Shachar Klaiman
Demystifying Higher-Order Graph Neural Networks
Jun 18, 2024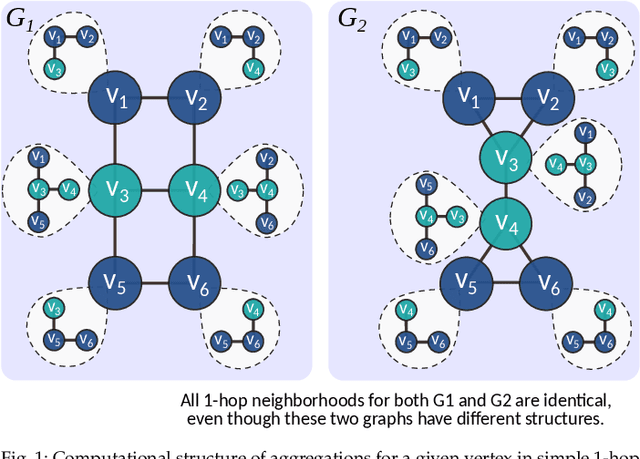
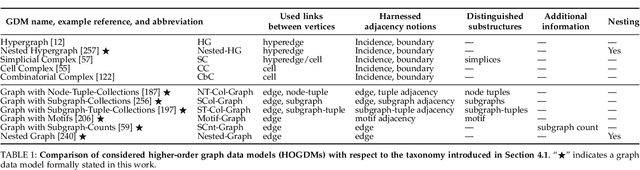
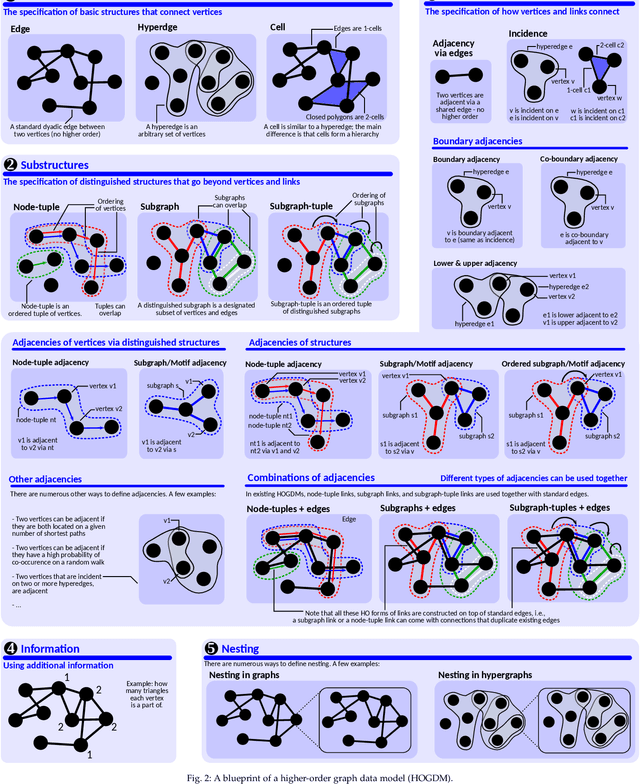
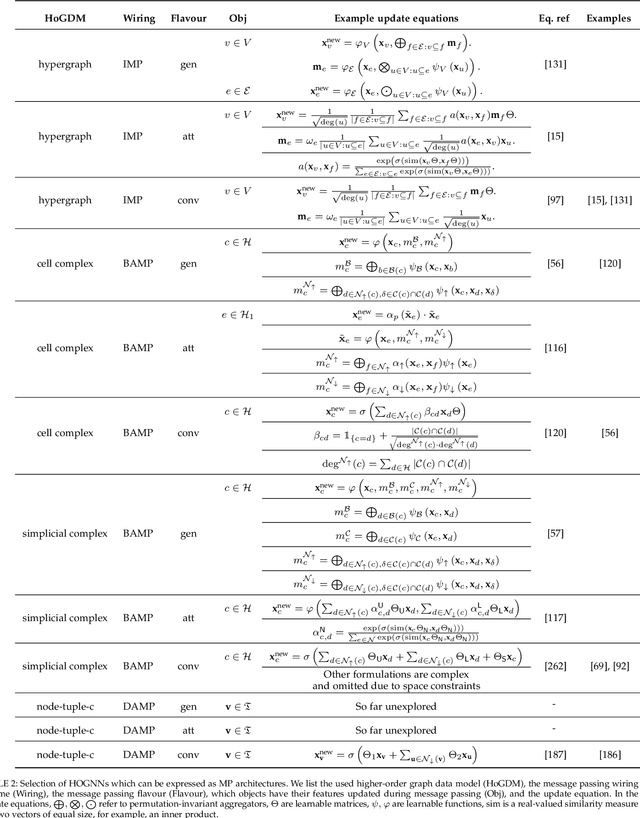
Abstract:Higher-order graph neural networks (HOGNNs) are an important class of GNN models that harness polyadic relations between vertices beyond plain edges. They have been used to eliminate issues such as over-smoothing or over-squashing, to significantly enhance the accuracy of GNN predictions, to improve the expressiveness of GNN architectures, and for numerous other goals. A plethora of HOGNN models have been introduced, and they come with diverse neural architectures, and even with different notions of what the "higher-order" means. This richness makes it very challenging to appropriately analyze and compare HOGNN models, and to decide in what scenario to use specific ones. To alleviate this, we first design an in-depth taxonomy and a blueprint for HOGNNs. This facilitates designing models that maximize performance. Then, we use our taxonomy to analyze and compare the available HOGNN models. The outcomes of our analysis are synthesized in a set of insights that help to select the most beneficial GNN model in a given scenario, and a comprehensive list of challenges and opportunities for further research into more powerful HOGNNs.
DocReader: Bounding-Box Free Training of a Document Information Extraction Model
May 10, 2021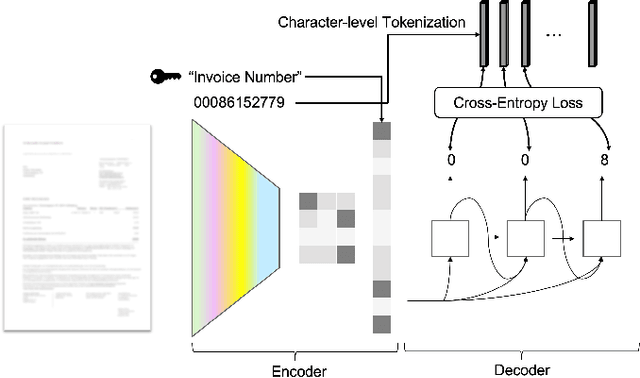
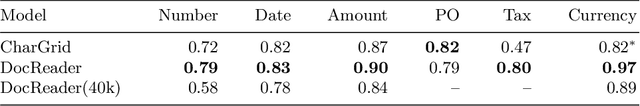
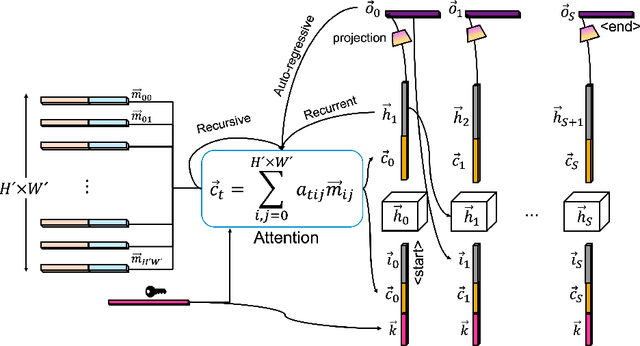
Abstract:Information extraction from documents is a ubiquitous first step in many business applications. During this step, the entries of various fields must first be read from the images of scanned documents before being further processed and inserted into the corresponding databases. While many different methods have been developed over the past years in order to automate the above extraction step, they all share the requirement of bounding-box or text segment annotations of their training documents. In this work we present DocReader, an end-to-end neural-network-based information extraction solution which can be trained using solely the images and the target values that need to be read. The DocReader can thus leverage existing historical extraction data, completely eliminating the need for any additional annotations beyond what is naturally available in existing human-operated service centres. We demonstrate that the DocReader can reach and surpass other methods which require bounding-boxes for training, as well as provide a clear path for continual learning during its deployment in production.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge