Somabha Mukherjee
Interaction Screening and Pseudolikelihood Approaches for Tensor Learning in Ising Models
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we study two well known methods of Ising structure learning, namely the pseudolikelihood approach and the interaction screening approach, in the context of tensor recovery in $k$-spin Ising models. We show that both these approaches, with proper regularization, retrieve the underlying hypernetwork structure using a sample size logarithmic in the number of network nodes, and exponential in the maximum interaction strength and maximum node-degree. We also track down the exact dependence of the rate of tensor recovery on the interaction order $k$, that is allowed to grow with the number of samples and nodes, for both the approaches. Finally, we provide a comparative discussion of the performance of the two approaches based on simulation studies, which also demonstrate the exponential dependence of the tensor recovery rate on the maximum coupling strength.
Estimation in Tensor Ising Models
Aug 29, 2020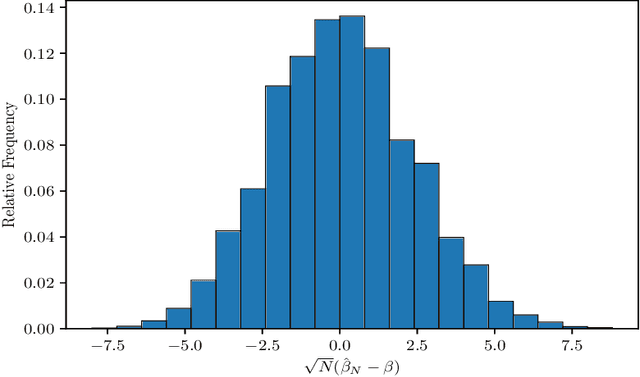
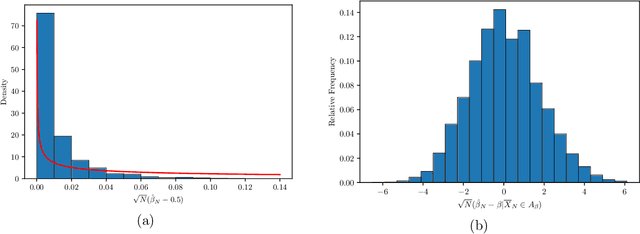
Abstract:The $p$-tensor Ising model is a one-parameter discrete exponential family for modeling dependent binary data, where the sufficient statistic is a multi-linear form of degree $p \geq 2$. This is a natural generalization of the matrix Ising model, that provides a convenient mathematical framework for capturing higher-order dependencies in complex relational data. In this paper, we consider the problem of estimating the natural parameter of the $p$-tensor Ising model given a single sample from the distribution on $N$ nodes. Our estimate is based on the maximum pseudo-likelihood (MPL) method, which provides a computationally efficient algorithm for estimating the parameter that avoids computing the intractable partition function. We derive general conditions under which the MPL estimate is $\sqrt N$-consistent, that is, it converges to the true parameter at rate $1/\sqrt N$. In particular, we show the $\sqrt N$-consistency of the MPL estimate in the $p$-spin Sherrington-Kirkpatrick (SK) model, spin systems on general $p$-uniform hypergraphs, and Ising models on the hypergraph stochastic block model (HSBM). In fact, for the HSBM we pin down the exact location of the phase transition threshold, which is determined by the positivity of a certain mean-field variational problem, such that above this threshold the MPL estimate is $\sqrt N$-consistent, while below the threshold no estimator is consistent. Finally, we derive the precise fluctuations of the MPL estimate in the special case of the $p$-tensor Curie-Weiss model. An interesting consequence of our results is that the MPL estimate in the Curie-Weiss model saturates the Cramer-Rao lower bound at all points above the estimation threshold, that is, the MPL estimate incurs no loss in asymptotic efficiency, even though it is obtained by minimizing only an approximation of the true likelihood function for computational tractability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge