Julia Mortera
Object-oriented Bayesian networks for a decision support system for antitrust enforcement
Dec 06, 2013



Abstract:We study an economic decision problem where the actors are two firms and the Antitrust Authority whose main task is to monitor and prevent firms' potential anti-competitive behaviour and its effect on the market. The Antitrust Authority's decision process is modelled using a Bayesian network where both the relational structure and the parameters of the model are estimated from a data set provided by the Authority itself. A number of economic variables that influence this decision process are also included in the model. We analyse how monitoring by the Antitrust Authority affects firms' strategies about cooperation. Firms' strategies are modelled as a repeated prisoner's dilemma using object-oriented Bayesian networks. We show how the integration of firms' decision process and external market information can be modelled in this way. Various decision scenarios and strategies are illustrated.
* Published in at http://dx.doi.org/10.1214/12-AOAS625 the Annals of Applied Statistics (http://www.imstat.org/aoas/) by the Institute of Mathematical Statistics (http://www.imstat.org)
MAIES: A Tool for DNA Mixture Analysis
Jun 27, 2012

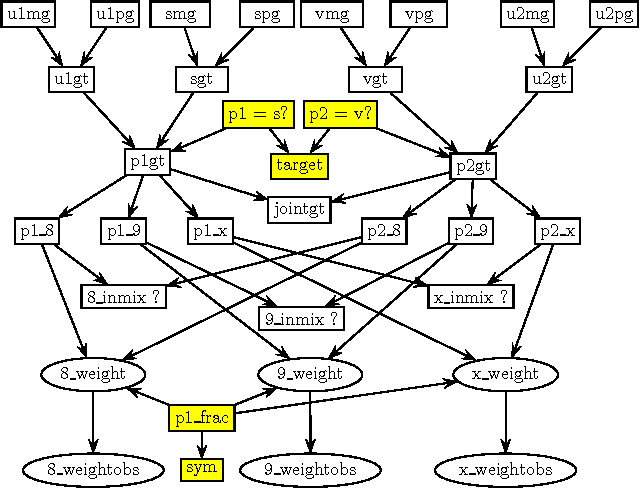
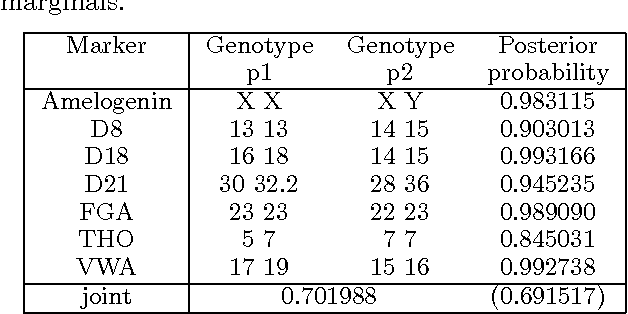
Abstract:We describe an expert system, MAIES, developed for analysing forensic identification problems involving DNA mixture traces using quantitative peak area information. Peak area information is represented by conditional Gaussian distributions, and inference based on exact junction tree propagation ascertains whether individuals, whose profiles have been measured, have contributed to the mixture. The system can also be used to predict DNA profiles of unknown contributors by separating the mixture into its individual components. The use of the system is illustrated with an application to a real world example. The system implements a novel MAP (maximum a posteriori) search algorithm that is described in an appendix.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge