Sreenivasa Hikkal Venugopala
Comparative study of 3D object detection frameworks based on LiDAR data and sensor fusion techniques
Feb 10, 2022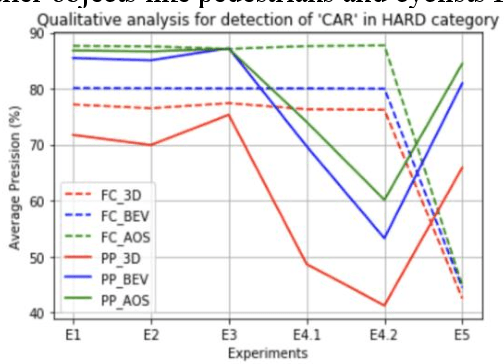

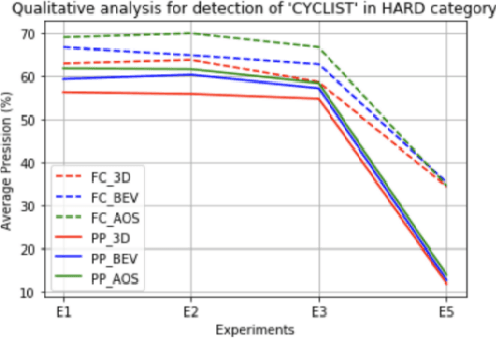
Abstract:Estimating and understanding the surroundings of the vehicle precisely forms the basic and crucial step for the autonomous vehicle. The perception system plays a significant role in providing an accurate interpretation of a vehicle's environment in real-time. Generally, the perception system involves various subsystems such as localization, obstacle (static and dynamic) detection, and avoidance, mapping systems, and others. For perceiving the environment, these vehicles will be equipped with various exteroceptive (both passive and active) sensors in particular cameras, Radars, LiDARs, and others. These systems are equipped with deep learning techniques that transform the huge amount of data from the sensors into semantic information on which the object detection and localization tasks are performed. For numerous driving tasks, to provide accurate results, the location and depth information of a particular object is necessary. 3D object detection methods, by utilizing the additional pose data from the sensors such as LiDARs, stereo cameras, provides information on the size and location of the object. Based on recent research, 3D object detection frameworks performing object detection and localization on LiDAR data and sensor fusion techniques show significant improvement in their performance. In this work, a comparative study of the effect of using LiDAR data for object detection frameworks and the performance improvement seen by using sensor fusion techniques are performed. Along with discussing various state-of-the-art methods in both the cases, performing experimental analysis, and providing future research directions.
A Study on the Ambiguity in Human Annotation of German Oral History Interviews for Perceived Emotion Recognition and Sentiment Analysis
Jan 18, 2022
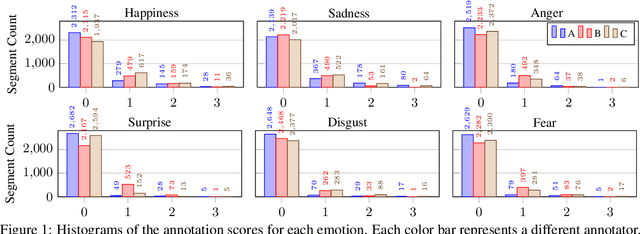
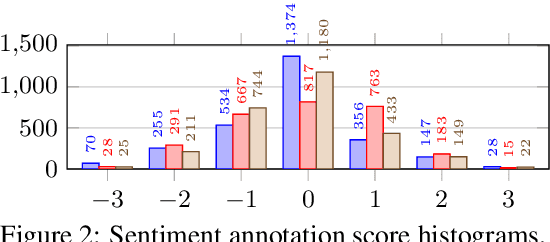
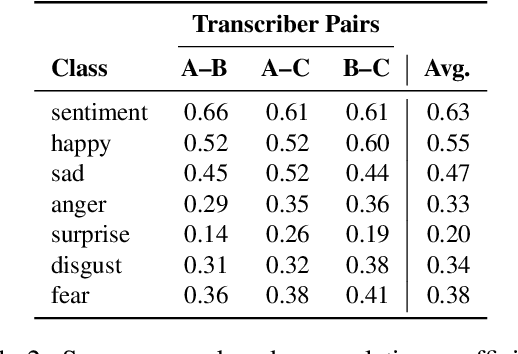
Abstract:For research in audiovisual interview archives often it is not only of interest what is said but also how. Sentiment analysis and emotion recognition can help capture, categorize and make these different facets searchable. In particular, for oral history archives, such indexing technologies can be of great interest. These technologies can help understand the role of emotions in historical remembering. However, humans often perceive sentiments and emotions ambiguously and subjectively. Moreover, oral history interviews have multi-layered levels of complex, sometimes contradictory, sometimes very subtle facets of emotions. Therefore, the question arises of the chance machines and humans have capturing and assigning these into predefined categories. This paper investigates the ambiguity in human perception of emotions and sentiment in German oral history interviews and the impact on machine learning systems. Our experiments reveal substantial differences in human perception for different emotions. Furthermore, we report from ongoing machine learning experiments with different modalities. We show that the human perceptual ambiguity and other challenges, such as class imbalance and lack of training data, currently limit the opportunities of these technologies for oral history archives. Nonetheless, our work uncovers promising observations and possibilities for further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge