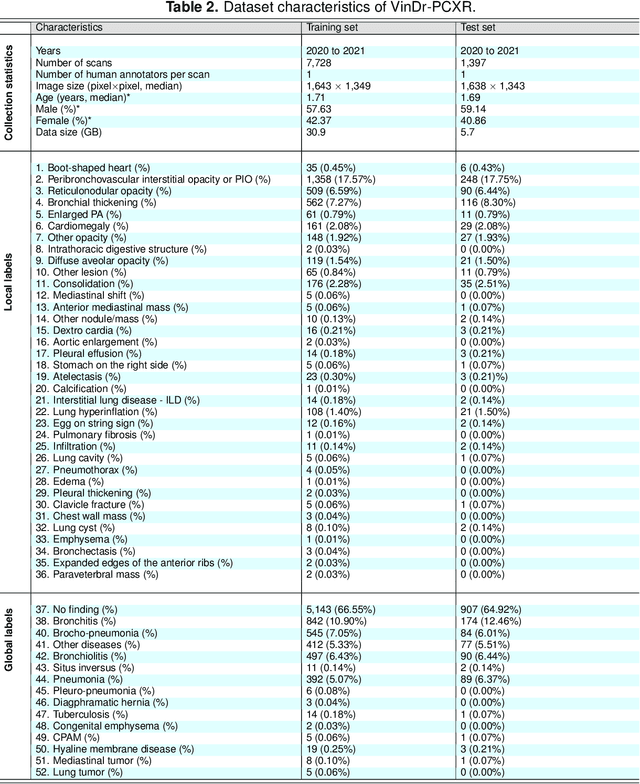
Abstract:Computer-aided diagnosis systems in adult chest radiography (CXR) have recently achieved great success thanks to the availability of large-scale, annotated datasets and the advent of high-performance supervised learning algorithms. However, the development of diagnostic models for detecting and diagnosing pediatric diseases in CXR scans is undertaken due to the lack of high-quality physician-annotated datasets. To overcome this challenge, we introduce and release VinDr-PCXR, a new pediatric CXR dataset of 9,125 studies retrospectively collected from a major pediatric hospital in Vietnam between 2020 and 2021. Each scan was manually annotated by a pediatric radiologist who has more than ten years of experience. The dataset was labeled for the presence of 36 critical findings and 15 diseases. In particular, each abnormal finding was identified via a rectangle bounding box on the image. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first and largest pediatric CXR dataset containing lesion-level annotations and image-level labels for the detection of multiple findings and diseases. For algorithm development, the dataset was divided into a training set of 7,728 and a test set of 1,397. To encourage new advances in pediatric CXR interpretation using data-driven approaches, we provide a detailed description of the VinDr-PCXR data sample and make the dataset publicly available on https://physionet.org/.
Learning to Automatically Diagnose Multiple Diseases in Pediatric Chest Radiographs Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Aug 14, 2021Abstract:Chest radiograph (CXR) interpretation in pediatric patients is error-prone and requires a high level of understanding of radiologic expertise. Recently, deep convolutional neural networks (D-CNNs) have shown remarkable performance in interpreting CXR in adults. However, there is a lack of evidence indicating that D-CNNs can recognize accurately multiple lung pathologies from pediatric CXR scans. In particular, the development of diagnostic models for the detection of pediatric chest diseases faces significant challenges such as (i) lack of physician-annotated datasets and (ii) class imbalance problems. In this paper, we retrospectively collect a large dataset of 5,017 pediatric CXR scans, for which each is manually labeled by an experienced radiologist for the presence of 10 common pathologies. A D-CNN model is then trained on 3,550 annotated scans to classify multiple pediatric lung pathologies automatically. To address the high-class imbalance issue, we propose to modify and apply "Distribution-Balanced loss" for training D-CNNs which reshapes the standard Binary-Cross Entropy loss (BCE) to efficiently learn harder samples by down-weighting the loss assigned to the majority classes. On an independent test set of 777 studies, the proposed approach yields an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUC) of 0.709 (95% CI, 0.690-0.729). The sensitivity, specificity, and F1-score at the cutoff value are 0.722 (0.694-0.750), 0.579 (0.563-0.595), and 0.389 (0.373-0.405), respectively. These results significantly outperform previous state-of-the-art methods on most of the target diseases. Moreover, our ablation studies validate the effectiveness of the proposed loss function compared to other standard losses, e.g., BCE and Focal Loss, for this learning task. Overall, we demonstrate the potential of D-CNNs in interpreting pediatric CXRs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge