Shoki Sakamoto
Speak Like a Dog: Human to Non-human creature Voice Conversion
Jun 09, 2022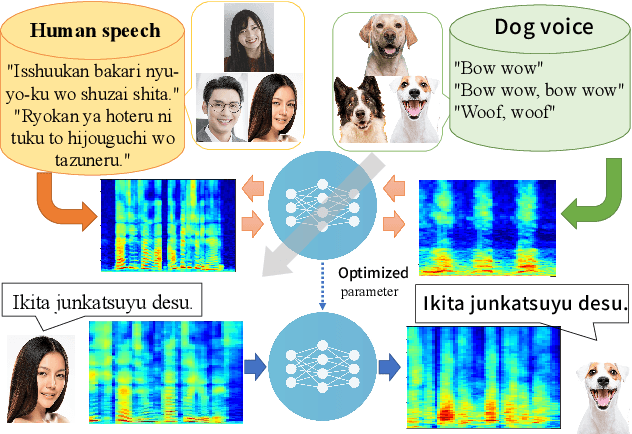
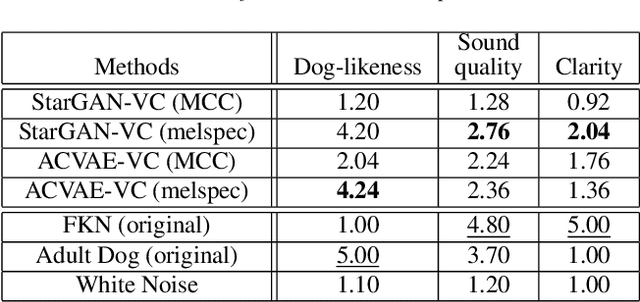
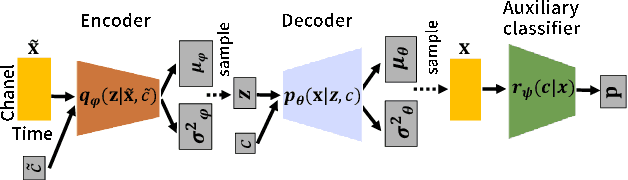
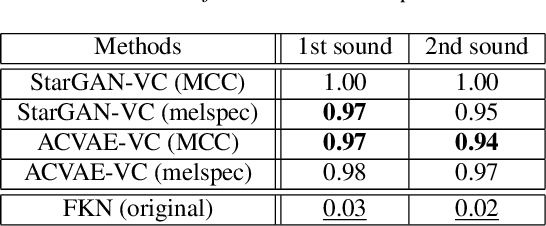
Abstract:This paper proposes a new voice conversion (VC) task from human speech to dog-like speech while preserving linguistic information as an example of human to non-human creature voice conversion (H2NH-VC) tasks. Although most VC studies deal with human to human VC, H2NH-VC aims to convert human speech into non-human creature-like speech. Non-parallel VC allows us to develop H2NH-VC, because we cannot collect a parallel dataset that non-human creatures speak human language. In this study, we propose to use dogs as an example of a non-human creature target domain and define the "speak like a dog" task. To clarify the possibilities and characteristics of the "speak like a dog" task, we conducted a comparative experiment using existing representative non-parallel VC methods in acoustic features (Mel-cepstral coefficients and Mel-spectrograms), network architectures (five different kernel-size settings), and training criteria (variational autoencoder (VAE)- based and generative adversarial network-based). Finally, the converted voices were evaluated using mean opinion scores: dog-likeness, sound quality and intelligibility, and character error rate (CER). The experiment showed that the employment of the Mel-spectrogram improved the dog-likeness of the converted speech, while it is challenging to preserve linguistic information. Challenges and limitations of the current VC methods for H2NH-VC are highlighted.
StarGAN-VC+ASR: StarGAN-based Non-Parallel Voice Conversion Regularized by Automatic Speech Recognition
Aug 10, 2021



Abstract:Preserving the linguistic content of input speech is essential during voice conversion (VC). The star generative adversarial network-based VC method (StarGAN-VC) is a recently developed method that allows non-parallel many-to-many VC. Although this method is powerful, it can fail to preserve the linguistic content of input speech when the number of available training samples is extremely small. To overcome this problem, we propose the use of automatic speech recognition to assist model training, to improve StarGAN-VC, especially in low-resource scenarios. Experimental results show that using our proposed method, StarGAN-VC can retain more linguistic information than vanilla StarGAN-VC.
StarGAN-based Emotional Voice Conversion for Japanese Phrases
Apr 05, 2021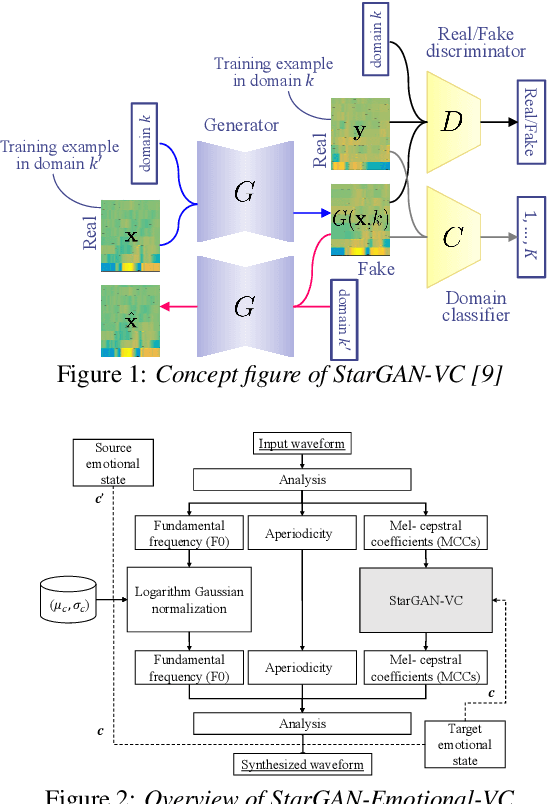
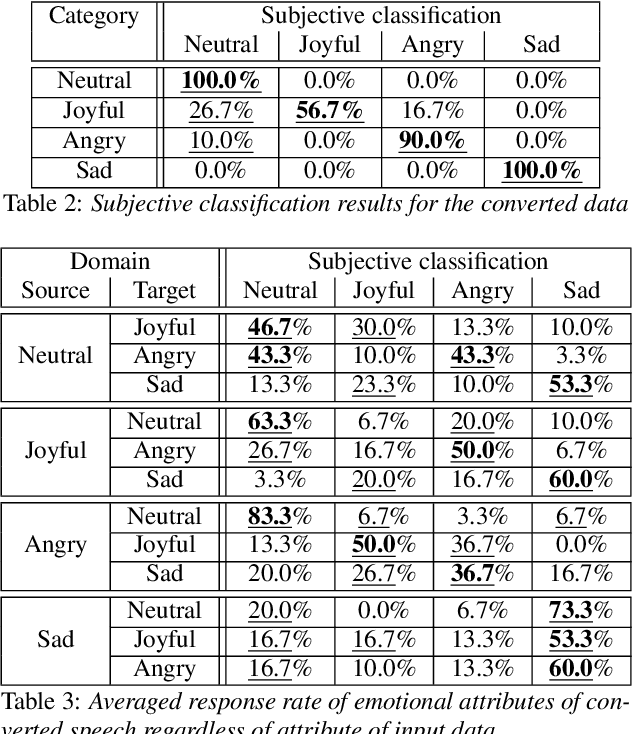
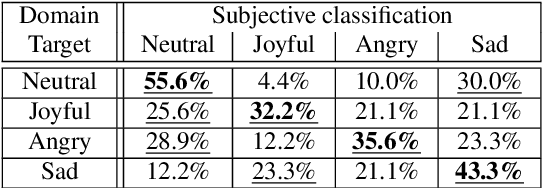
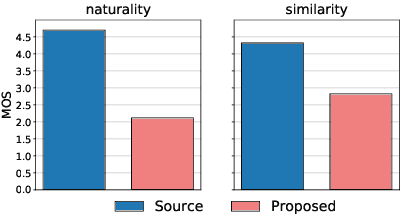
Abstract:This paper shows that StarGAN-VC, a spectral envelope transformation method for non-parallel many-to-many voice conversion (VC), is capable of emotional VC (EVC). Although StarGAN-VC has been shown to enable speaker identity conversion, its capability for EVC for Japanese phrases has not been clarified. In this paper, we describe the direct application of StarGAN-VC to an EVC task with minimal fundamental frequency and aperiodicity processing. Through subjective evaluation experiments, we evaluated the performance of our StarGAN-EVC system in terms of its ability to achieve EVC for Japanese phrases. The subjective evaluation is conducted in terms of subjective classification and mean opinion score of neutrality and similarity. In addition, the interdependence between the source and target emotional domains was investigated from the perspective of the quality of EVC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge