Stefano Beretta
Learning the structure of Bayesian Networks: A quantitative assessment of the effect of different algorithmic schemes
Aug 03, 2018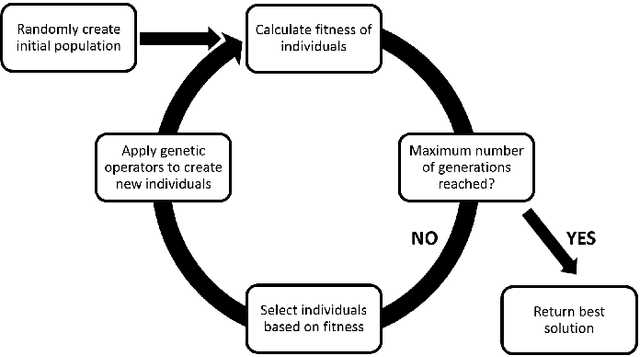
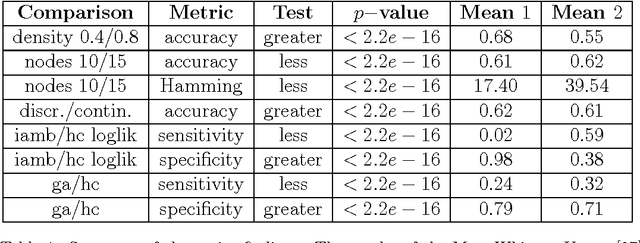
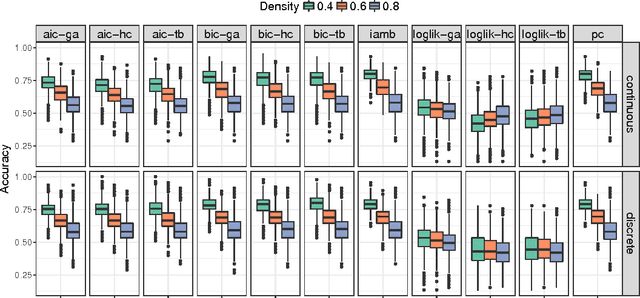
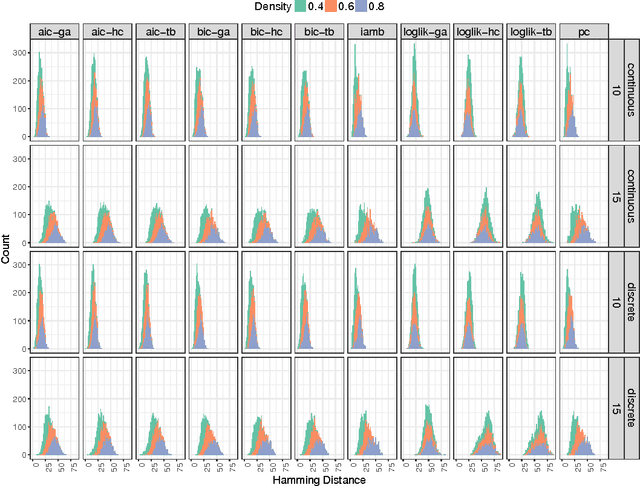
Abstract:One of the most challenging tasks when adopting Bayesian Networks (BNs) is the one of learning their structure from data. This task is complicated by the huge search space of possible solutions, and by the fact that the problem is NP-hard. Hence, full enumeration of all the possible solutions is not always feasible and approximations are often required. However, to the best of our knowledge, a quantitative analysis of the performance and characteristics of the different heuristics to solve this problem has never been done before. For this reason, in this work, we provide a detailed comparison of many different state-of-the-arts methods for structural learning on simulated data considering both BNs with discrete and continuous variables, and with different rates of noise in the data. In particular, we investigate the performance of different widespread scores and algorithmic approaches proposed for the inference and the statistical pitfalls within them.
Combining Bayesian Approaches and Evolutionary Techniques for the Inference of Breast Cancer Networks
Mar 08, 2017


Abstract:Gene and protein networks are very important to model complex large-scale systems in molecular biology. Inferring or reverseengineering such networks can be defined as the process of identifying gene/protein interactions from experimental data through computational analysis. However, this task is typically complicated by the enormously large scale of the unknowns in a rather small sample size. Furthermore, when the goal is to study causal relationships within the network, tools capable of overcoming the limitations of correlation networks are required. In this work, we make use of Bayesian Graphical Models to attach this problem and, specifically, we perform a comparative study of different state-of-the-art heuristics, analyzing their performance in inferring the structure of the Bayesian Network from breast cancer data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge