Steffen L. Lauritzen
aHUGIN: A System Creating Adaptive Causal Probabilistic Networks
Mar 13, 2013



Abstract:The paper describes aHUGIN, a tool for creating adaptive systems. aHUGIN is an extension of the HUGIN shell, and is based on the methods reported by Spiegelhalter and Lauritzen (1990a). The adaptive systems resulting from aHUGIN are able to adjust the C011ditional probabilities in the model. A short analysis of the adaptation task is given and the features of aHUGIN are described. Finally a session with experiments is reported and the results are discussed.
Evaluating Influence Diagrams using LIMIDs
Jan 16, 2013



Abstract:We present a new approach to the solution of decision problems formulated as influence diagrams. The approach converts the influence diagram into a simpler structure, the LImited Memory Influence Diagram (LIMID), where only the requisite information for the computation of optimal policies is depicted. Because the requisite information is explicitly represented in the diagram, the evaluation procedure can take advantage of it. In this paper we show how to convert an influence diagram to a LIMID and describe the procedure for finding an optimal strategy. Our approach can yield significant savings of memory and computational time when compared to traditional methods.
MAIES: A Tool for DNA Mixture Analysis
Jun 27, 2012

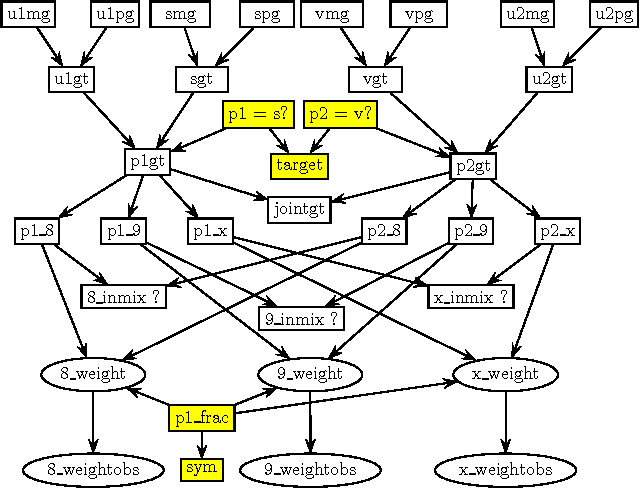
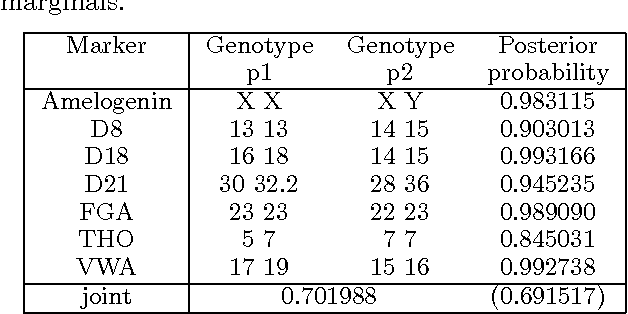
Abstract:We describe an expert system, MAIES, developed for analysing forensic identification problems involving DNA mixture traces using quantitative peak area information. Peak area information is represented by conditional Gaussian distributions, and inference based on exact junction tree propagation ascertains whether individuals, whose profiles have been measured, have contributed to the mixture. The system can also be used to predict DNA profiles of unknown contributors by separating the mixture into its individual components. The use of the system is illustrated with an application to a real world example. The system implements a novel MAP (maximum a posteriori) search algorithm that is described in an appendix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge