Sixue Liu
A Novel Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Automated Stock Trading System Using Cascaded LSTM Networks
Dec 06, 2022Abstract:More and more stock trading strategies are constructed using deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms, but DRL methods originally widely used in the gaming community are not directly adaptable to financial data with low signal-to-noise ratios and unevenness, and thus suffer from performance shortcomings. In this paper, to capture the hidden information, we propose a DRL based stock trading system using cascaded LSTM, which first uses LSTM to extract the time-series features from stock daily data, and then the features extracted are fed to the agent for training, while the strategy functions in reinforcement learning also use another LSTM for training. Experiments in DJI in the US market and SSE50 in the Chinese stock market show that our model outperforms previous baseline models in terms of cumulative returns and Sharp ratio, and this advantage is more significant in the Chinese stock market, a merging market. It indicates that our proposed method is a promising way to build a automated stock trading system.
Should Algorithms for Random SAT and Max-SAT be Different?
Nov 02, 2018
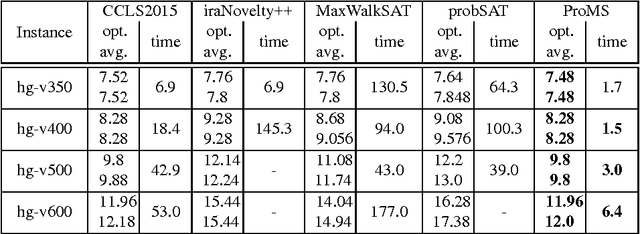

Abstract:We analyze to what extent the random SAT and Max-SAT problems differ in their properties. Our findings suggest that for random $k$-CNF with ratio in a certain range, Max-SAT can be solved by any SAT algorithm with subexponential slowdown, while for formulae with ratios greater than some constant, algorithms under the random walk framework require substantially different heuristics. In light of these results, we propose a novel probabilistic approach for random Max-SAT called ProMS. Experimental results illustrate that ProMS outperforms many state-of-the-art local search solvers on random Max-SAT benchmarks.
An Efficient Implementation for WalkSAT
Dec 04, 2015
Abstract:Stochastic local search (SLS) algorithms have exhibited great effectiveness in finding models of random instances of the Boolean satisfiability problem (SAT). As one of the most widely known and used SLS algorithm, WalkSAT plays a key role in the evolutions of SLS for SAT, and also hold state-of-the-art performance on random instances. This work proposes a novel implementation for WalkSAT which decreases the redundant calculations leading to a dramatically speeding up, thus dominates the latest version of WalkSAT including its advanced variants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge