Soudeep Shahriar
Soybean Disease Detection via Interpretable Hybrid CNN-GNN: Integrating MobileNetV2 and GraphSAGE with Cross-Modal Attention
Mar 03, 2025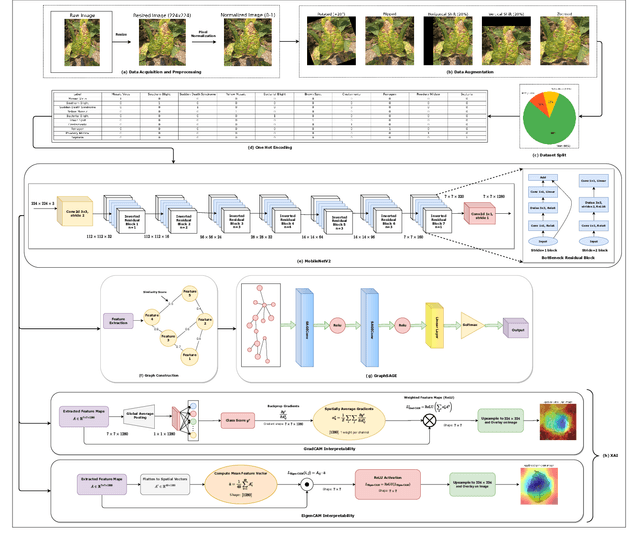
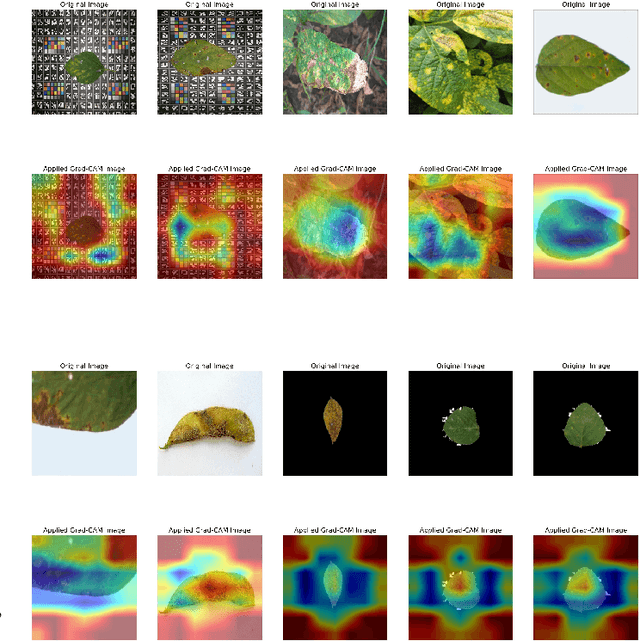
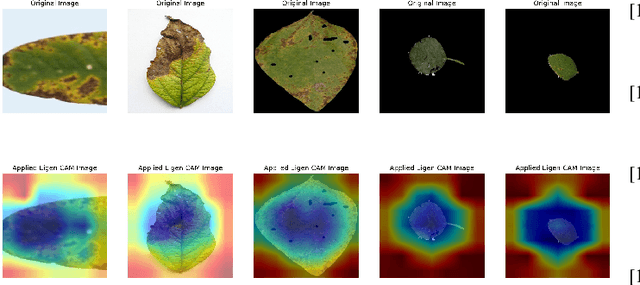
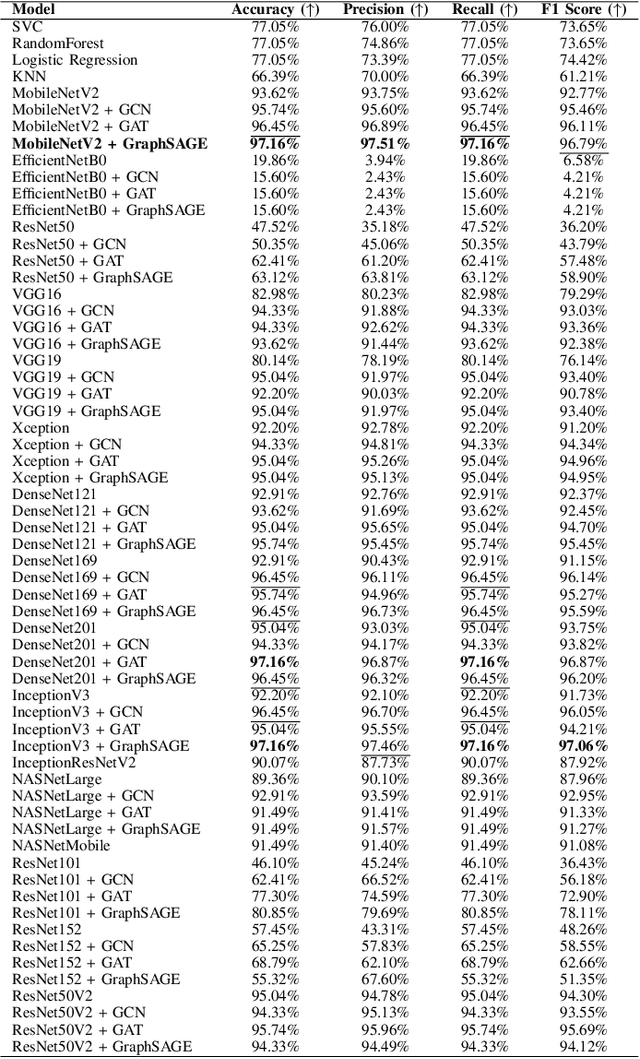
Abstract:Soybean leaf disease detection is critical for agricultural productivity but faces challenges due to visually similar symptoms and limited interpretability in conventional methods. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) excel in spatial feature extraction, they often neglect inter-image relational dependencies, leading to misclassifications. This paper proposes an interpretable hybrid Sequential CNN-Graph Neural Network (GNN) framework that synergizes MobileNetV2 for localized feature extraction and GraphSAGE for relational modeling. The framework constructs a graph where nodes represent leaf images, with edges defined by cosine similarity-based adjacency matrices and adaptive neighborhood sampling. This design captures fine-grained lesion features and global symptom patterns, addressing inter-class similarity challenges. Cross-modal interpretability is achieved via Grad-CAM and Eigen-CAM visualizations, generating heatmaps to highlight disease-influential regions. Evaluated on a dataset of ten soybean leaf diseases, the model achieves $97.16\%$ accuracy, surpassing standalone CNNs ($\le95.04\%$) and traditional machine learning models ($\le77.05\%$). Ablation studies validate the sequential architecture's superiority over parallel or single-model configurations. With only 2.3 million parameters, the lightweight MobileNetV2-GraphSAGE combination ensures computational efficiency, enabling real-time deployment in resource-constrained environments. The proposed approach bridges the gap between accurate classification and practical applicability, offering a robust, interpretable tool for agricultural diagnostics while advancing CNN-GNN integration in plant pathology research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge