Sixing Liu
Best Transition Matrix Esitimation or Best Label Noise Robustness Classifier? Two Possible Methods to Enhance the Performance of T-revision
Jan 02, 2025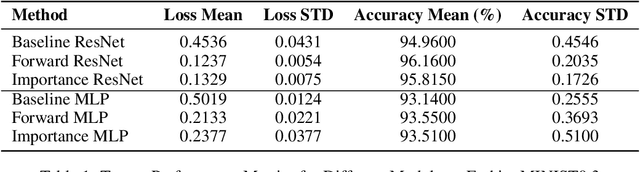
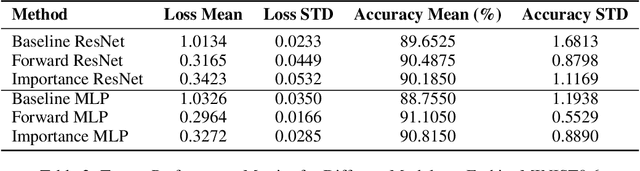
Abstract:Label noise refers to incorrect labels in a dataset caused by human errors or collection defects, which is common in real-world applications and can significantly reduce the accuracy of models. This report explores how to estimate noise transition matrices and construct deep learning classifiers that are robust against label noise. In cases where the transition matrix is known, we apply forward correction and importance reweighting methods to correct the impact of label noise using the transition matrix. When the transition matrix is unknown or inaccurate, we use the anchor point assumption and T-Revision series methods to estimate or correct the noise matrix. In this study, we further improved the T-Revision method by developing T-Revision-Alpha and T-Revision-Softmax to enhance stability and robustness. Additionally, we designed and implemented two baseline classifiers, a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) and ResNet-18, based on the cross-entropy loss function. We compared the performance of these methods on predicting clean labels and estimating transition matrices using the FashionMINIST dataset with known noise transition matrices. For the CIFAR-10 dataset, where the noise transition matrix is unknown, we estimated the noise matrix and evaluated the ability of the methods to predict clean labels.
DCTTS: Discrete Diffusion Model with Contrastive Learning for Text-to-speech Generation
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:In the Text-to-speech(TTS) task, the latent diffusion model has excellent fidelity and generalization, but its expensive resource consumption and slow inference speed have always been a challenging. This paper proposes Discrete Diffusion Model with Contrastive Learning for Text-to-Speech Generation(DCTTS). The following contributions are made by DCTTS: 1) The TTS diffusion model based on discrete space significantly lowers the computational consumption of the diffusion model and improves sampling speed; 2) The contrastive learning method based on discrete space is used to enhance the alignment connection between speech and text and improve sampling quality; and 3) It uses an efficient text encoder to simplify the model's parameters and increase computational efficiency. The experimental results demonstrate that the approach proposed in this paper has outstanding speech synthesis quality and sampling speed while significantly reducing the resource consumption of diffusion model. The synthesized samples are available at https://github.com/lawtherWu/DCTTS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge