Tae-Hee Cho
A Novel Autoencoders-LSTM Model for Stroke Outcome Prediction using Multimodal MRI Data
Mar 16, 2023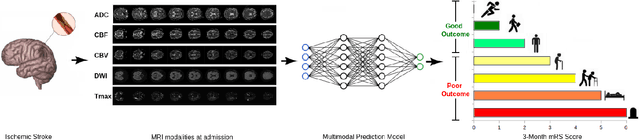
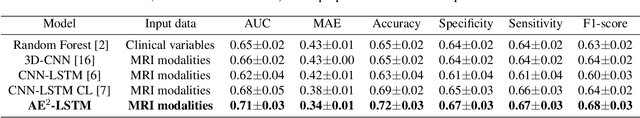
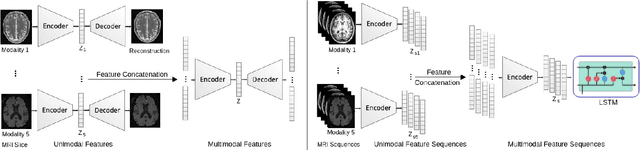
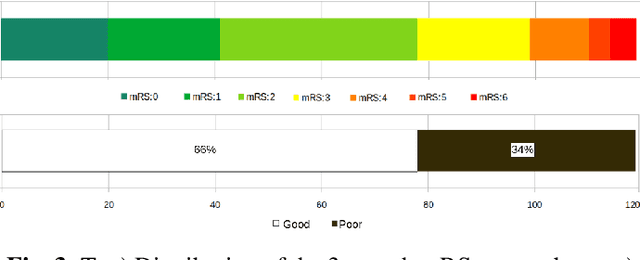
Abstract:Patient outcome prediction is critical in management of ischemic stroke. In this paper, a novel machine learning model is proposed for stroke outcome prediction using multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The proposed model consists of two serial levels of Autoencoders (AEs), where different AEs at level 1 are used for learning unimodal features from different MRI modalities and a AE at level 2 is used to combine the unimodal features into compressed multimodal features. The sequences of multimodal features of a given patient are then used by an LSTM network for predicting outcome score. The proposed AE2-LSTM model is proved to be an effective approach for better addressing the multimodality and volumetric nature of MRI data. Experimental results show that the proposed AE2-LSTM outperforms the existing state-of-the art models by achieving highest AUC=0.71 and lowest MAE=0.34.
CNN-LSTM Based Multimodal MRI and Clinical Data Fusion for Predicting Functional Outcome in Stroke Patients
May 11, 2022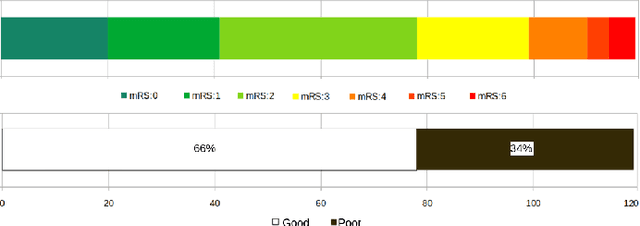
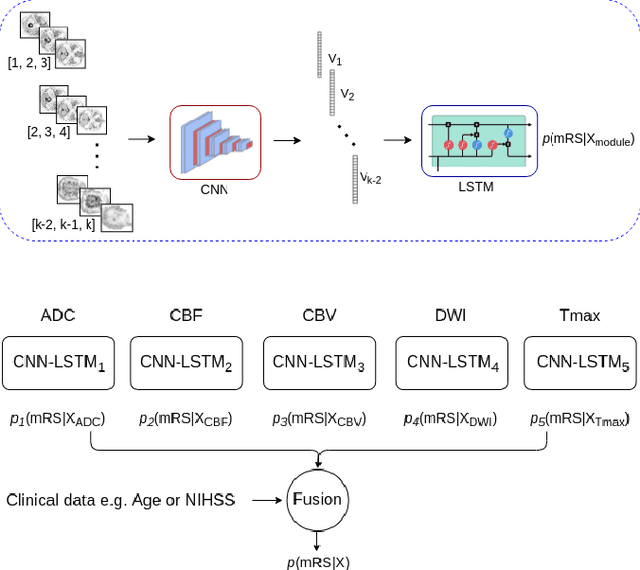
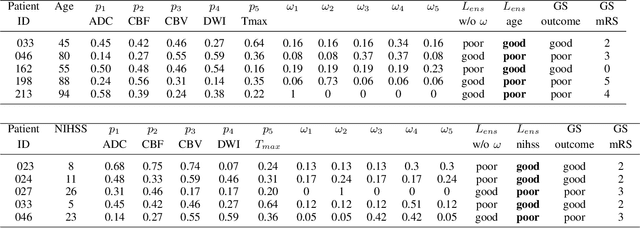
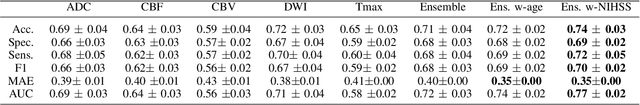
Abstract:Clinical outcome prediction plays an important role in stroke patient management. From a machine learning point-of-view, one of the main challenges is dealing with heterogeneous data at patient admission, i.e. the image data which are multidimensional and the clinical data which are scalars. In this paper, a multimodal convolutional neural network - long short-term memory (CNN-LSTM) based ensemble model is proposed. For each MR image module, a dedicated network provides preliminary prediction of the clinical outcome using the modified Rankin scale (mRS). The final mRS score is obtained by merging the preliminary probabilities of each module dedicated to a specific type of MR image weighted by the clinical metadata, here age or the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS). The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model surpasses the baselines and offers an original way to automatically encode the spatio-temporal context of MR images in a deep learning architecture. The highest AUC (0.77) was achieved for the proposed model with NIHSS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge