Tatsuya Konishi
Parameter-Level Soft-Masking for Continual Learning
Jun 26, 2023



Abstract:Existing research on task incremental learning in continual learning has primarily focused on preventing catastrophic forgetting (CF). Although several techniques have achieved learning with no CF, they attain it by letting each task monopolize a sub-network in a shared network, which seriously limits knowledge transfer (KT) and causes over-consumption of the network capacity, i.e., as more tasks are learned, the performance deteriorates. The goal of this paper is threefold: (1) overcoming CF, (2) encouraging KT, and (3) tackling the capacity problem. A novel technique (called SPG) is proposed that soft-masks (partially blocks) parameter updating in training based on the importance of each parameter to old tasks. Each task still uses the full network, i.e., no monopoly of any part of the network by any task, which enables maximum KT and reduction in capacity usage. To our knowledge, this is the first work that soft-masks a model at the parameter-level for continual learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of SPG in achieving all three objectives. More notably, it attains significant transfer of knowledge not only among similar tasks (with shared knowledge) but also among dissimilar tasks (with little shared knowledge) while mitigating CF.
Learnability and Algorithm for Continual Learning
Jun 22, 2023Abstract:This paper studies the challenging continual learning (CL) setting of Class Incremental Learning (CIL). CIL learns a sequence of tasks consisting of disjoint sets of concepts or classes. At any time, a single model is built that can be applied to predict/classify test instances of any classes learned thus far without providing any task related information for each test instance. Although many techniques have been proposed for CIL, they are mostly empirical. It has been shown recently that a strong CIL system needs a strong within-task prediction (WP) and a strong out-of-distribution (OOD) detection for each task. However, it is still not known whether CIL is actually learnable. This paper shows that CIL is learnable. Based on the theory, a new CIL algorithm is also proposed. Experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness.
Open-World Continual Learning: Unifying Novelty Detection and Continual Learning
Apr 20, 2023Abstract:As AI agents are increasingly used in the real open world with unknowns or novelties, they need the ability to (1) recognize objects that (i) they have learned and (ii) detect items that they have not seen or learned before, and (2) learn the new items incrementally to become more and more knowledgeable and powerful. (1) is called novelty detection or out-of-distribution (OOD) detection and (2) is called class incremental learning (CIL), which is a setting of continual learning (CL). In existing research, OOD detection and CIL are regarded as two completely different problems. This paper theoretically proves that OOD detection actually is necessary for CIL. We first show that CIL can be decomposed into two sub-problems: within-task prediction (WP) and task-id prediction (TP). We then prove that TP is correlated with OOD detection. The key theoretical result is that regardless of whether WP and OOD detection (or TP) are defined explicitly or implicitly by a CIL algorithm, good WP and good OOD detection are necessary and sufficient conditions for good CIL, which unifies novelty or OOD detection and continual learning (CIL, in particular). A good CIL algorithm based on our theory can naturally be used in open world learning, which is able to perform both novelty/OOD detection and continual learning. Based on the theoretical result, new CIL methods are also designed, which outperform strong baselines in terms of CIL accuracy and its continual OOD detection by a large margin.
Continual Learning of Language Models
Feb 10, 2023Abstract:Language models (LMs) have been instrumental for the rapid advance of natural language processing. This paper studies continual learning of LMs, in particular, continual domain-adaptive pre-training (or continual DAP-training). Existing research has shown that further pre-training an LM using a domain corpus to adapt the LM to the domain can improve the end-task performance in the domain. This paper proposes a novel method to continually DAP-train an LM with a sequence of unlabeled domain corpora to adapt the LM to these domains to improve their end-task performances. The key novelty of our method is a soft-masking mechanism that directly controls the update to the LM. A novel proxy is also proposed to preserve the general knowledge in the original LM. Additionally, it contrasts the representations of the previously learned domain knowledge (including the general knowledge in the pre-trained LM) and the knowledge from the current full network to achieve knowledge integration. The method not only overcomes catastrophic forgetting, but also achieves knowledge transfer to improve end-task performances. Empirical evaluation demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method.
A Theoretical Study on Solving Continual Learning
Nov 04, 2022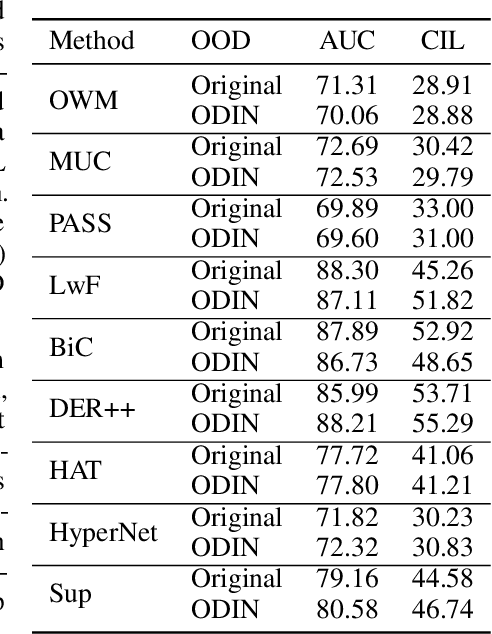
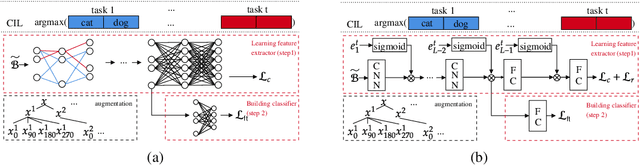

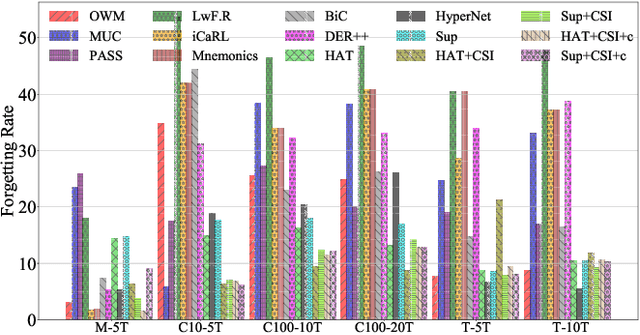
Abstract:Continual learning (CL) learns a sequence of tasks incrementally. There are two popular CL settings, class incremental learning (CIL) and task incremental learning (TIL). A major challenge of CL is catastrophic forgetting (CF). While a number of techniques are already available to effectively overcome CF for TIL, CIL remains to be highly challenging. So far, little theoretical study has been done to provide a principled guidance on how to solve the CIL problem. This paper performs such a study. It first shows that probabilistically, the CIL problem can be decomposed into two sub-problems: Within-task Prediction (WP) and Task-id Prediction (TP). It further proves that TP is correlated with out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, which connects CIL and OOD detection. The key conclusion of this study is that regardless of whether WP and TP or OOD detection are defined explicitly or implicitly by a CIL algorithm, good WP and good TP or OOD detection are necessary and sufficient for good CIL performances. Additionally, TIL is simply WP. Based on the theoretical result, new CIL methods are also designed, which outperform strong baselines in both CIL and TIL settings by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge