Shulin Wen
Active Noise Control based on the Momentum Multichannel Normalized Filtered-x Least Mean Square Algorithm
Aug 07, 2023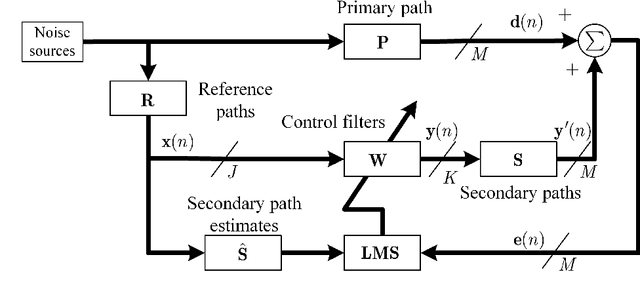
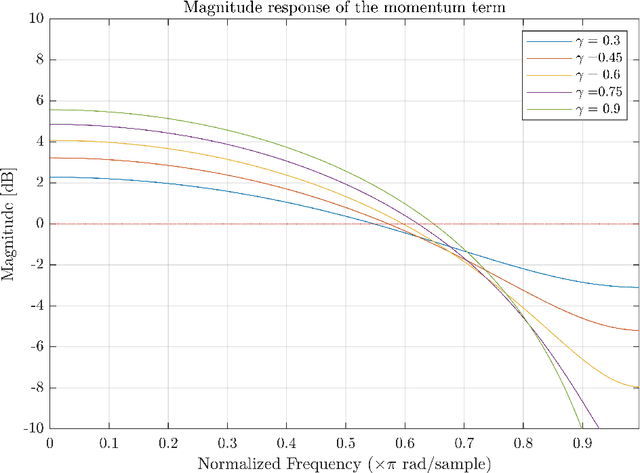
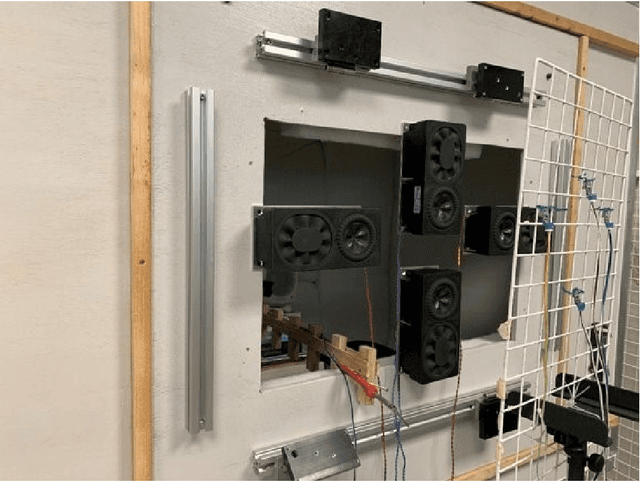
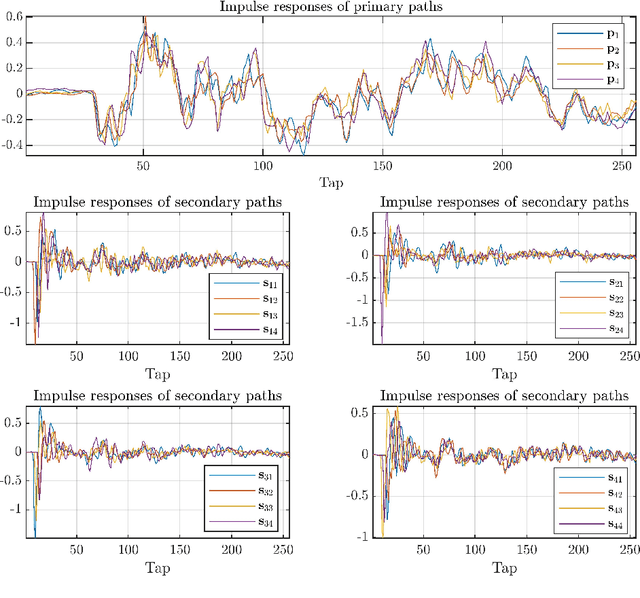
Abstract:Multichannel active noise control (MCANC) is widely utilized to achieve significant noise cancellation area in the complicated acoustic field. Meanwhile, the filter-x least mean square (FxLMS) algorithm gradually becomes the benchmark solution for the implementation of MCANC due to its low computational complexity. However, its slow convergence speed more or less undermines the performance of dealing with quickly varying disturbances, such as piling noise. Furthermore, the noise power variation also deteriorates the robustness of the algorithm when it adopts the fixed step size. To solve these issues, we integrated the normalized multichannel FxLMS with the momentum method, which hence, effectively avoids the interference of the primary noise power and accelerates the convergence of the algorithm. To validate its effectiveness, we deployed this algorithm in a multichannel noise control window to control the real machine noise.
Design and Evaluation of Active Noise Control on Machinery Noise
Nov 02, 2021



Abstract:Construction workers and residents live near around construction sites are exposed to noises that might cause hearing loss, high blood pressure, heart disease, sleep disturbance and stress. Regulations has been carried out by national governments to limit the maximum permissible noise levels for construction works. A four-channel active noise control system mounted on the opening of an enclosure is designed to prevent the machinery noise from spreading around and retaining the heat diffusion path. Multi-channel FxLMS algorithm in time domain is implemented on the main controller. A Genelec speaker is placed inside the box as the primary noise source to play back different types of noises. Analyses and experiments are carried out to investigate the controllable frequency range of this ANC system in detail. Considerable noise reduction performance is achieved for different recorded practical construction noises.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge