Simon Prince
fAux: Testing Individual Fairness via Gradient Alignment
Oct 10, 2022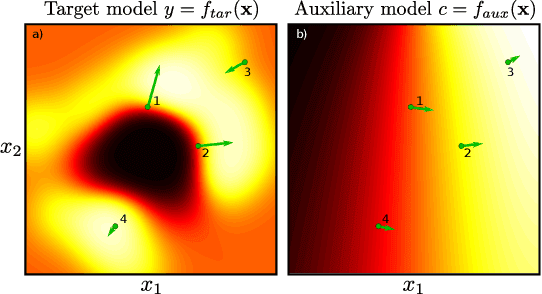
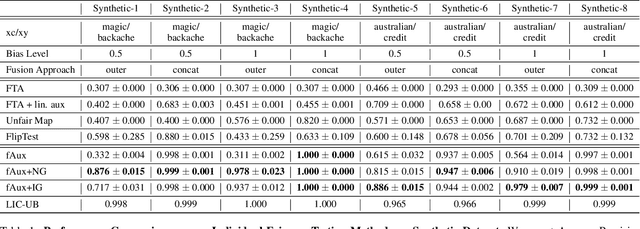


Abstract:Machine learning models are vulnerable to biases that result in unfair treatment of individuals from different populations. Recent work that aims to test a model's fairness at the individual level either relies on domain knowledge to choose metrics, or on input transformations that risk generating out-of-domain samples. We describe a new approach for testing individual fairness that does not have either requirement. We propose a novel criterion for evaluating individual fairness and develop a practical testing method based on this criterion which we call fAux (pronounced fox). This is based on comparing the derivatives of the predictions of the model to be tested with those of an auxiliary model, which predicts the protected variable from the observed data. We show that the proposed method effectively identifies discrimination on both synthetic and real-world datasets, and has quantitative and qualitative advantages over contemporary methods.
Normalizing Flows: Introduction and Ideas
Aug 25, 2019



Abstract:Normalizing Flows are generative models which produce tractable distributions where both sampling and density evaluation can be efficient and exact. The goal of this survey article is to give a coherent and comprehensive review of the literature around the construction and use of Normalizing Flows for distribution learning. We aim to provide context and explanation of the models, review current state-of-the-art literature, and identify open questions and promising future directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge