Tanguy Bosser
Preventing Conflicting Gradients in Neural Marked Temporal Point Processes
Dec 11, 2024
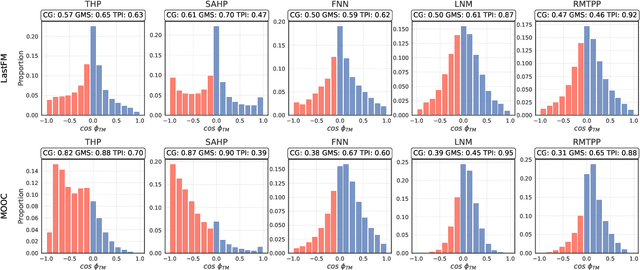

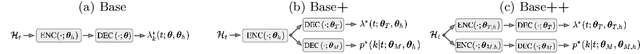
Abstract:Neural Marked Temporal Point Processes (MTPP) are flexible models to capture complex temporal inter-dependencies between labeled events. These models inherently learn two predictive distributions: one for the arrival times of events and another for the types of events, also known as marks. In this study, we demonstrate that learning a MTPP model can be framed as a two-task learning problem, where both tasks share a common set of trainable parameters that are optimized jointly. We show that this often leads to the emergence of conflicting gradients during training, where task-specific gradients are pointing in opposite directions. When such conflicts arise, following the average gradient can be detrimental to the learning of each individual tasks, resulting in overall degraded performance. To overcome this issue, we introduce novel parametrizations for neural MTPP models that allow for separate modeling and training of each task, effectively avoiding the problem of conflicting gradients. Through experiments on multiple real-world event sequence datasets, we demonstrate the benefits of our framework compared to the original model formulations.
Distribution-Free Conformal Joint Prediction Regions for Neural Marked Temporal Point Processes
Jan 09, 2024



Abstract:Sequences of labeled events observed at irregular intervals in continuous time are ubiquitous across various fields. Temporal Point Processes (TPPs) provide a mathematical framework for modeling these sequences, enabling inferences such as predicting the arrival time of future events and their associated label, called mark. However, due to model misspecification or lack of training data, these probabilistic models may provide a poor approximation of the true, unknown underlying process, with prediction regions extracted from them being unreliable estimates of the underlying uncertainty. This paper develops more reliable methods for uncertainty quantification in neural TPP models via the framework of conformal prediction. A primary objective is to generate a distribution-free joint prediction region for the arrival time and mark, with a finite-sample marginal coverage guarantee. A key challenge is to handle both a strictly positive, continuous response and a categorical response, without distributional assumptions. We first consider a simple but overly conservative approach that combines individual prediction regions for the event arrival time and mark. Then, we introduce a more effective method based on bivariate highest density regions derived from the joint predictive density of event arrival time and mark. By leveraging the dependencies between these two variables, this method exclude unlikely combinations of the two, resulting in sharper prediction regions while still attaining the pre-specified coverage level. We also explore the generation of individual univariate prediction regions for arrival times and marks through conformal regression and classification techniques. Moreover, we investigate the stronger notion of conditional coverage. Finally, through extensive experimentation on both simulated and real-world datasets, we assess the validity and efficiency of these methods.
On the Predictive Accuracy of Neural Temporal Point Process Models for Continuous-time Event Data
Jul 10, 2023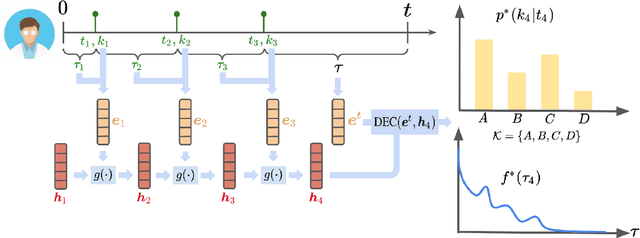
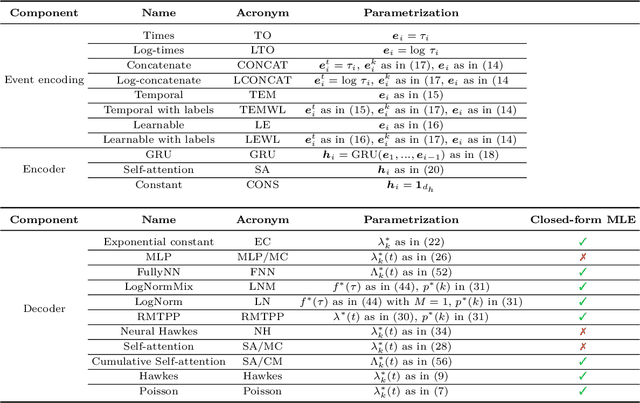
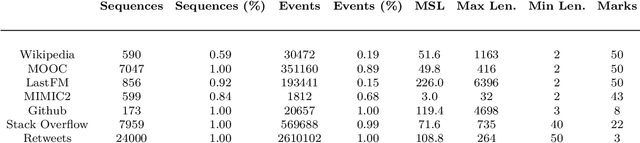
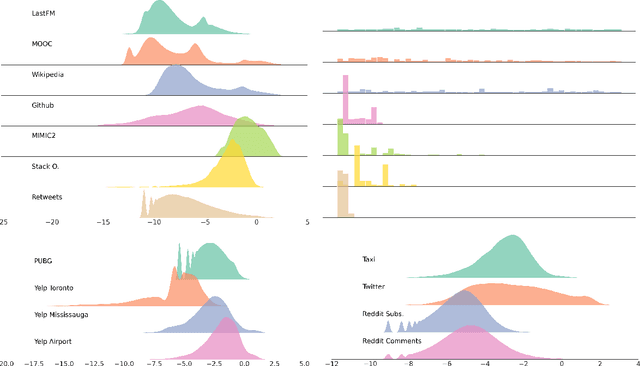
Abstract:Temporal Point Processes (TPPs) serve as the standard mathematical framework for modeling asynchronous event sequences in continuous time. However, classical TPP models are often constrained by strong assumptions, limiting their ability to capture complex real-world event dynamics. To overcome this limitation, researchers have proposed Neural TPPs, which leverage neural network parametrizations to offer more flexible and efficient modeling. While recent studies demonstrate the effectiveness of Neural TPPs, they often lack a unified setup, relying on different baselines, datasets, and experimental configurations. This makes it challenging to identify the key factors driving improvements in predictive accuracy, hindering research progress. To bridge this gap, we present a comprehensive large-scale experimental study that systematically evaluates the predictive accuracy of state-of-the-art neural TPP models. Our study encompasses multiple real-world and synthetic event sequence datasets, following a carefully designed unified setup. We thoroughly investigate the influence of major architectural components such as event encoding, history encoder, and decoder parametrization on both time and mark prediction tasks. Additionally, we delve into the less explored area of probabilistic calibration for neural TPP models. By analyzing our results, we draw insightful conclusions regarding the significance of history size and the impact of architectural components on predictive accuracy. Furthermore, we shed light on the miscalibration of mark distributions in neural TPP models. Our study aims to provide valuable insights into the performance and characteristics of neural TPP models, contributing to a better understanding of their strengths and limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge