Somnath Hazra
Incentivizing Safer Actions in Policy Optimization for Constrained Reinforcement Learning
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Constrained Reinforcement Learning (RL) aims to maximize the return while adhering to predefined constraint limits, which represent domain-specific safety requirements. In continuous control settings, where learning agents govern system actions, balancing the trade-off between reward maximization and constraint satisfaction remains a significant challenge. Policy optimization methods often exhibit instability near constraint boundaries, resulting in suboptimal training performance. To address this issue, we introduce a novel approach that integrates an adaptive incentive mechanism in addition to the reward structure to stay within the constraint bound before approaching the constraint boundary. Building on this insight, we propose Incrementally Penalized Proximal Policy Optimization (IP3O), a practical algorithm that enforces a progressively increasing penalty to stabilize training dynamics. Through empirical evaluation on benchmark environments, we demonstrate the efficacy of IP3O compared to the performance of state-of-the-art Safe RL algorithms. Furthermore, we provide theoretical guarantees by deriving a bound on the worst-case error of the optimality achieved by our algorithm.
Tackling Uncertainties in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning through Integration of Agent Termination Dynamics
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) has gained significant traction for solving complex real-world tasks, but the inherent stochasticity and uncertainty in these environments pose substantial challenges to efficient and robust policy learning. While Distributional Reinforcement Learning has been successfully applied in single-agent settings to address risk and uncertainty, its application in MARL is substantially limited. In this work, we propose a novel approach that integrates distributional learning with a safety-focused loss function to improve convergence in cooperative MARL tasks. Specifically, we introduce a Barrier Function based loss that leverages safety metrics, identified from inherent faults in the system, into the policy learning process. This additional loss term helps mitigate risks and encourages safer exploration during the early stages of training. We evaluate our method in the StarCraft II micromanagement benchmark, where our approach demonstrates improved convergence and outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in terms of both safety and task completion. Our results suggest that incorporating safety considerations can significantly enhance learning performance in complex, multi-agent environments.
Penalizing Proposals using Classifiers for Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Jun 02, 2022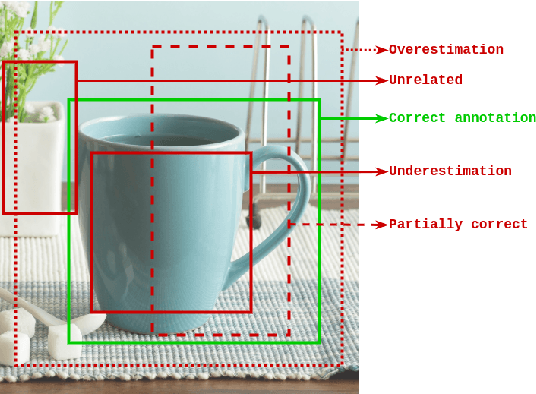

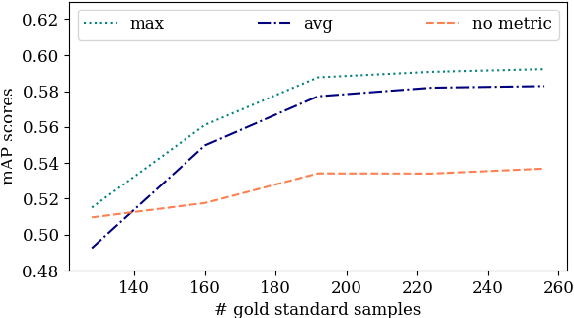

Abstract:Obtaining gold standard annotated data for object detection is often costly, involving human-level effort. Semi-supervised object detection algorithms solve the problem with a small amount of gold-standard labels and a large unlabelled dataset used to generate silver-standard labels. But training on the silver standard labels does not produce good results, because they are machine-generated annotations. In this work, we design a modified loss function to train on large silver standard annotated sets generated by a weak annotator. We include a confidence metric associated with the annotation as an additional term in the loss function, signifying the quality of the annotation. We test the effectiveness of our approach on various test sets and use numerous variations to compare the results with some of the current approaches to object detection. In comparison with the baseline where no confidence metric is used, we achieved a 4% gain in mAP with 25% labeled data and 10% gain in mAP with 50% labeled data by using the proposed confidence metric.
Semi-Lexical Languages -- A Formal Basis for Unifying Machine Learning and Symbolic Reasoning in Computer Vision
Apr 25, 2020
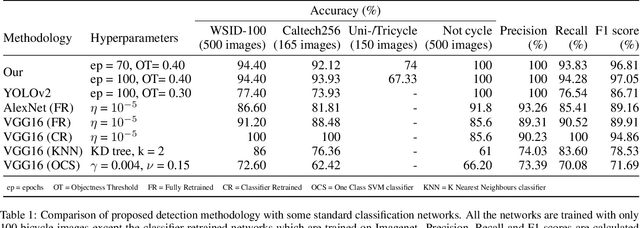

Abstract:Human vision is able to compensate imperfections in sensory inputs from the real world by reasoning based on prior knowledge about the world. Machine learning has had a significant impact on computer vision due to its inherent ability in handling imprecision, but the absence of a reasoning framework based on domain knowledge limits its ability to interpret complex scenarios. We propose semi-lexical languages as a formal basis for dealing with imperfect tokens provided by the real world. The power of machine learning is used to map the imperfect tokens into the alphabet of the language and symbolic reasoning is used to determine the membership of input in the language. Semi-lexical languages also have bindings that prevent the variations in which a semi-lexical token is interpreted in different parts of the input, thereby leaning on deduction to enhance the quality of recognition of individual tokens. We present case studies that demonstrate the advantage of using such a framework over pure machine learning and pure symbolic methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge