Sugata Sanyal
Finding Numerical Solutions of Diophantine Equations using Ant Colony Optimization
Jun 04, 2013
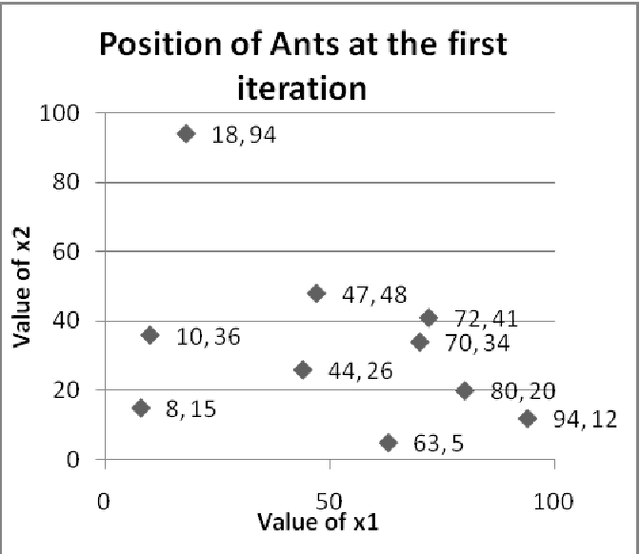
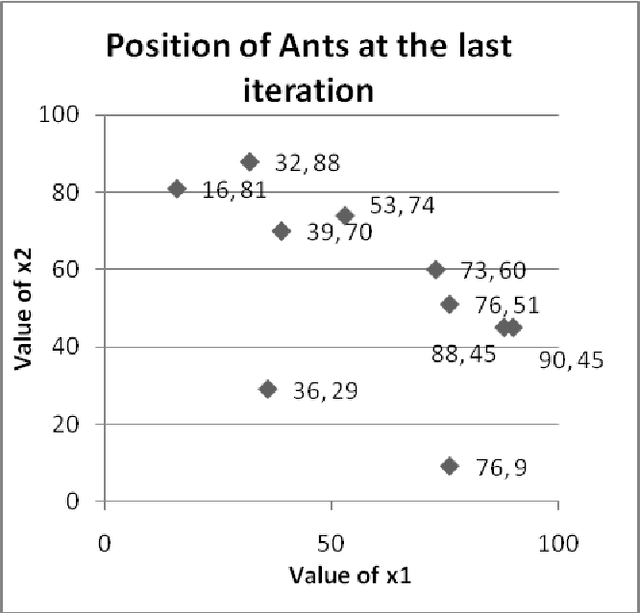
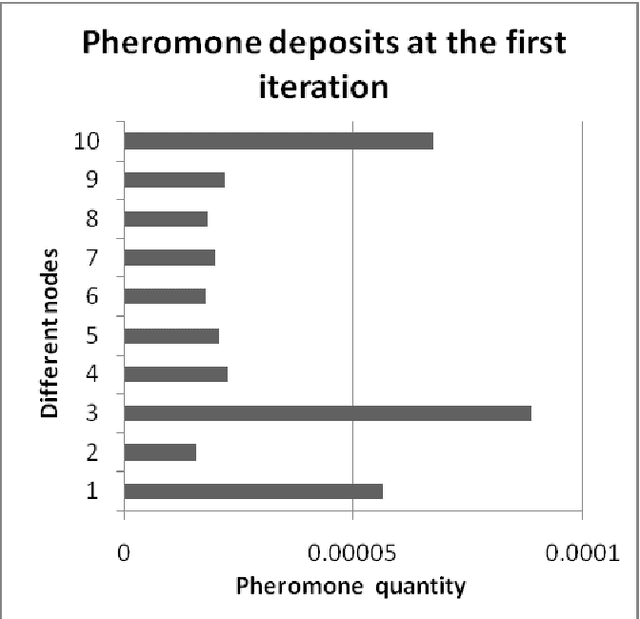
Abstract:The paper attempts to find numerical solutions of Diophantine equations, a challenging problem as there are no general methods to find solutions of such equations. It uses the metaphor of foraging habits of real ants. The ant colony optimization based procedure starts with randomly assigned locations to a fixed number of artificial ants. Depending upon the quality of these positions, ants deposit pheromone at the nodes. A successor node is selected from the topological neighborhood of each of the nodes based on this stochastic pheromone deposit. If an ant bumps into an already encountered node, the pheromone is updated correspondingly. A suitably defined pheromone evaporation strategy guarantees that premature convergence does not take place. The experimental results, which compares with those of other machine intelligence techniques, validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Machine Translation Systems in India
Apr 29, 2013



Abstract:Machine Translation is the translation of one natural language into another using automated and computerized means. For a multilingual country like India, with the huge amount of information exchanged between various regions and in different languages in digitized format, it has become necessary to find an automated process from one language to another. In this paper, we take a look at the various Machine Translation System in India which is specifically built for the purpose of translation between the Indian languages. We discuss the various approaches taken for building the machine translation system and then discuss some of the Machine Translation Systems in India along with their features.
A Connectionist Network Approach to Find Numerical Solutions of Diophantine Equations
Oct 08, 2012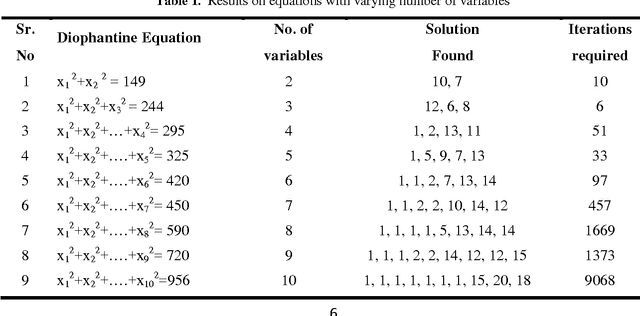
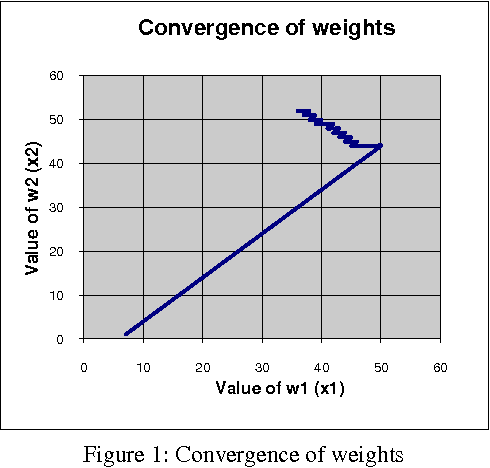
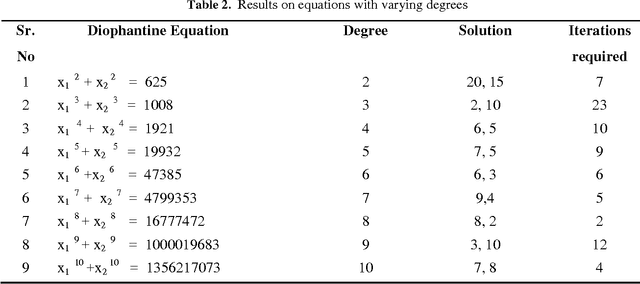
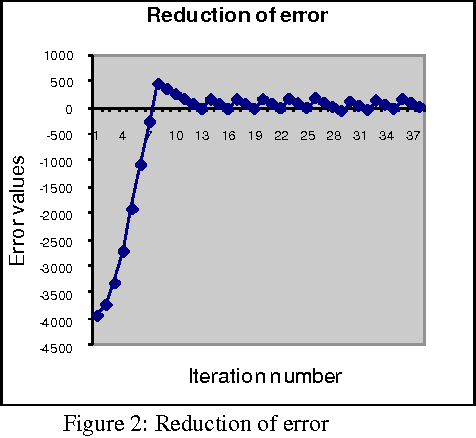
Abstract:The paper introduces a connectionist network approach to find numerical solutions of Diophantine equations as an attempt to address the famous Hilbert's tenth problem. The proposed methodology uses a three layer feed forward neural network with back propagation as sequential learning procedure to find numerical solutions of a class of Diophantine equations. It uses a dynamically constructed network architecture where number of nodes in the input layer is chosen based on the number of variables in the equation. The powers of the given Diophantine equation are taken as input to the input layer. The training of the network starts with initial random integral weights. The weights are updated based on the back propagation of the error values at the output layer. The optimization of weights is augmented by adding a momentum factor into the network. The optimized weights of the connection between the input layer and the hidden layer are taken as numerical solution of the given Diophantine equation. The procedure is validated using different Diophantine Equations of different number of variables and different powers.
Rule Based Expert System for Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Disorders
Jul 09, 2012
Abstract:In this paper, we discuss the implementation of a rule based expert system for diagnosing neuromuscular diseases. The proposed system is implemented as a rule based expert system in JESS for the diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy, Multiple Sclerosis, Muscular Dystrophy and Parkinson's disease. In the system, the user is presented with a list of questionnaires about the symptoms of the patients based on which the disease of the patient is diagnosed and possible treatment is suggested. The system can aid and support the patients suffering from neuromuscular diseases to get an idea of their disease and possible treatment for the disease.
Rule Based Expert System for Cerebral Palsy Diagnosis
Jun 30, 2012

Abstract:The use of Artificial Intelligence is finding prominence not only in core computer areas, but also in cross disciplinary areas including medical diagnosis. In this paper, we present a rule based Expert System used in diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy. The expert system takes user input and depending on the symptoms of the patient, diagnoses if the patient is suffering from Cerebral Palsy. The Expert System also classifies the Cerebral Palsy as mild, moderate or severe based on the presented symptoms.
A Microwave Imaging and Enhancement Technique from Noisy Synthetic Data
Oct 02, 2010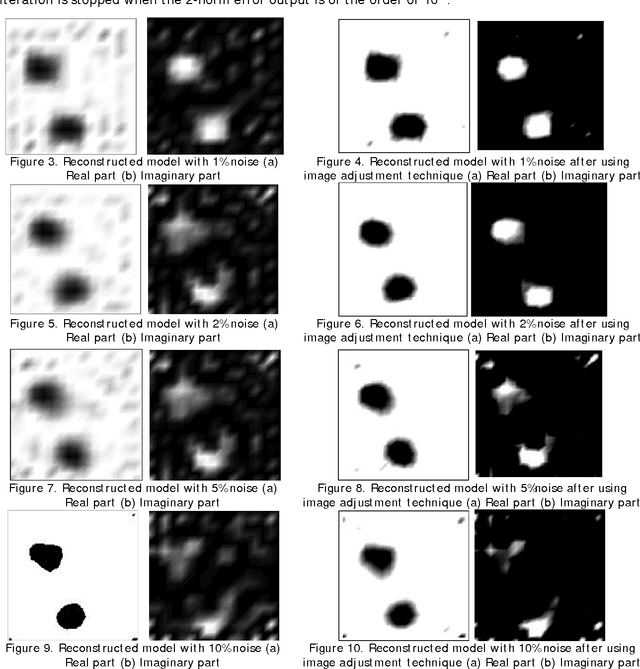
Abstract:An inverse iterative algorithm for microwave imaging based on moment method solution is presented here. The iterative scheme has been developed on constrained optimization technique and is certain to converge. Different mesh size for the model has been used here to overcome the Inverse Crime. The synthetic data at the receivers is contaminated with different percentage of noise. The ill-posedness of the problem is solved by Levenberg-Marquardt method. The algorithm is applied to synthetic data and the reconstructed image is then further enhanced through the Image enhancement technique
Steepest Ascent Hill Climbing For A Mathematical Problem
Oct 02, 2010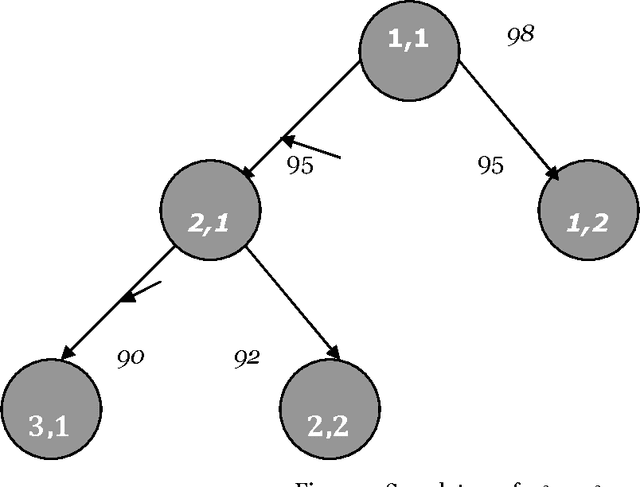
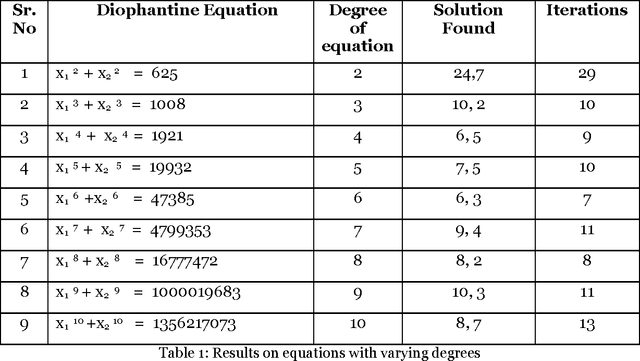
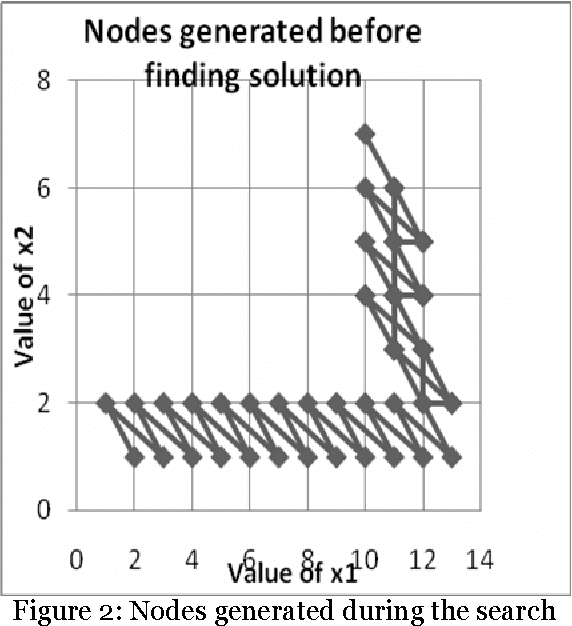

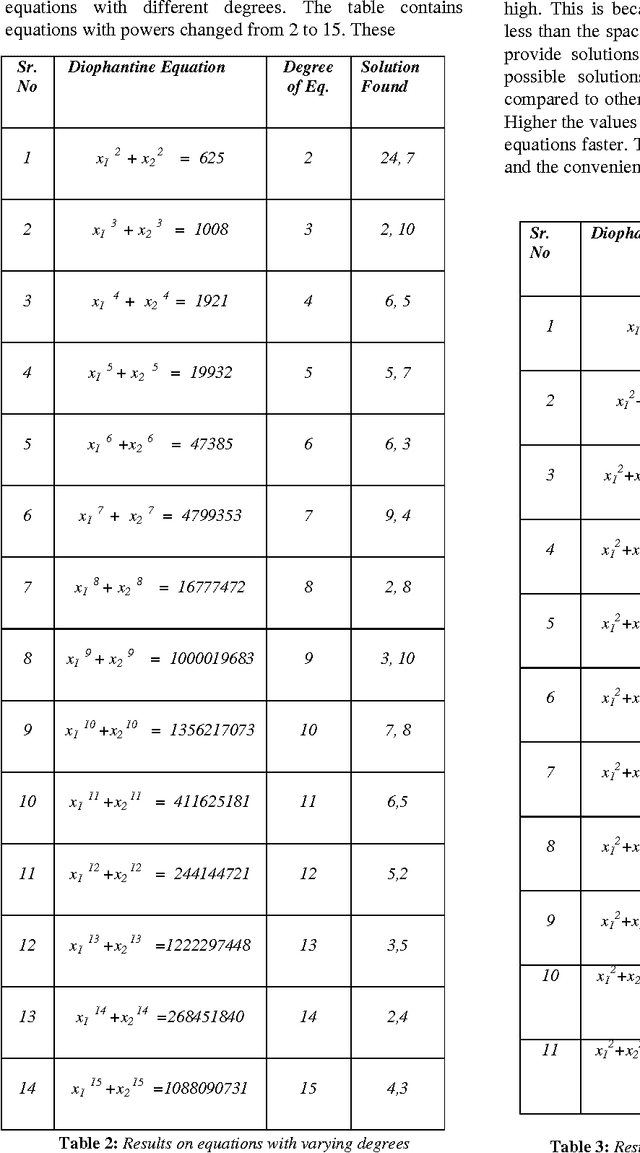
Abstract:The paper proposes artificial intelligence technique called hill climbing to find numerical solutions of Diophantine Equations. Such equations are important as they have many applications in fields like public key cryptography, integer factorization, algebraic curves, projective curves and data dependency in super computers. Importantly, it has been proved that there is no general method to find solutions of such equations. This paper is an attempt to find numerical solutions of Diophantine equations using steepest ascent version of Hill Climbing. The method, which uses tree representation to depict possible solutions of Diophantine equations, adopts a novel methodology to generate successors. The heuristic function used help to make the process of finding solution as a minimization process. The work illustrates the effectiveness of the proposed methodology using a class of Diophantine equations given by a1. x1 p1 + a2. x2 p2 + ...... + an . xn pn = N where ai and N are integers. The experimental results validate that the procedure proposed is successful in finding solutions of Diophantine Equations with sufficiently large powers and large number of variables.
Particle Swarm Optimization Based Diophantine Equation Solver
Mar 13, 2010

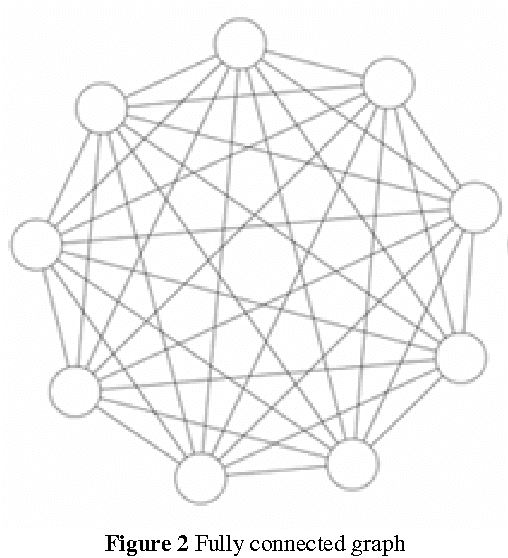
Abstract:The paper introduces particle swarm optimization as a viable strategy to find numerical solution of Diophantine equation, for which there exists no general method of finding solutions. The proposed methodology uses a population of integer particles. The candidate solutions in the feasible space are optimized to have better positions through particle best and global best positions. The methodology, which follows fully connected neighborhood topology, can offer many solutions of such equations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge