Sourabh Kumar Bhattacharjee
HIT: A Hierarchically Fused Deep Attention Network for Robust Code-mixed Language Representation
May 30, 2021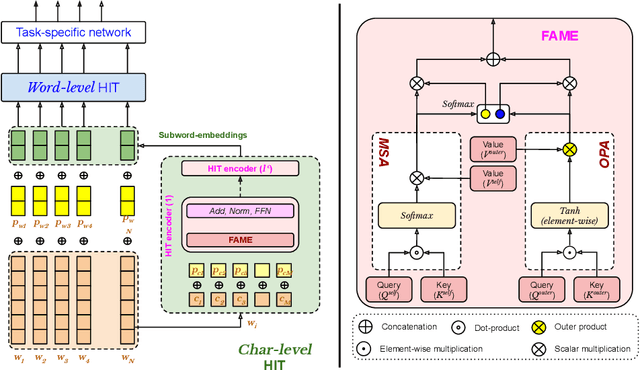
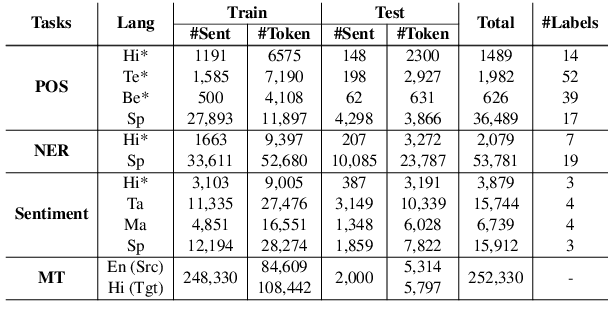
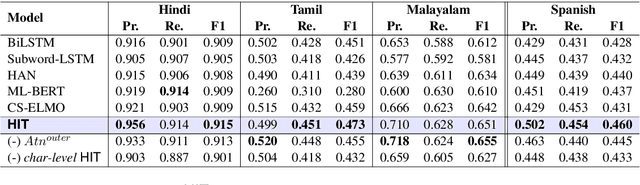
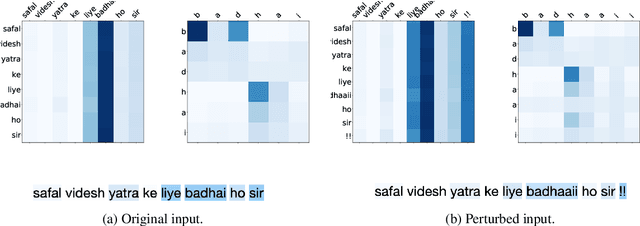
Abstract:Understanding linguistics and morphology of resource-scarce code-mixed texts remains a key challenge in text processing. Although word embedding comes in handy to support downstream tasks for low-resource languages, there are plenty of scopes in improving the quality of language representation particularly for code-mixed languages. In this paper, we propose HIT, a robust representation learning method for code-mixed texts. HIT is a hierarchical transformer-based framework that captures the semantic relationship among words and hierarchically learns the sentence-level semantics using a fused attention mechanism. HIT incorporates two attention modules, a multi-headed self-attention and an outer product attention module, and computes their weighted sum to obtain the attention weights. Our evaluation of HIT on one European (Spanish) and five Indic (Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam) languages across four NLP tasks on eleven datasets suggests significant performance improvement against various state-of-the-art systems. We further show the adaptability of learned representation across tasks in a transfer learning setup (with and without fine-tuning).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge