Shuyan Yu
Open Information Extraction: A Review of Baseline Techniques, Approaches, and Applications
Oct 18, 2023



Abstract:With the abundant amount of available online and offline text data, there arises a crucial need to extract the relation between phrases and summarize the main content of each document in a few words. For this purpose, there have been many studies recently in Open Information Extraction (OIE). OIE improves upon relation extraction techniques by analyzing relations across different domains and avoids requiring hand-labeling pre-specified relations in sentences. This paper surveys recent approaches of OIE and its applications on Knowledge Graph (KG), text summarization, and Question Answering (QA). Moreover, the paper describes OIE basis methods in relation extraction. It briefly discusses the main approaches and the pros and cons of each method. Finally, it gives an overview about challenges, open issues, and future work opportunities for OIE, relation extraction, and OIE applications.
Learning 3D Mineral Prospectivity from 3D Geological Models with Convolutional Neural Networks: Application to a Structure-controlled Hydrothermal Gold Deposit
Sep 02, 2021



Abstract:The three-dimensional (3D) geological models are the typical and key data source in the 3D mineral prospecitivity modeling. Identifying prospectivity-informative predictor variables from the 3D geological models is a challenging and tedious task. Motivated by the ability of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to learn the intrinsic features, in this paper, we present a novel method that leverages CNNs to learn 3D mineral prospectivity from the 3D geological models. By exploiting the learning ability of CNNs, the presented method allows for disentangling complex correlation to the mineralization and thus opens a door to circumvent the tedious work for designing the predictor variables. Specifically, to explore the unstructured 3D geological models with the CNNs whose input should be structured, we develop a 2D CNN framework in which the geometry of geological boundary is compiled and reorganized into multi-channel images and fed into the CNN. This ensures an effective and efficient training of CNNs while allowing the prospective model to approximate the ore-forming process. The presented method is applied to a typical structure-controlled hydrothermal deposit, the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, eastern China, in which the presented method was compared with the prospectivity modeling methods using hand-designed predictor variables. The results demonstrate the presented method capacitates a performance boost of the 3D prospectivity modeling and empowers us to decrease work-load and prospecting risk in prediction of deep-seated orebodies.
Tablext: A Combined Neural Network And Heuristic Based Table Extractor
Apr 22, 2021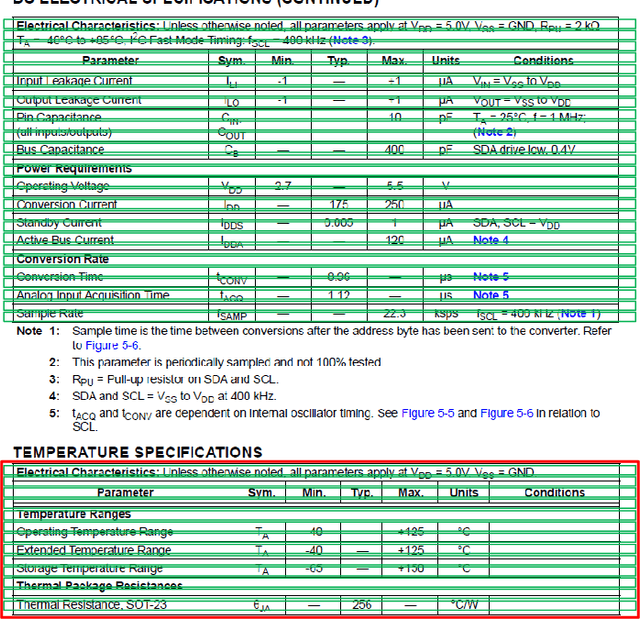
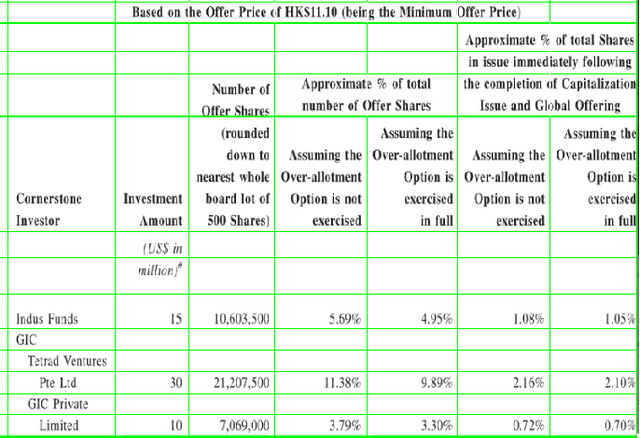
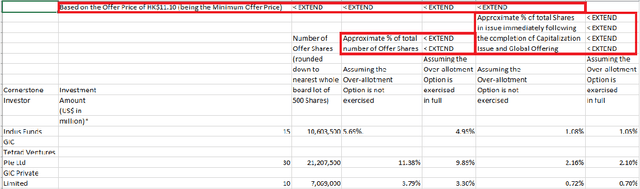
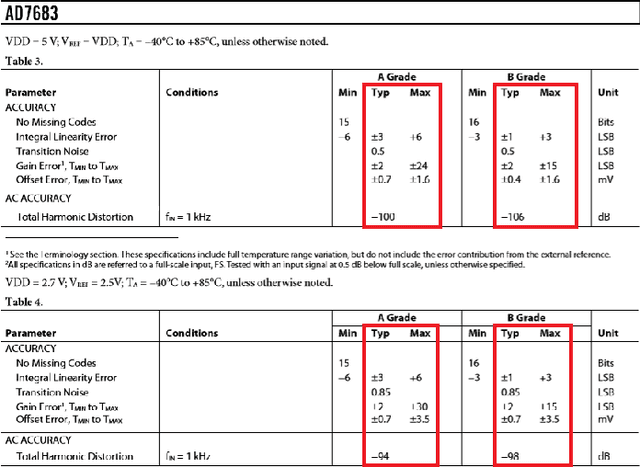
Abstract:A significant portion of the data available today is found within tables. Therefore, it is necessary to use automated table extraction to obtain thorough results when data-mining. Today's popular state-of-the-art methods for table extraction struggle to adequately extract tables with machine-readable text and structural data. To make matters worse, many tables do not have machine-readable data, such as tables saved as images, making most extraction methods completely ineffective. In order to address these issues, a novel, general format table extractor tool, Tablext, is proposed. This tool uses a combination of computer vision techniques and machine learning methods to efficiently and effectively identify and extract data from tables. Tablext begins by using a custom Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to identify and separate all potential tables. The identification process is optimized by combining the custom CNN with the YOLO object detection network. Then, the high-level structure of each table is identified with computer vision methods. This high-level, structural meta-data is used by another CNN to identify exact cell locations. As a final step, Optical Characters Recognition (OCR) is performed on every individual cell to extract their content without needing machine-readable text. This multi-stage algorithm allows for the neural networks to focus on completing complex tasks, while letting image processing methods efficiently complete the simpler ones. This leads to the proposed approach to be general-purpose enough to handle a large batch of tables regardless of their internal encodings or their layout complexity. Additionally, it becomes accurate enough to outperform competing state-of-the-art table extractors on the ICDAR 2013 table dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge