Sheng Ren
Sparse Sampling is All You Need for Fast Wrong-way Cycling Detection in CCTV Videos
May 12, 2024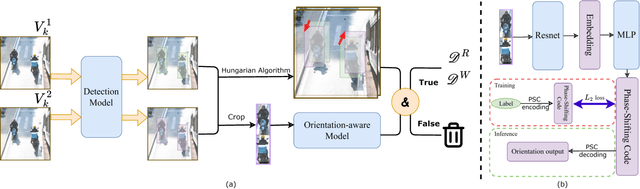
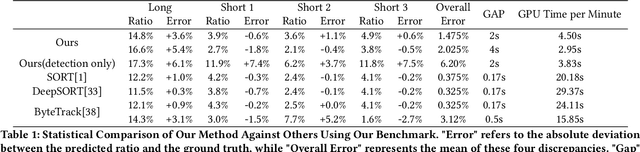

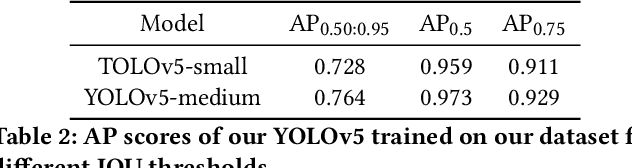
Abstract:In the field of transportation, it is of paramount importance to address and mitigate illegal actions committed by both motor and non-motor vehicles. Among those actions, wrong-way cycling (i.e., riding a bicycle or e-bike in the opposite direction of the designated traffic flow) poses significant risks to both cyclists and other road users. To this end, this paper formulates a problem of detecting wrong-way cycling ratios in CCTV videos. Specifically, we propose a sparse sampling method called WWC-Predictor to efficiently solve this problem, addressing the inefficiencies of direct tracking methods. Our approach leverages both detection-based information, which utilizes the information from bounding boxes, and orientation-based information, which provides insights into the image itself, to enhance instantaneous information capture capability. On our proposed benchmark dataset consisting of 35 minutes of video sequences and minute-level annotation, our method achieves an average error rate of a mere 1.475% while taking only 19.12% GPU time of straightforward tracking methods under the same detection model. This remarkable performance demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach in identifying and predicting instances of wrong-way cycling.
Towards Class-incremental Object Detection with Nearest Mean of Exemplars
Aug 19, 2020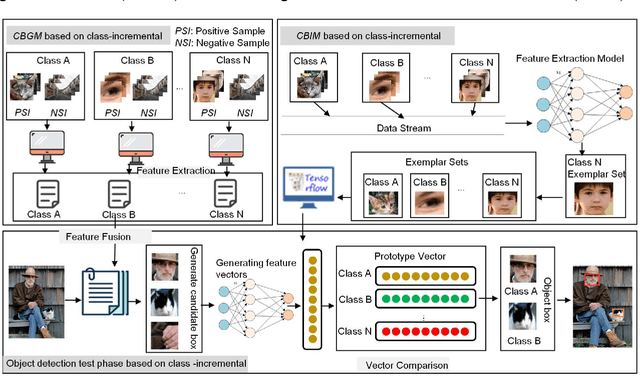
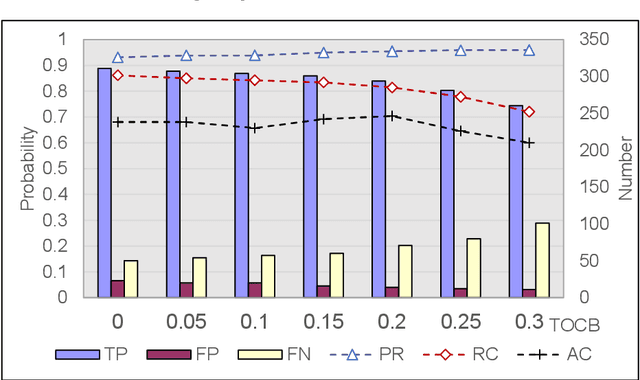
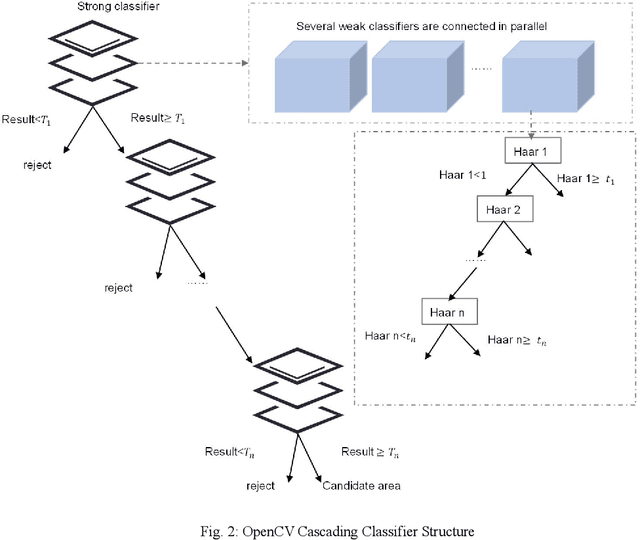
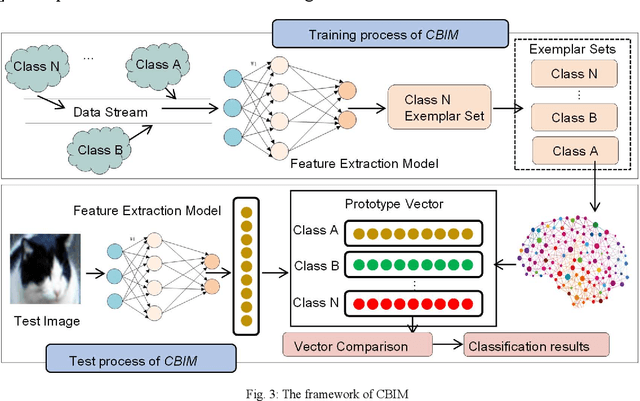
Abstract:Object detection has been widely used in the field of Internet, and deep learning plays a very important role in object detection. However, the existing object detection methods need to be trained in the static setting, which requires obtaining all the data at one time, and it does not support training in the way of class-incremental. In this paper, an object detection framework named class-incremental object detection (CIOD) is proposed. CIOD divides object detection into two stages. Firstly, the traditional OpenCV cascade classifier is improved in the object candidate box generation stage to meet the needs of class increment. Secondly, we use the concept of prototype vector on the basis of deep learning to train a classifier based on class-incremental to identify the generated object candidate box, so as to extract the real object box. A large number of experiments on CIOD have been carried out to verify that CIOD can detect the object in the way of class-incremental and can control the training time and memory capacity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge