Shazia Dharssi
A deep learning approach for automated detection of geographic atrophy from color fundus photographs
Jun 07, 2019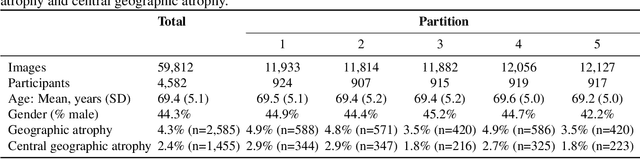
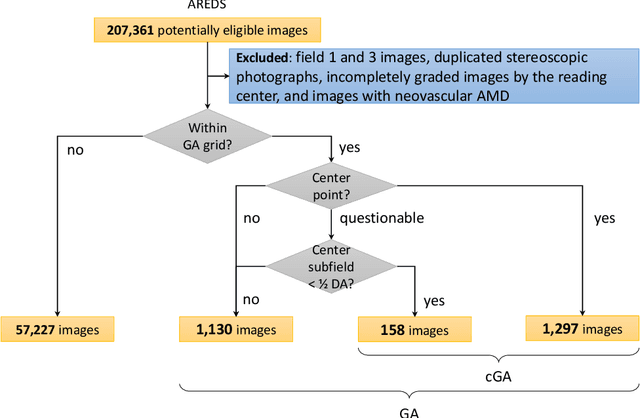
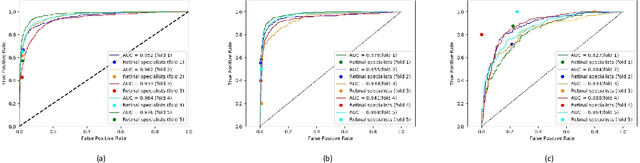
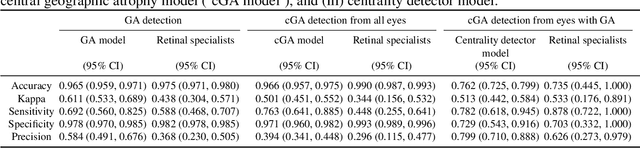
Abstract:Purpose: To assess the utility of deep learning in the detection of geographic atrophy (GA) from color fundus photographs; secondary aim to explore potential utility in detecting central GA (CGA). Design: A deep learning model was developed to detect the presence of GA in color fundus photographs, and two additional models to detect CGA in different scenarios. Participants: 59,812 color fundus photographs from longitudinal follow up of 4,582 participants in the AREDS dataset. Gold standard labels were from human expert reading center graders using a standardized protocol. Methods: A deep learning model was trained to use color fundus photographs to predict GA presence from a population of eyes with no AMD to advanced AMD. A second model was trained to predict CGA presence from the same population. A third model was trained to predict CGA presence from the subset of eyes with GA. For training and testing, 5-fold cross-validation was employed. For comparison with human clinician performance, model performance was compared with that of 88 retinal specialists. Results: The deep learning models (GA detection, CGA detection from all eyes, and centrality detection from GA eyes) had AUC of 0.933-0.976, 0.939-0.976, and 0.827-0.888, respectively. The GA detection model had accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision of 0.965, 0.692, 0.978, and 0.584, respectively. The CGA detection model had equivalent values of 0.966, 0.763, 0.971, and 0.394. The centrality detection model had equivalent values of 0.762, 0.782, 0.729, and 0.799. Conclusions: A deep learning model demonstrated high accuracy for the automated detection of GA. The AUC was non-inferior to that of human retinal specialists. Deep learning approaches may also be applied to the identification of CGA. The code and pretrained models are publicly available at https://github.com/ncbi-nlp/DeepSeeNet.
A multi-task deep learning model for the classification of Age-related Macular Degeneration
Dec 02, 2018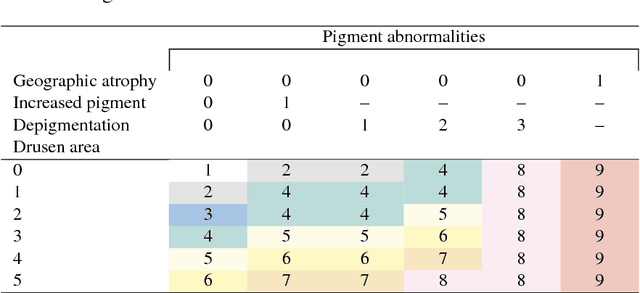
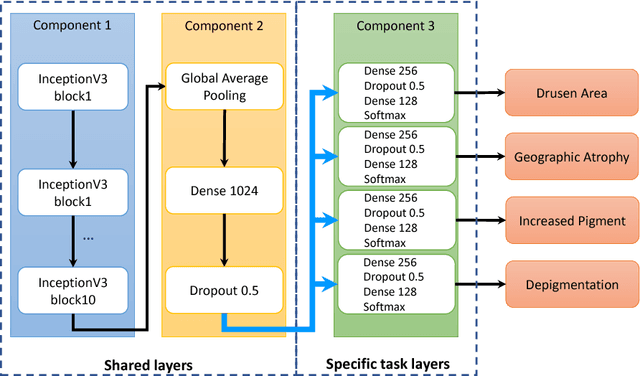
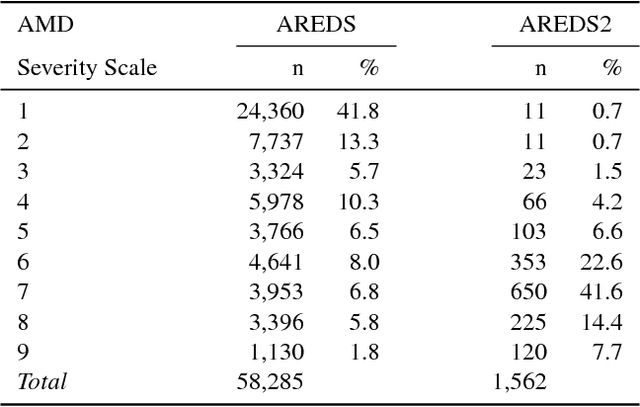
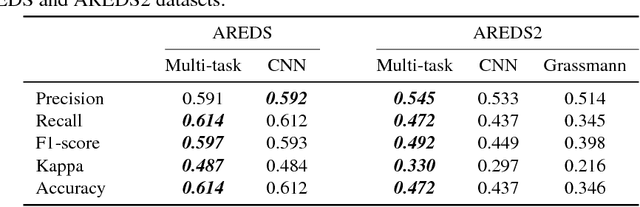
Abstract:Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of blindness. Although the Age-Related Eye Disease Study group previously developed a 9-step AMD severity scale for manual classification of AMD severity from color fundus images, manual grading of images is time-consuming and expensive. Built on our previous work DeepSeeNet, we developed a novel deep learning model for automated classification of images into the 9-step scale. Instead of predicting the 9-step score directly, our approach simulates the reading center grading process. It first detects four AMD characteristics (drusen area, geographic atrophy, increased pigment, and depigmentation), then combines these to derive the overall 9-step score. Importantly, we applied multi-task learning techniques, which allowed us to train classification of the four characteristics in parallel, share representation, and prevent overfitting. Evaluation on two image datasets showed that the accuracy of the model exceeded the current state-of-the-art model by > 10%.
DeepSeeNet: A deep learning model for automated classification of patient-based age-related macular degeneration severity from color fundus photographs
Nov 19, 2018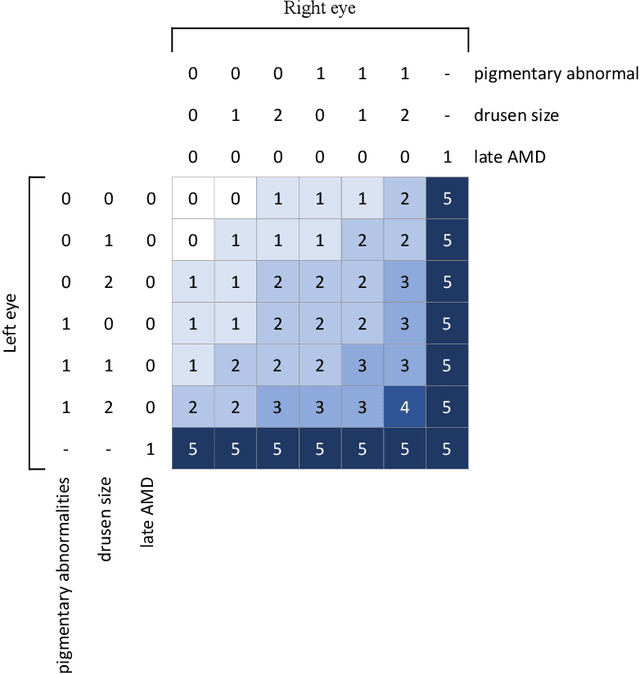
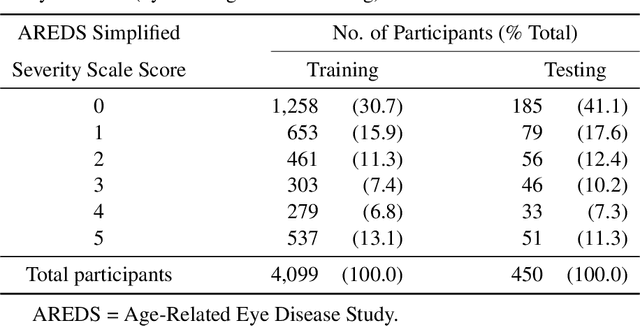
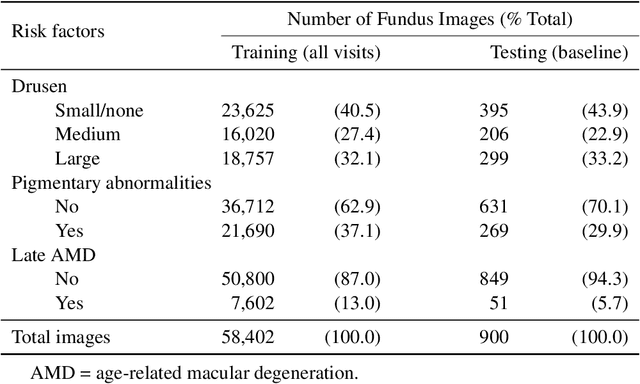
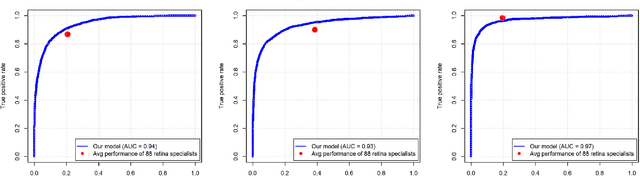
Abstract:In assessing the severity of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) Simplified Severity Scale predicts the risk of progression to late AMD. However, its manual use requires the time-consuming participation of expert practitioners. While several automated deep learning (DL) systems have been developed for classifying color fundus photographs of individual eyes by AREDS severity score, none to date has utilized a patient-based scoring system that employs images from both eyes to assign a severity score. DeepSeeNet, a DL model, was developed to classify patients automatically by the AREDS Simplified Severity Scale (score 0-5) using bilateral color fundus images. DeepSeeNet was trained on 58,402 and tested on 900 images from the longitudinal follow up of 4,549 participants from AREDS. Gold standard labels were obtained using reading center grades. DeepSeeNet simulates the human grading process by first detecting individual AMD risk factors (drusen size; pigmentary abnormalities) for each eye and then calculating a patient-based AMD severity score using the AREDS Simplified Severity Scale. DeepSeeNet performed better on patient-based, multi-class classification (accuracy=0.671; kappa=0.558) than retinal specialists (accuracy=0.599; kappa=0.467) with high AUCs in the detection of large drusen (0.94), pigmentary abnormalities (0.93) and late AMD (0.97), respectively. DeepSeeNet demonstrated high accuracy with increased transparency in the automated assignment of individual patients to AMD risk categories based on the AREDS Simplified Severity Scale. These results highlight the potential of deep learning systems to assist and enhance clinical decision-making processes in AMD patients such as early AMD detection and risk prediction for developing late AMD. DeepSeeNet is publicly available on https://github.com/ncbi-nlp/DeepSeeNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge