Sotiris Nikoletseas
Exploring the Impact of Synthetic Data on Human Gesture Recognition Tasks Using GANs
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:In the evolving domain of Human Activity Recognition (HAR) using Internet of Things (IoT) devices, there is an emerging interest in employing Deep Generative Models (DGMs) to address data scarcity, enhance data quality, and improve classification metrics scores. Among these types of models, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have arisen as a powerful tool for generating synthetic data that mimic real-world scenarios with high fidelity. However, Human Gesture Recognition (HGR), a subset of HAR, particularly in healthcare applications, using time series data such as allergic gestures, remains highly unexplored. In this paper, we examine and evaluate the performance of two GANs in the generation of synthetic gesture motion data that compose a part of an open-source benchmark dataset. The data is related to the disease identification domain and healthcare, specifically to allergic rhinitis. We also focus on these AI models' performance in terms of fidelity, diversity, and privacy. Furthermore, we examine the scenario if the synthetic data can substitute real data, in training scenarios and how well models trained on synthetic data can be generalized for the allergic rhinitis gestures. In our work, these gestures are related to 6-axes accelerometer and gyroscope data, serving as multi-variate time series instances, and retrieved from smart wearable devices. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to explore the feasibility of synthesizing motion gestures for allergic rhinitis from wearable IoT device data using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and testing their impact on the generalization of gesture recognition systems. It is worth noting that, even if our method has been applied to a specific category of gestures, it is designed to be generalized and can be deployed also to other motion data in the HGR domain.
* 8 pages, 5 figures, 20th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), 2024
Combining psychoanalysis and computer science: an empirical study of the relationship between emotions and the Lacanian discourses
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:This research explores the interdisciplinary interaction between psychoanalysis and computer science, suggesting a mutually beneficial exchange. Indeed, psychoanalytic concepts can enrich technological applications involving unconscious, elusive aspects of the human factor, such as social media and other interactive digital platforms. Conversely, computer science, especially Artificial Intelligence (AI), can contribute quantitative concepts and methods to psychoanalysis, identifying patterns and emotional cues in human expression. In particular, this research aims to apply computer science methods to establish fundamental relationships between emotions and Lacanian discourses. Such relations are discovered in our approach via empirical investigation and statistical analysis, and are eventually validated in a theoretical (psychoanalytic) way. It is worth noting that, although emotions have been sporadically studied in Lacanian theory, to the best of our knowledge a systematic, detailed investigation of their role is missing. Such fine-grained understanding of the role of emotions can also make the identification of Lacanian discourses more effective and easy in practise. In particular, our methods indicate the emotions with highest differentiation power in terms of corresponding discourses; conversely, we identify for each discourse the most characteristic emotions it admits. As a matter of fact, we develop a method which we call Lacanian Discourse Discovery (LDD), that simplifies (via systematizing) the identification of Lacanian discourses in texts. Although the main contribution of this paper is inherently theoretical (psychoanalytic), it can also facilitate major practical applications in the realm of interactive digital systems. Indeed, our approach can be automated through Artificial Intelligence methods that effectively identify emotions (and corresponding discourses) in texts.
Agnostic Learning for Packing Machine Stoppage Prediction in Smart Factories
Dec 12, 2022



Abstract:The cyber-physical convergence is opening up new business opportunities for industrial operators. The need for deep integration of the cyber and the physical worlds establishes a rich business agenda towards consolidating new system and network engineering approaches. This revolution would not be possible without the rich and heterogeneous sources of data, as well as the ability of their intelligent exploitation, mainly due to the fact that data will serve as a fundamental resource to promote Industry 4.0. One of the most fruitful research and practice areas emerging from this data-rich, cyber-physical, smart factory environment is the data-driven process monitoring field, which applies machine learning methodologies to enable predictive maintenance applications. In this paper, we examine popular time series forecasting techniques as well as supervised machine learning algorithms in the applied context of Industry 4.0, by transforming and preprocessing the historical industrial dataset of a packing machine's operational state recordings (real data coming from the production line of a manufacturing plant from the food and beverage domain). In our methodology, we use only a single signal concerning the machine's operational status to make our predictions, without considering other operational variables or fault and warning signals, hence its characterization as ``agnostic''. In this respect, the results demonstrate that the adopted methods achieve a quite promising performance on three targeted use cases.
Concepts and Experiments on Psychoanalysis Driven Computing
Sep 29, 2022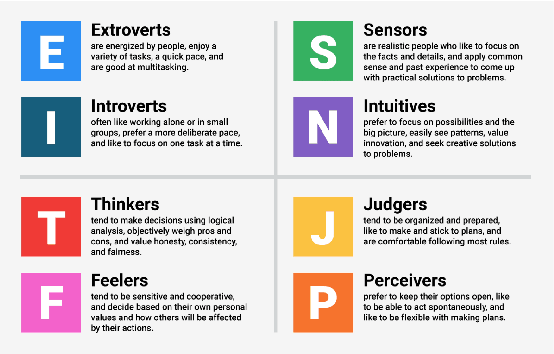
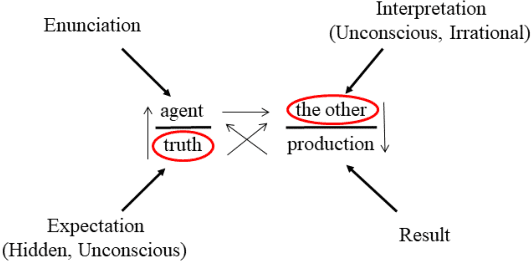
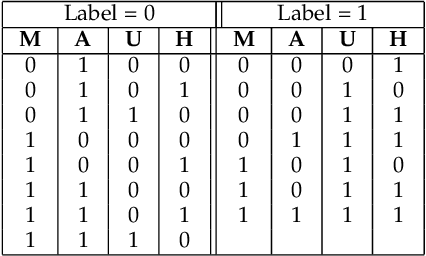
Abstract:This research investigates the effective incorporation of the human factor and user perception in text-based interactive media. In such contexts, the reliability of user texts is often compromised by behavioural and emotional dimensions. To this end, several attempts have been made in the state of the art, to introduce psychological approaches in such systems, including computational psycholinguistics, personality traits and cognitive psychology methods. In contrast, our method is fundamentally different since we employ a psychoanalysis-based approach; in particular, we use the notion of Lacanian discourse types, to capture and deeply understand real (possibly elusive) characteristics, qualities and contents of texts, and evaluate their reliability. As far as we know, this is the first time computational methods are systematically combined with psychoanalysis. We believe such psychoanalytic framework is fundamentally more effective than standard methods, since it addresses deeper, quite primitive elements of human personality, behaviour and expression which usually escape methods functioning at "higher", conscious layers. In fact, this research is a first attempt to form a new paradigm of psychoanalysis-driven interactive technologies, with broader impact and diverse applications. To exemplify this generic approach, we apply it to the case-study of fake news detection; we first demonstrate certain limitations of the well-known Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality type method, and then propose and evaluate our new method of analysing user texts and detecting fake news based on the Lacanian discourses psychoanalytic approach.
Dataset: Impact Events for Structural Health Monitoring of a Plastic Thin Plate
Sep 20, 2022



Abstract:Nowadays, more and more datasets are published towards research and development of systems and models, enabling direct comparisons, continuous improvement of solutions, and researchers engagement with experimental, real life data. However, especially in the Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) domain, there are plenty of cases where new research projects have a unique combination of structure design and implementation, sensor selection and technological enablers that does not fit with the configuration of relevant individual studies in the literature. Thus, we share the data from our case study to the research community as we did not find any relevant repository available. More specifically, in this paper, we present a novel time-series dataset for impact detection and localization on a plastic thin-plate, towards Structural Health Monitoring applications, using ceramic piezoelectric transducers (PZTs) connected to an Internet of Things (IoT) device. The dataset was collected from an experimental procedure of low-velocity, low-energy impact events that includes at least 3 repetitions for each unique experiment, while the input measurements come from 4 PZT sensors placed at the corners of the plate. For each repetition and sensor, 5000 values are stored with 100 KHz sampling rate. The system is excited with a steel ball, and the height from which it is released varies from 10 cm to 20 cm. The dataset is available in GitHub (https://github.com/Smart-Objects/Impact-Events-Dataset).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge