Shota Takashiro
$\infty$-MoE: Generalizing Mixture of Experts to Infinite Experts
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:The Mixture of Experts (MoE) selects a few feed-forward networks (FFNs) per token, achieving an effective trade-off between computational cost and performance. In conventional MoE, each expert is treated as entirely independent, and experts are combined in a discrete space. As a result, when the number of experts increases, it becomes difficult to train each expert effectively. To stabilize training while increasing the number of experts, we propose $\infty$-MoE that selects a portion of the parameters of large FFNs based on continuous values sampled for each token. By considering experts in a continuous space, this approach allows for an infinite number of experts while maintaining computational efficiency. Experiments show that a GPT-2 Small-based $\infty$-MoE model, with 129M active and 186M total parameters, achieves comparable performance to a dense GPT-2 Medium with 350M parameters. Adjusting the number of sampled experts at inference time allows for a flexible trade-off between accuracy and speed, with an improvement of up to 2.5\% in accuracy over conventional MoE.
Answer When Needed, Forget When Not: Language Models Pretend to Forget via In-Context Knowledge Unlearning
Oct 01, 2024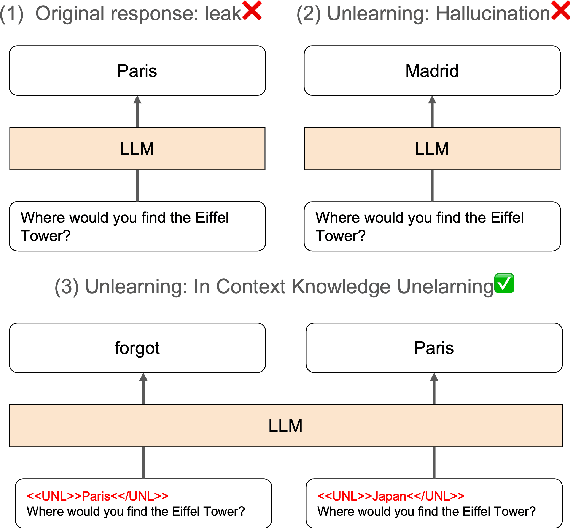

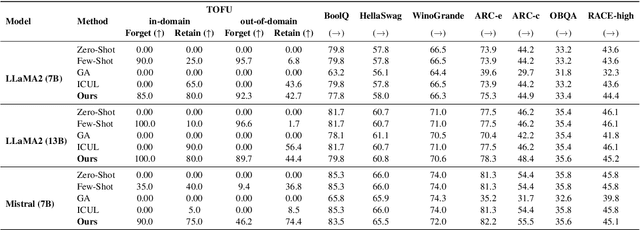
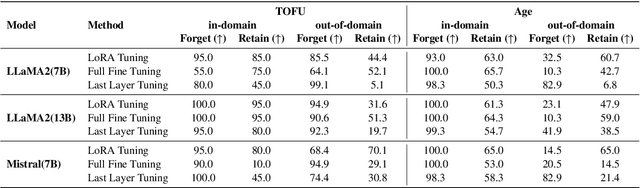
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are applied across diverse domains, the ability to selectively unlearn specific information has become increasingly essential. For instance, LLMs are expected to provide confidential information to authorized internal users, such as employees or trusted partners, while withholding it from external users, including the general public and unauthorized entities. In response to this challenge, we propose a novel method termed ``in-context knowledge unlearning'', which enables the model to selectively forget information in test-time based on the context of the query. Our method fine-tunes pre-trained LLMs to enable prompt unlearning of target knowledge within the context, while preserving other knowledge. Experiments on the TOFU and AGE datasets using Llama2-7B/13B and Mistral-7B models show our method achieves up to 95% forgetting accuracy while retaining 80% of unrelated knowledge, significantly outperforming baselines in both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios. Further investigation into the model's internal behavior revealed that while fine-tuned LLMs generate correct predictions in the middle layers and maintain them up to the final layer, they make the decision to forget at the last layer, i.e., ``LLMs pretend to forget''. Our findings offer valuable insights into enhancing the robustness of unlearning mechanisms in LLMs, setting a foundation for future research in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge