Shivam Ratnakar
Beyond QA Pairs: Assessing Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Fact Embedding in LLMs
Mar 03, 2025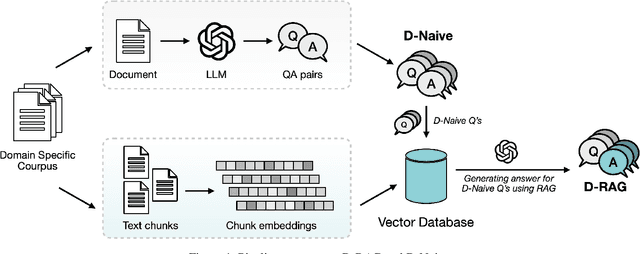
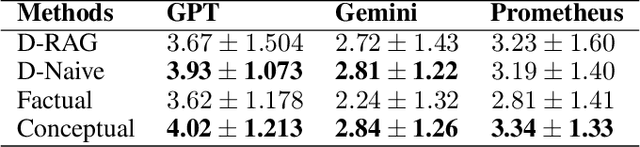
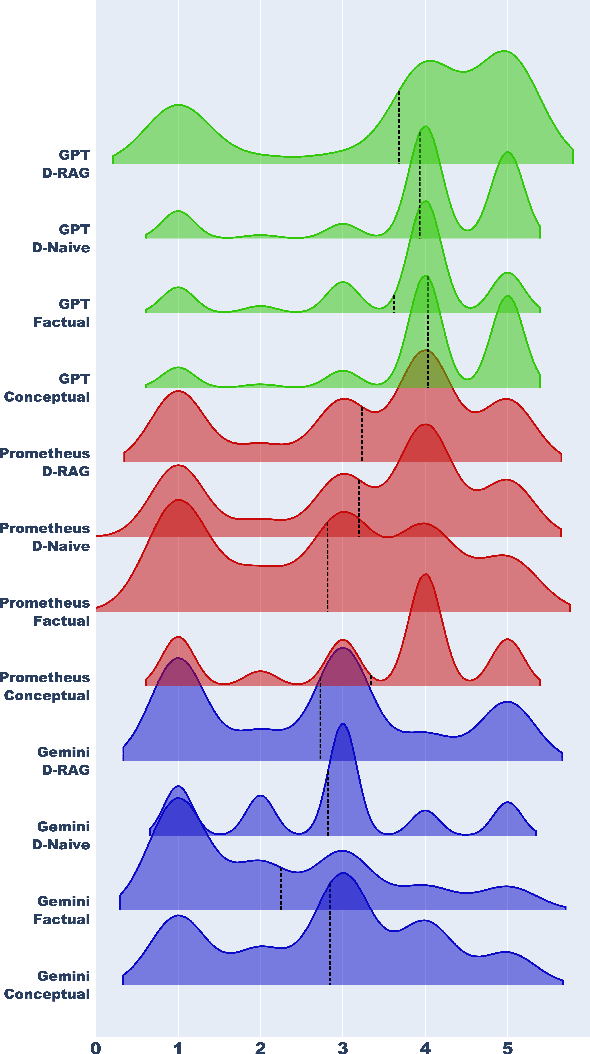
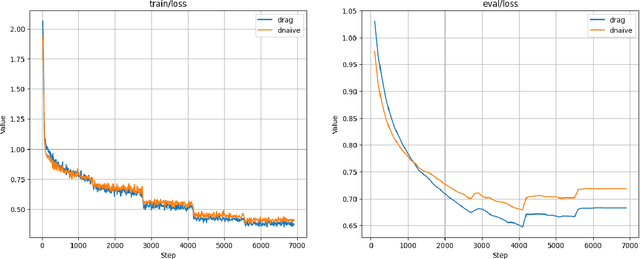
Abstract:This paper presents an extensive examination of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) for embedding domain specific facts into Large Language Models (LLMs), focusing on improving the fine-tuning process by categorizing question-answer (QA) pairs into Factual and Conceptual classes using a BERT-based classifier. Two distinct Llama-2 models are fine-tuned based on these classifications and evaluated using larger models like GPT-3.5 Turbo and Gemini. Our results indicate that models trained on conceptual datasets outperform those trained on factual datasets. Additionally, we compare the efficiency of two synthetic fine-tuning dataset generation techniques, D-RAG and D-Naive, with D-Naive demonstrating superior performance. Although PEFT has shown effectiveness, our research indicates that it may not be the most optimal method for embedding facts into LLMs. However, it has demonstrated exceptional performance in instruction-based tasks. Our findings are reinforced by a 1000-sample dataset in the data center domain, where the fine-tuned Llama-2 7B model significantly outperforms the baseline model in generating product recommendations. Our study highlights the importance of QA pair categorization and synthetic dataset generation techniques in enhancing the performance of LLMs in specific domains.
* Presented at the Workshop on Preparing Good Data for Generative AI: Challenges and Approaches (Good-Data) in conjunction with AAAI 2025. The authors retain the copyright
STARLING: Self-supervised Training of Text-based Reinforcement Learning Agent with Large Language Models
Jun 09, 2024Abstract:Interactive fiction games have emerged as an important application to improve the generalization capabilities of language-based reinforcement learning (RL) agents. Existing environments for interactive fiction games are domain-specific or time-consuming to generate and do not train the RL agents to master a specific set of skills. In this work, we introduce an interactive environment for self-supervised RL, STARLING, for text-based games that bootstraps the text-based RL agents with automatically generated games (based on the seed set of game ideas) to boost the performance and generalization capabilities to reach a goal of the target environment. These games let the agent hone their skills on a predefined set of tasks. We create and test an environment with 100 games, generated using this automated framework that uses large language models (GPT-3) and an interactive fiction game engine (based on Inform7) to provide the user with the ability to generate more games under minimal human supervision. Experimental results based on both the human participants and baseline text-based RL agents reveal that current state-of-the-art text-based RL agents cannot use previously learned skills in new situations at the level humans can. These results enforce STARLING's potential to serve as a sandbox environment for further research in self-supervised text-based RL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge