Shenjin Huang
Rethinking Attention-Based Multiple Instance Learning for Whole-Slide Pathological Image Classification: An Instance Attribute Viewpoint
Mar 30, 2024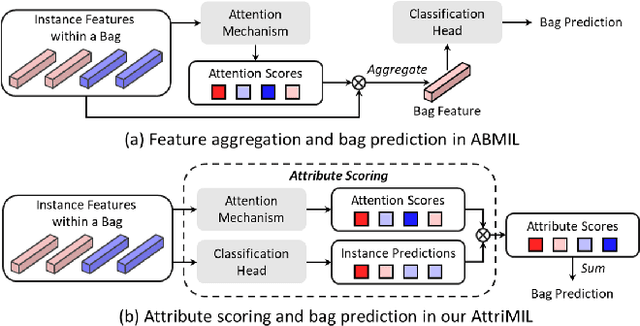
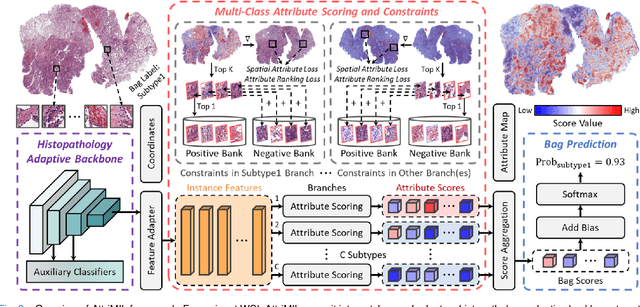
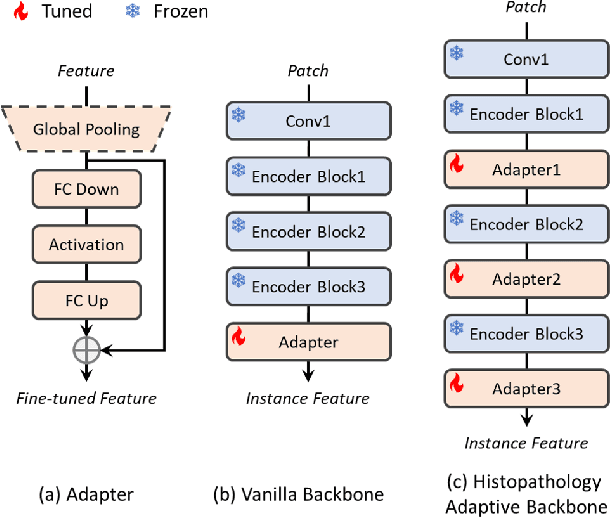
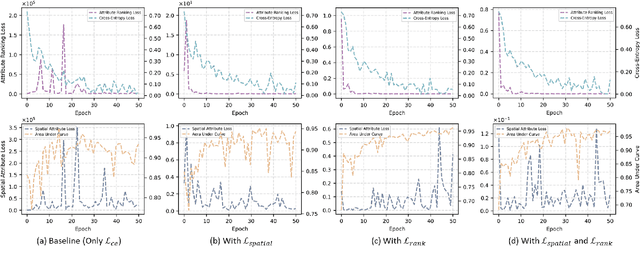
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is a robust paradigm for whole-slide pathological image (WSI) analysis, processing gigapixel-resolution images with slide-level labels. As pioneering efforts, attention-based MIL (ABMIL) and its variants are increasingly becoming popular due to the characteristics of simultaneously handling clinical diagnosis and tumor localization. However, the attention mechanism exhibits limitations in discriminating between instances, which often misclassifies tissues and potentially impairs MIL performance. This paper proposes an Attribute-Driven MIL (AttriMIL) framework to address these issues. Concretely, we dissect the calculation process of ABMIL and present an attribute scoring mechanism that measures the contribution of each instance to bag prediction effectively, quantifying instance attributes. Based on attribute quantification, we develop a spatial attribute constraint and an attribute ranking constraint to model instance correlations within and across slides, respectively. These constraints encourage the network to capture the spatial correlation and semantic similarity of instances, improving the ability of AttriMIL to distinguish tissue types and identify challenging instances. Additionally, AttriMIL employs a histopathology adaptive backbone that maximizes the pre-trained model's feature extraction capability for collecting pathological features. Extensive experiments on three public benchmarks demonstrate that our AttriMIL outperforms existing state-of-the-art frameworks across multiple evaluation metrics. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/MedCAI/AttriMIL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge