Snir Hordan
Spectral Graph Neural Networks are Incomplete on Graphs with a Simple Spectrum
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Spectral features are widely incorporated within Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to improve their expressive power, or their ability to distinguish among non-isomorphic graphs. One popular example is the usage of graph Laplacian eigenvectors for positional encoding in MPNNs and Graph Transformers. The expressive power of such Spectrally-enhanced GNNs (SGNNs) is usually evaluated via the k-WL graph isomorphism test hierarchy and homomorphism counting. Yet, these frameworks align poorly with the graph spectra, yielding limited insight into SGNNs' expressive power. We leverage a well-studied paradigm of classifying graphs by their largest eigenvalue multiplicity to introduce an expressivity hierarchy for SGNNs. We then prove that many SGNNs are incomplete even on graphs with distinct eigenvalues. To mitigate this deficiency, we adapt rotation equivariant neural networks to the graph spectra setting to propose a method to provably improve SGNNs' expressivity on simple spectrum graphs. We empirically verify our theoretical claims via an image classification experiment on the MNIST Superpixel dataset and eigenvector canonicalization on graphs from ZINC.
Weisfeiler Leman for Euclidean Equivariant Machine Learning
Feb 04, 2024



Abstract:The $k$-Weifeiler-Leman ($k$-WL) graph isomorphism test hierarchy is a common method for assessing the expressive power of graph neural networks (GNNs). Recently, the $2$-WL test was proven to be complete on weighted graphs which encode $3\mathrm{D}$ point cloud data. Consequently, GNNs whose expressive power is equivalent to the $2$-WL test are provably universal on point clouds. Yet, this result is limited to invariant continuous functions on point clouds. In this paper we extend this result in three ways: Firstly, we show that $2$-WL tests can be extended to point clouds which include both positions and velocity, a scenario often encountered in applications. Secondly, we show that PPGN (Maron et al., 2019) can simulate $2$-WL uniformly on all point clouds with low complexity. Finally, we show that a simple modification of this PPGN architecture can be used to obtain a universal equivariant architecture that can approximate all continuous equivariant functions uniformly. Building on our results, we develop our WeLNet architecture, which can process position-velocity pairs, compute functions fully equivariant to permutations and rigid motions, and is provably complete and universal. Remarkably, WeLNet is provably complete precisely in the setting in which it is implemented in practice. Our theoretical results are complemented by experiments showing WeLNet sets new state-of-the-art results on the N-Body dynamics task and the GEOM-QM9 molecular conformation generation task.
Complete Neural Networks for Euclidean Graphs
Feb 01, 2023
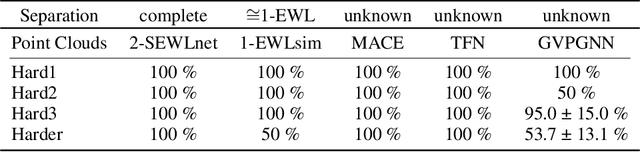

Abstract:We propose a 2-WL-like geometric graph isomorphism test and prove it is complete when applied to Euclidean Graphs in $\mathbb{R}^3$. We then use recent results on multiset embeddings to devise an efficient geometric GNN model with equivalent separation power. We verify empirically that our GNN model is able to separate particularly challenging synthetic examples, and demonstrate its usefulness for a chemical property prediction problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge