Shengqiang Shen
Intrinsic Cramér-Rao Bound based 6D Localization and Tracking for 5G/6G Systems
Feb 19, 2025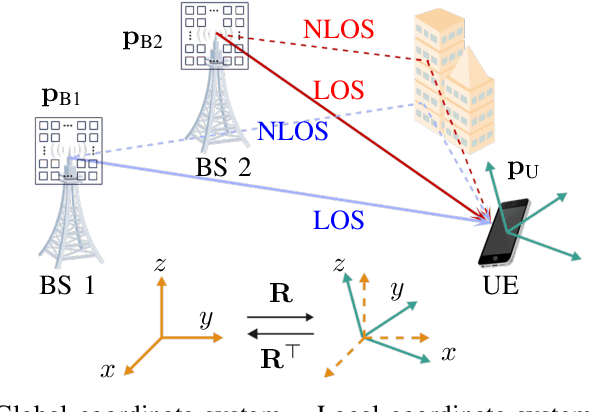
Abstract:Localization and tracking are critical components of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems, enhancing resource management, beamforming accuracy, and overall system reliability through precise sensing. Due to the high path loss of the high-frequency systems, antenna arrays are required at the transmitter and receiver sides for beamforming gain. However, beam misalignment may occur, which requires accurate tracking of the six-dimensional (6D) state, namely, 3D position and 3D orientation. In this work, we first address the challenge that the rotation matrix, being part of the Lie group rather than Euclidean space, necessitates the derivation of the ICRB for an intrinsic performance benchmark. Then, leveraging the derived ICRB, we develop two filters-one utilizing pose fusion and the other employing error-state Kalman filter to estimate the UE's 6D state for different computational resource consumption and accuracy requirements. Simulation results validate the ICRB and assess the performance of the proposed filters, demonstrating their effectiveness and improved accuracy in 6D state tracking.
A Projective Geometric View for 6D Pose Estimation in mmWave MIMO Systems
Feb 02, 2023



Abstract:Millimeter-wave (mmWave) systems in the 30--300 GHz bands are among the fundamental enabling technologies of 5G and beyond 5G, providing large bandwidths, not only for high data rate communication, but also for precise positioning services, in support of high accuracy demanding applications such as vehicle positioning. With the possibility to introduce relatively large arrays on user devices with a small footprint, the ability to determine the user orientation becomes unlocked. The estimation of the full user pose (joint 3D position and 3D orientation) is referred to as 6D localization. Conventionally, the problem of 6D localization using antenna arrays has been considered difficult and was solved through a combination of heuristics and optimization. In this paper, we reveal a close connection between the AoA and AoD and the well-studied perspective projection model from computer vision. This connection allows us to solve the 6D localization problem, by adapting state-of-the-art methods from computer vision. More specifically, two problems, namely 6D pose estimation from AoA from multiple single-antenna base stations and 6D SLAM based on single-BS mmWave communication, are first modeled with the perspective projection model, and then solved. Numerical simulations show that the proposed estimators operate close to the theoretical performance bounds. Moreover, the proposed SLAM method is effective even in the absence of the LoS path, or knowledge of the LoS/NLoS condition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge