Steve Sloan
Imbalance-Aware Culvert-Sewer Defect Segmentation Using an Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Imbalanced datasets are a significant challenge in real-world scenarios. They lead to models that underperform on underrepresented classes, which is a critical issue in infrastructure inspection. This paper introduces the Enhanced Feature Pyramid Network (E-FPN), a deep learning model for the semantic segmentation of culverts and sewer pipes within imbalanced datasets. The E-FPN incorporates architectural innovations like sparsely connected blocks and depth-wise separable convolutions to improve feature extraction and handle object variations. To address dataset imbalance, the model employs strategies like class decomposition and data augmentation. Experimental results on the culvert-sewer defects dataset and a benchmark aerial semantic segmentation drone dataset show that the E-FPN outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving an average Intersection over Union (IoU) improvement of 13.8% and 27.2%, respectively. Additionally, class decomposition and data augmentation together boost the model's performance by approximately 6.9% IoU. The proposed E-FPN presents a promising solution for enhancing object segmentation in challenging, multi-class real-world datasets, with potential applications extending beyond culvert-sewer defect detection.
SHARP-Net: A Refined Pyramid Network for Deficiency Segmentation in Culverts and Sewer Pipes
Aug 02, 2024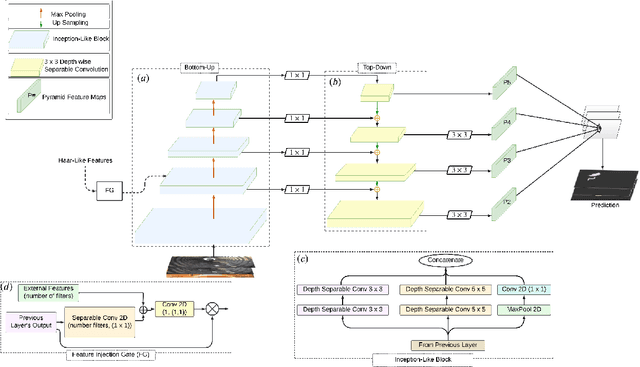
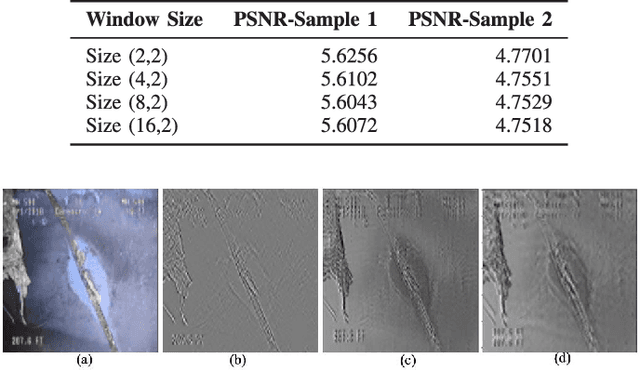
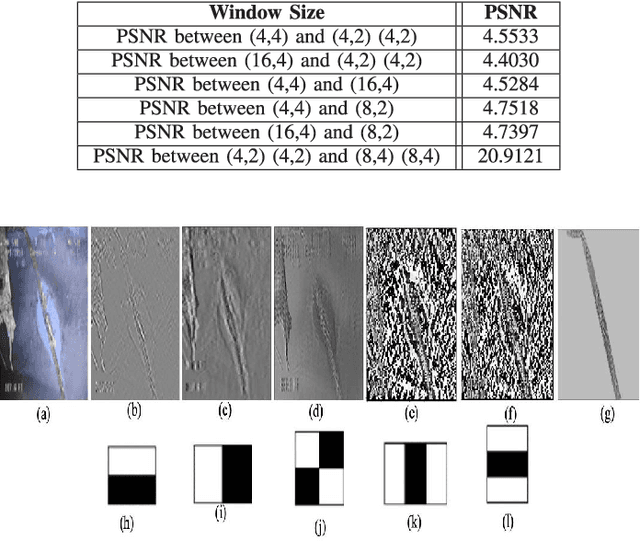
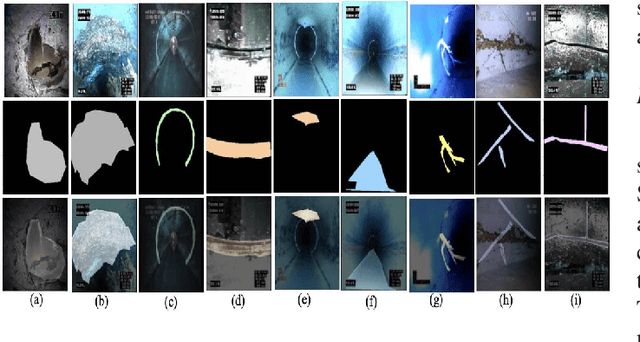
Abstract:This paper introduces Semantic Haar-Adaptive Refined Pyramid Network (SHARP-Net), a novel architecture for semantic segmentation. SHARP-Net integrates a bottom-up pathway featuring Inception-like blocks with varying filter sizes (3x3$ and 5x5), parallel max-pooling, and additional spatial detection layers. This design captures multi-scale features and fine structural details. Throughout the network, depth-wise separable convolutions are used to reduce complexity. The top-down pathway of SHARP-Net focuses on generating high-resolution features through upsampling and information fusion using $1\times1$ and $3\times3$ depth-wise separable convolutions. We evaluated our model using our developed challenging Culvert-Sewer Defects dataset and the benchmark DeepGlobe Land Cover dataset. Our experimental evaluation demonstrated the base model's (excluding Haar-like features) effectiveness in handling irregular defect shapes, occlusions, and class imbalances. It outperformed state-of-the-art methods, including U-Net, CBAM U-Net, ASCU-Net, FPN, and SegFormer, achieving average improvements of 14.4% and 12.1% on the Culvert-Sewer Defects and DeepGlobe Land Cover datasets, respectively, with IoU scores of 77.2% and 70.6%. Additionally, the training time was reduced. Furthermore, the integration of carefully selected and fine-tuned Haar-like features enhanced the performance of deep learning models by at least 20%. The proposed SHARP-Net, incorporating Haar-like features, achieved an impressive IoU of 94.75%, representing a 22.74% improvement over the base model. These features were also applied to other deep learning models, showing a 35.0% improvement, proving their versatility and effectiveness. SHARP-Net thus provides a powerful and efficient solution for accurate semantic segmentation in challenging real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge