Shengze Jin
Department of Computer Science, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
Multiway Point Cloud Mosaicking with Diffusion and Global Optimization
Mar 30, 2024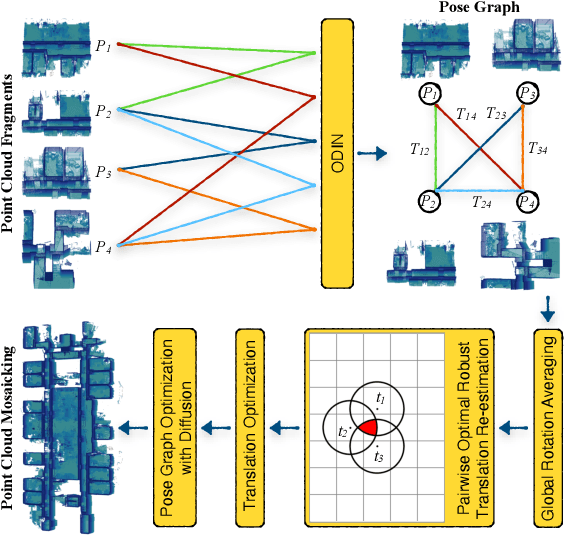
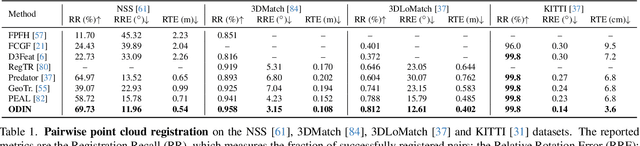
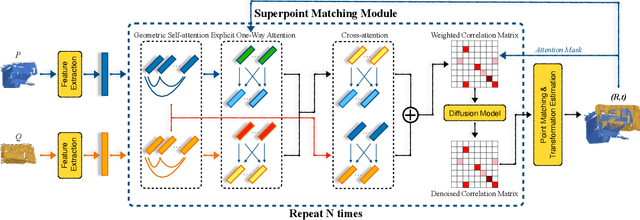
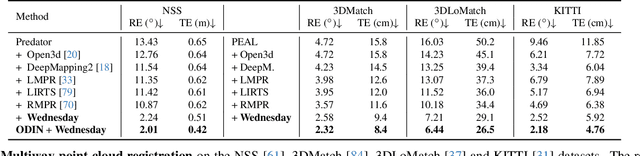
Abstract:We introduce a novel framework for multiway point cloud mosaicking (named Wednesday), designed to co-align sets of partially overlapping point clouds -- typically obtained from 3D scanners or moving RGB-D cameras -- into a unified coordinate system. At the core of our approach is ODIN, a learned pairwise registration algorithm that iteratively identifies overlaps and refines attention scores, employing a diffusion-based process for denoising pairwise correlation matrices to enhance matching accuracy. Further steps include constructing a pose graph from all point clouds, performing rotation averaging, a novel robust algorithm for re-estimating translations optimally in terms of consensus maximization and translation optimization. Finally, the point cloud rotations and positions are optimized jointly by a diffusion-based approach. Tested on four diverse, large-scale datasets, our method achieves state-of-the-art pairwise and multiway registration results by a large margin on all benchmarks. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/jinsz/Multiway-Point-Cloud-Mosaicking-with-Diffusion-and-Global-Optimization.
Q-REG: End-to-End Trainable Point Cloud Registration with Surface Curvature
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:Point cloud registration has seen recent success with several learning-based methods that focus on correspondence matching and, as such, optimize only for this objective. Following the learning step of correspondence matching, they evaluate the estimated rigid transformation with a RANSAC-like framework. While it is an indispensable component of these methods, it prevents a fully end-to-end training, leaving the objective to minimize the pose error nonserved. We present a novel solution, Q-REG, which utilizes rich geometric information to estimate the rigid pose from a single correspondence. Q-REG allows to formalize the robust estimation as an exhaustive search, hence enabling end-to-end training that optimizes over both objectives of correspondence matching and rigid pose estimation. We demonstrate in the experiments that Q-REG is agnostic to the correspondence matching method and provides consistent improvement both when used only in inference and in end-to-end training. It sets a new state-of-the-art on the 3DMatch, KITTI, and ModelNet benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge