Seungwoo Son
TurboBoA: Faster and Exact Attention-aware Quantization without Backpropagation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The rapid growth of large language models (LLMs) has heightened the importance of post-training quantization (PTQ) for reducing memory and computation costs. Among PTQ methods, GPTQ has gained significant attention for its efficiency, enabling billion-scale LLMs to be quantized within a few GPU hours. However, GPTQ's assumption of layer-wise independence leads to severe accuracy drops in low-bit regimes. Recently, BoA improved upon GPTQ by incorporating inter-layer dependencies within attention modules, but its reliance on sequential quantization across all out-channels makes it substantially less efficient. In this paper, we propose TurboBoA, a new backpropagation-free PTQ algorithm that preserves the accuracy benefits of BoA while significantly accelerating the process. The proposed TurboBoA introduces three key innovations: (i) joint quantization of multiple out-channels with a closed-form error compensation rule, which reduces sequential bottlenecks and yields more than a three-fold speedup; (ii) a correction mechanism for errors propagated from preceding quantized layers; and (iii) adaptive grid computation with coordinate descent refinement to maintain alignment during iterative updates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TurboBoA delivers substantial acceleration over BoA while consistently improving accuracy. When combined with outlier suppression techniques, it achieves state-of-the-art results in both weight-only and weight-activation quantization. The code will be available at https://github.com/SamsungLabs/TurboBoA.
Two-Stage Grid Optimization for Group-wise Quantization of LLMs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Group-wise quantization is an effective strategy for mitigating accuracy degradation in low-bit quantization of large language models (LLMs). Among existing methods, GPTQ has been widely adopted due to its efficiency; however, it neglects input statistics and inter-group correlations when determining group scales, leading to a mismatch with its goal of minimizing layer-wise reconstruction loss. In this work, we propose a two-stage optimization framework for group scales that explicitly minimizes the layer-wise reconstruction loss. In the first stage, performed prior to GPTQ, we initialize each group scale to minimize the group-wise reconstruction loss, thereby incorporating input statistics. In the second stage, we freeze the integer weights obtained via GPTQ and refine the group scales to minimize the layer-wise reconstruction loss. To this end, we employ the coordinate descent algorithm and derive a closed-form update rule, which enables efficient refinement without costly numerical optimization. Notably, our derivation incorporates the quantization errors from preceding layers to prevent error accumulation. Experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently enhances group-wise quantization, achieving higher accuracy with negligible overhead.
Prefixing Attention Sinks can Mitigate Activation Outliers for Large Language Model Quantization
Jun 17, 2024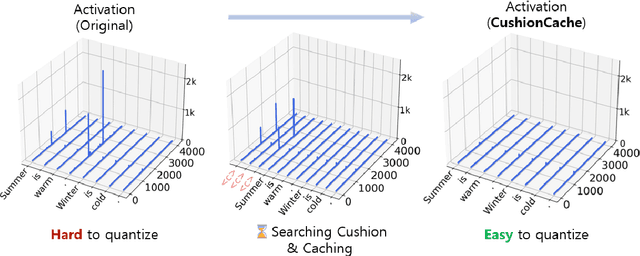
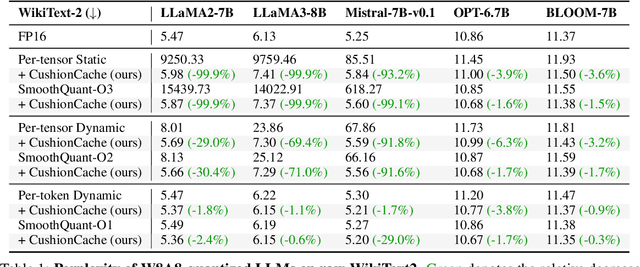
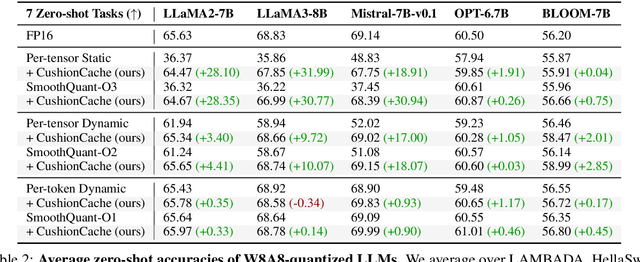
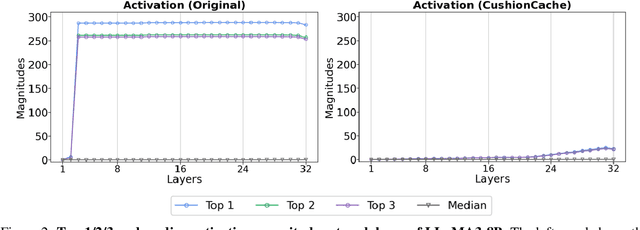
Abstract:Despite recent advances in LLM quantization, activation quantization remains to be challenging due to the activation outliers. Conventional remedies, e.g., mixing precisions for different channels, introduce extra overhead and reduce the speedup. In this work, we develop a simple yet effective strategy to facilitate per-tensor activation quantization by preventing the generation of problematic tokens. Precisely, we propose a method to find a set of key-value cache, coined CushionCache, which mitigates outliers in subsequent tokens when inserted as a prefix. CushionCache works in two steps: First, we greedily search for a prompt token sequence that minimizes the maximum activation values in subsequent tokens. Then, we further tune the token cache to regularize the activations of subsequent tokens to be more quantization-friendly. The proposed method successfully addresses activation outliers of LLMs, providing a substantial performance boost for per-tensor activation quantization methods. We thoroughly evaluate our method over a wide range of models and benchmarks and find that it significantly surpasses the established baseline of per-tensor W8A8 quantization and can be seamlessly integrated with the recent activation quantization method.
MaskedKD: Efficient Distillation of Vision Transformers with Masked Images
Feb 21, 2023Abstract:Knowledge distillation is a popular and effective regularization technique for training lightweight models, but it also adds significant overhead to the training cost. The drawback is most pronounced when we use large-scale models as our teachers, such as vision transformers (ViTs). We present MaskedKD, a simple yet effective method for reducing the training cost of ViT distillation. MaskedKD masks a fraction of image patch tokens fed to the teacher to save the teacher inference cost. The tokens to mask are determined based on the last layer attention score of the student model, to which we provide the full image. Without requiring any architectural change of the teacher or making sacrifices in the student performance, MaskedKD dramatically reduces the computations and time required for distilling ViTs. We demonstrate that MaskedKD can save up to $50\%$ of the cost of running inference on the teacher model without any performance drop on the student, leading to approximately $28\%$ drop in the teacher and student compute combined.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge