Shingo Ando
Unsupervised Intrinsic Image Decomposition with LiDAR Intensity
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:Intrinsic image decomposition (IID) is the task that decomposes a natural image into albedo and shade. While IID is typically solved through supervised learning methods, it is not ideal due to the difficulty in observing ground truth albedo and shade in general scenes. Conversely, unsupervised learning methods are currently underperforming supervised learning methods since there are no criteria for solving the ill-posed problems. Recently, light detection and ranging (LiDAR) is widely used due to its ability to make highly precise distance measurements. Thus, we have focused on the utilization of LiDAR, especially LiDAR intensity, to address this issue. In this paper, we propose unsupervised intrinsic image decomposition with LiDAR intensity (IID-LI). Since the conventional unsupervised learning methods consist of image-to-image transformations, simply inputting LiDAR intensity is not an effective approach. Therefore, we design an intensity consistency loss that computes the error between LiDAR intensity and gray-scaled albedo to provide a criterion for the ill-posed problem. In addition, LiDAR intensity is difficult to handle due to its sparsity and occlusion, hence, a LiDAR intensity densification module is proposed. We verified the estimating quality using our own dataset, which include RGB images, LiDAR intensity and human judged annotations. As a result, we achieved an estimation accuracy that outperforms conventional unsupervised learning methods. Dataset link : (https://github.com/ntthilab-cv/NTT-intrinsic-dataset).
Non-learning Stereo-aided Depth Completion under Mis-projection via Selective Stereo Matching
Oct 04, 2022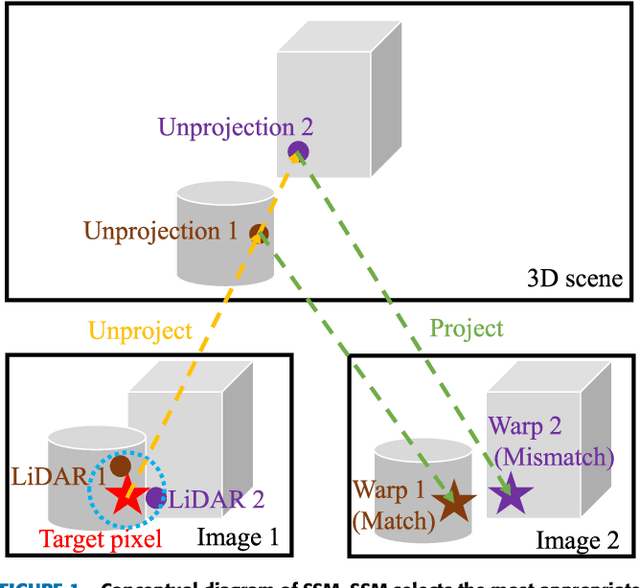
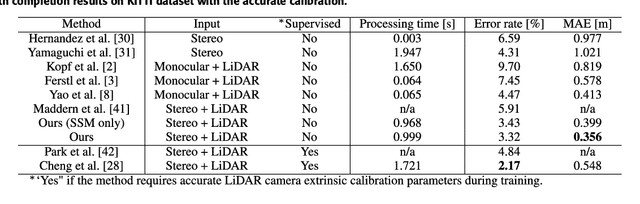
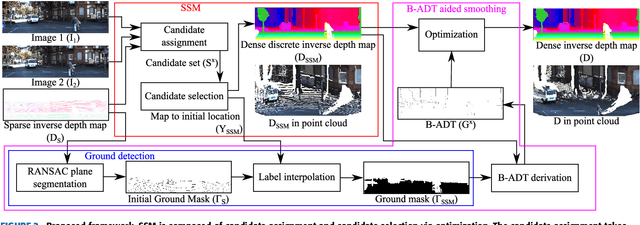

Abstract:We propose a non-learning depth completion method for a sparse depth map captured using a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) sensor guided by a pair of stereo images. Generally, conventional stereo-aided depth completion methods have two limiations. (i) They assume the given sparse depth map is accurately aligned to the input image, whereas the alignment is difficult to achieve in practice. (ii) They have limited accuracy in the long range because the depth is estimated by pixel disparity. To solve the abovementioned limitations, we propose selective stereo matching (SSM) that searches the most appropriate depth value for each image pixel from its neighborly projected LiDAR points based on an energy minimization framework. This depth selection approach can handle any type of mis-projection. Moreover, SSM has an advantage in terms of long-range depth accuracy because it directly uses the LiDAR measurement rather than the depth acquired from the stereo. SSM is a discrete process; thus, we apply variational smoothing with binary anisotropic diffusion tensor (B-ADT) to generate a continuous depth map while preserving depth discontinuity across object boundaries. Experimentally, compared with the previous state-of-the-art stereo-aided depth completion, the proposed method reduced the mean absolute error (MAE) of the depth estimation to 0.65 times and demonstrated approximately twice more accurate estimation in the long range. Moreover, under various LiDAR-camera calibration errors, the proposed method reduced the depth estimation MAE to 0.34-0.93 times from previous depth completion methods.
* 15 pages, 13 figures
Discontinuous and Smooth Depth Completion with Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor
Jun 25, 2020
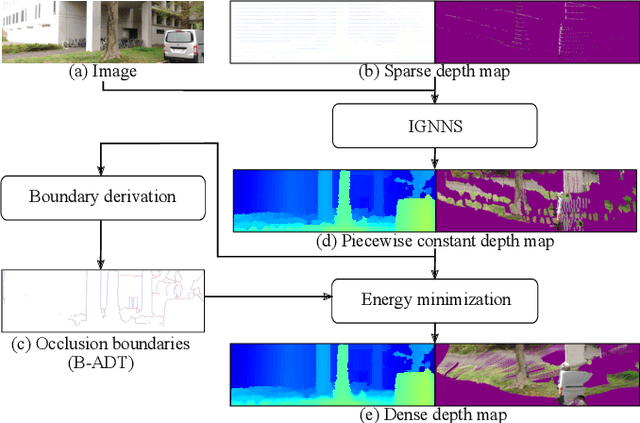
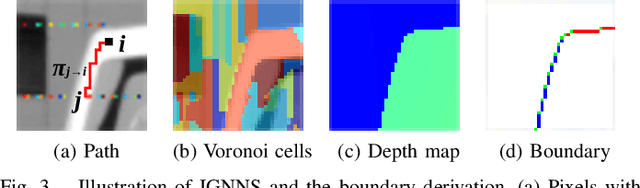
Abstract:We propose an unsupervised real-time dense depth completion from a sparse depth map guided by a single image. Our method generates a smooth depth map while preserving discontinuity between different objects. Our key idea is a Binary Anisotropic Diffusion Tensor (B-ADT) which can completely eliminate smoothness constraint at intended positions and directions by applying it to variational regularization. We also propose an Image-guided Nearest Neighbor Search (IGNNS) to derive a piecewise constant depth map which is used for B-ADT derivation and in the data term of the variational energy. Our experiments show that our method can outperform previous unsupervised and semi-supervised depth completion methods in terms of accuracy. Moreover, since our resulting depth map preserves the discontinuity between objects, the result can be converted to a visually plausible point cloud. This is remarkable since previous methods generate unnatural surface-like artifacts between discontinuous objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge