Sudeep Katakol
UniFusion: Vision-Language Model as Unified Encoder in Image Generation
Oct 14, 2025
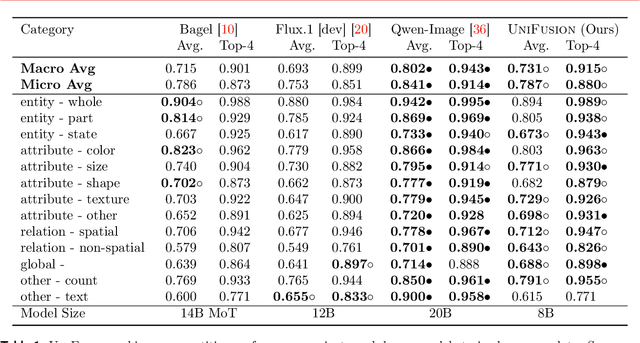

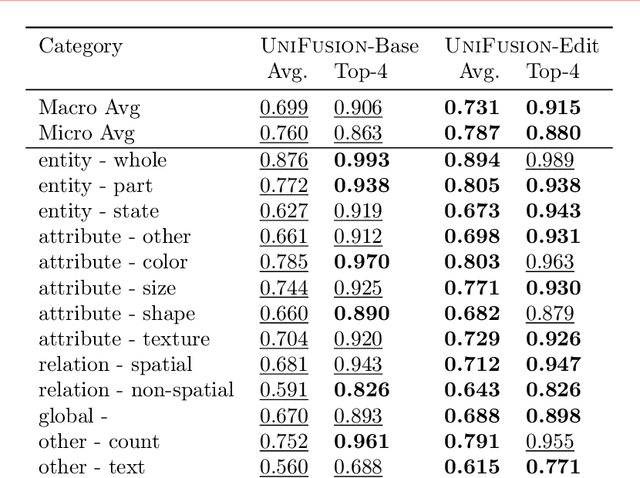
Abstract:Although recent advances in visual generation have been remarkable, most existing architectures still depend on distinct encoders for images and text. This separation constrains diffusion models' ability to perform cross-modal reasoning and knowledge transfer. Prior attempts to bridge this gap often use the last layer information from VLM, employ multiple visual encoders, or train large unified models jointly for text and image generation, which demands substantial computational resources and large-scale data, limiting its accessibility.We present UniFusion, a diffusion-based generative model conditioned on a frozen large vision-language model (VLM) that serves as a unified multimodal encoder. At the core of UniFusion is the Layerwise Attention Pooling (LAP) mechanism that extracts both high level semantics and low level details from text and visual tokens of a frozen VLM to condition a diffusion generative model. We demonstrate that LAP outperforms other shallow fusion architectures on text-image alignment for generation and faithful transfer of visual information from VLM to the diffusion model which is key for editing. We propose VLM-Enabled Rewriting Injection with Flexibile Inference (VERIFI), which conditions a diffusion transformer (DiT) only on the text tokens generated by the VLM during in-model prompt rewriting. VERIFI combines the alignment of the conditioning distribution with the VLM's reasoning capabilities for increased capabilities and flexibility at inference. In addition, finetuning on editing task not only improves text-image alignment for generation, indicative of cross-modality knowledge transfer, but also exhibits tremendous generalization capabilities. Our model when trained on single image editing, zero-shot generalizes to multiple image references further motivating the unified encoder design of UniFusion.
DANICE: Domain adaptation without forgetting in neural image compression
Apr 19, 2021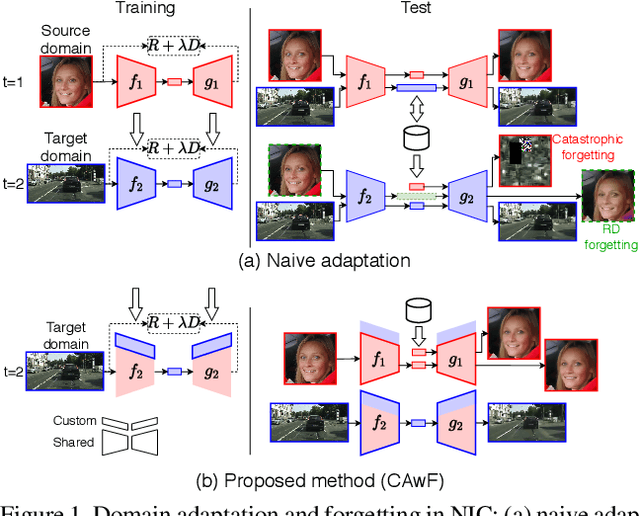
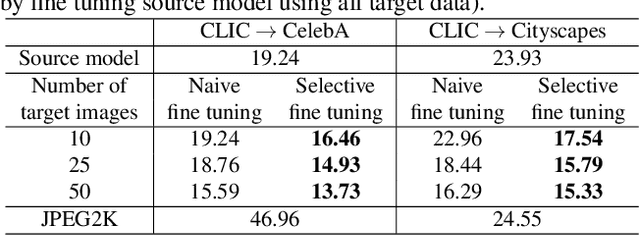
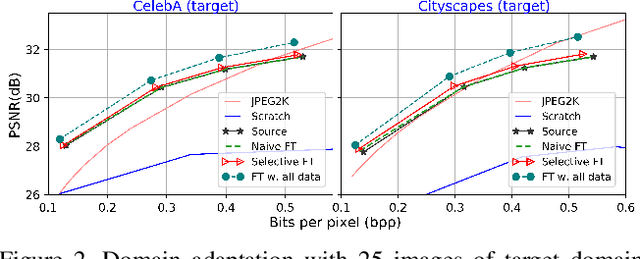
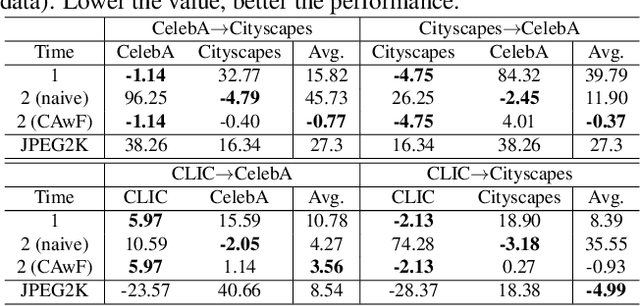
Abstract:Neural image compression (NIC) is a new coding paradigm where coding capabilities are captured by deep models learned from data. This data-driven nature enables new potential functionalities. In this paper, we study the adaptability of codecs to custom domains of interest. We show that NIC codecs are transferable and that they can be adapted with relatively few target domain images. However, naive adaptation interferes with the solution optimized for the original source domain, resulting in forgetting the original coding capabilities in that domain, and may even break the compatibility with previously encoded bitstreams. Addressing these problems, we propose Codec Adaptation without Forgetting (CAwF), a framework that can avoid these problems by adding a small amount of custom parameters, where the source codec remains embedded and unchanged during the adaptation process. Experiments demonstrate its effectiveness and provide useful insights on the characteristics of catastrophic interference in NIC.
Distributed Learning and Inference with Compressed Images
Apr 22, 2020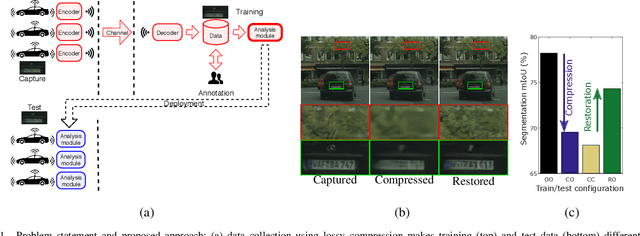
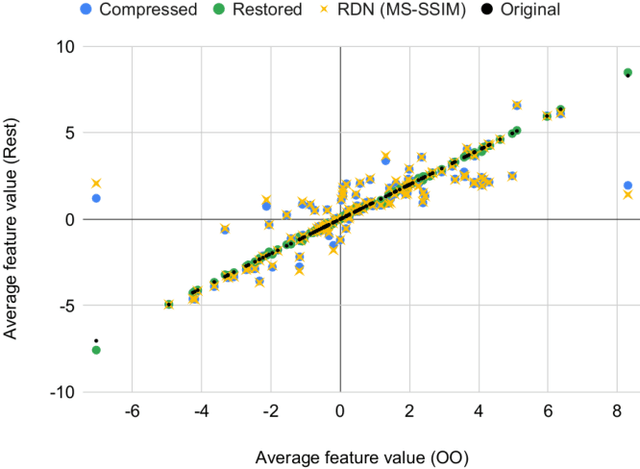

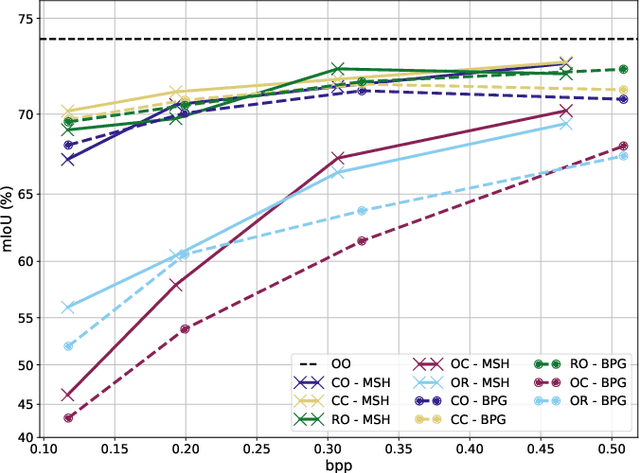
Abstract:Modern computer vision requires processing large amounts of data, both while training the model and/or during inference, once the model is deployed. Scenarios where images are captured and processed in physically separated locations are increasingly common (e.g. autonomous vehicles, cloud computing). In addition, many devices suffer from limited resources to store or transmit data (e.g. storage space, channel capacity). In these scenarios, lossy image compression plays a crucial role to effectively increase the number of images collected under such constraints. However, lossy compression entails some undesired degradation of the data that may harm the performance of the downstream analysis task at hand, since important semantic information may be lost in the process. Moreover, we may only have compressed images at training time but are able to use original images at inference time, or vice versa, and in such a case, the downstream model suffers from covariate shift. In this paper, we analyze this phenomenon, with a special focus on vision-based perception for autonomous driving as a paradigmatic scenario. We see that loss of semantic information and covariate shift do indeed exist, resulting in a drop in performance that depends on the compression rate. In order to address the problem, we propose dataset restoration, based on image restoration with generative adversarial networks (GANs). Our method is agnostic to both the particular image compression method and the downstream task; and has the advantage of not adding additional cost to the deployed models, which is particularly important in resource-limited devices. The presented experiments focus on semantic segmentation as a challenging use case, cover a broad range of compression rates and diverse datasets, and show how our method is able to significantly alleviate the negative effects of compression on the downstream visual task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge